Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the structures found in the PNS
Ganglia
A ganglion is a group of neuron cell bodies in the periphery (a.k.a. the peripheral nervous system). Ganglia can be categorized, for the most part, as either sensory ganglia or autonomic ganglia, referring to their primary functions. The most common type of sensory ganglion is a dorsal (posterior) root ganglion. These ganglia are the cell bodies of neurons with axons that are associated with sensory endings in the periphery, such as in the skin, and that extend into the CNS through the dorsal nerve root. The ganglion is an enlargement of the nerve root. Note that nerve roots are not surrounded by the pia mater, and as such are part of the peripheral nervous system. Under microscopic inspection, it can be seen to include the cell bodies of the neurons, as well as bundles of fibers that are the dorsal nerve root (Figure 13.2.1). The cells of the dorsal root ganglion are unipolar cells, classifying them by shape. Also, the small round nuclei of satellite cells can be seen surrounding—as if they were orbiting—the neuron cell bodies.
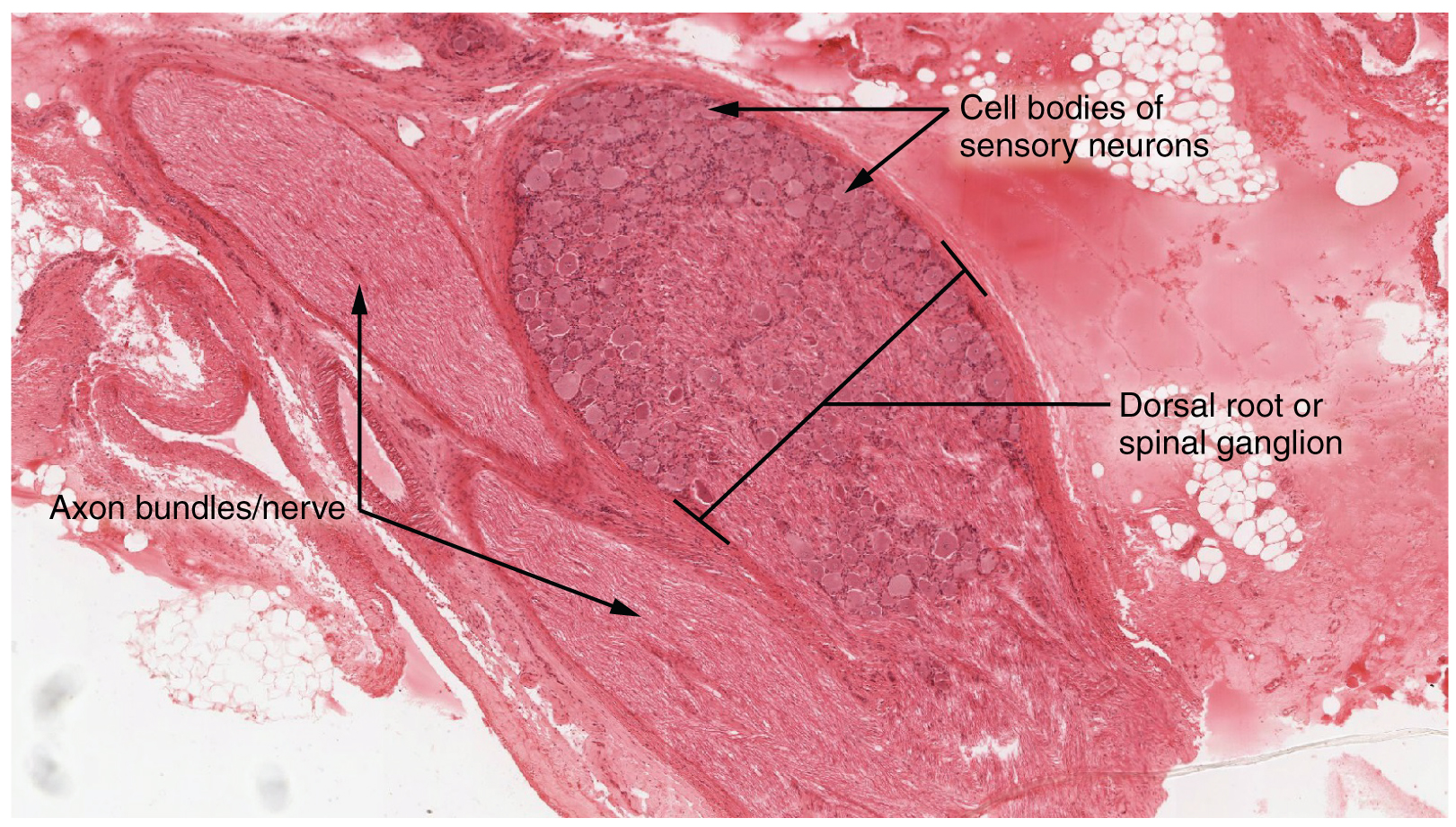
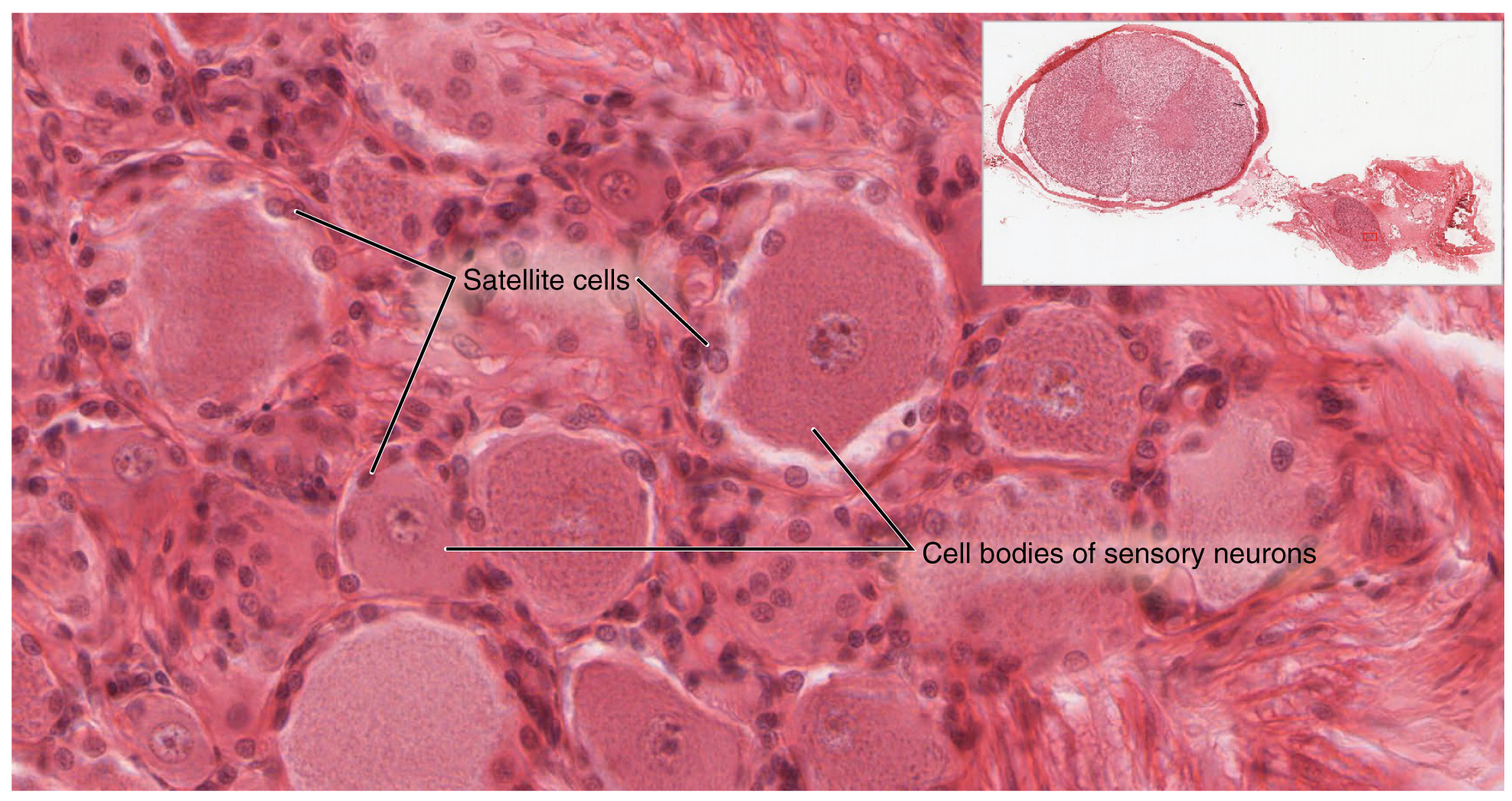
External Website

View the University of Michigan WebScope at http://virtualslides.med.umich.edu/Histology/Basic%20Tissues/Nervous%20Tissue/065-2_HISTO_40X.svs/view.apml to explore the tissue sample in greater detail. If you zoom in on the dorsal root ganglion, you can see smaller satellite glial cells surrounding the large cell bodies of the sensory neurons. From what structure do satellite cells derive during embryologic development?
Another type of sensory ganglion is a cranial nerve ganglion. This is analogous to the dorsal root ganglion, except that it is associated with a cranial nerve (associated with the brain) instead of a spinal nerve (associated with the spinal cord). The roots of cranial nerves are within the cranium, whereas the ganglia are outside the skull. For example, the trigeminal ganglion is superficial to the temporal bone whereas its associated nerve is attached to the mid-pons region of the brain stem. Like the sensory neurons associated with the spinal cord, the sensory neurons of cranial nerve ganglia are unipolar in shape with associated satellite cells.
The other major category of ganglia are those of the autonomic nervous system, which is divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic chain ganglia constitute a row of ganglia along the vertebral column that receive central input from the lateral horn of the thoracic and upper lumbar spinal cord. At the superior end of the chain ganglia are three paravertebral ganglia in the cervical region. Three other autonomic ganglia that are related to the sympathetic chain are the prevertebral ganglia, which are located outside of the chain but have similar functions. They are referred to as prevertebral because they are anterior to the vertebral column. The neurons of these autonomic ganglia are multipolar in shape, with dendrites radiating out around the cell body where synapses from the spinal cord neurons are made. The neurons of the chain, paravertebral, and prevertebral ganglia then project to organs in the head and neck, thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic cavities to regulate the sympathetic aspect of homeostatic mechanisms.
Another group of autonomic ganglia are the terminal ganglia that receive central input from cranial nerves or sacral spinal nerves and are responsible for regulating the parasympathetic aspect of homeostatic mechanisms. These two sets of ganglia, sympathetic and parasympathetic, often project to the same organs—one input from the chain ganglia and one input from a terminal ganglion—to regulate the overall function of an organ. For example, the heart receives two inputs such as these; one increases heart rate, and the other decreases it. The terminal ganglia that receive input from cranial nerves are found in the head and neck, as well as the thoracic and upper abdominal cavities, whereas the terminal ganglia that receive sacral input are in the lower abdominal and pelvic cavities.
Terminal ganglia below the head and neck are often incorporated into the wall of the target organ as a plexus. A plexus, in a general sense, is a network of branching interconnected fibers or vessels. This can apply to nervous tissue (as in this instance) or structures containing blood vessels (such as a choroid plexus). For example, the enteric plexus is the extensive network of axons and neurons in the wall of the small and large intestines. The enteric plexus is actually part of the enteric nervous system, along with the gastric plexuses and the esophageal plexus. Though the enteric nervous system receives input originating from central neurons of the autonomic nervous system, it does not require CNS input to function. In fact, it operates independently to regulate the digestive system.
Nerves
Bundles of axons in the PNS are referred to as nerves. These structures in the periphery are different than the central counterpart, called a tract. Unlike tracts, nerves are composed of more than just nervous tissue. They have connective tissues invested in their structure, as well as blood vessels supplying the tissues with nourishment. The outer surface of a nerve is a surrounding layer of fibrous connective tissue called the epineurium. Within the nerve, axons are further bundled into fascicles, which are each surrounded by their own layer of fibrous connective tissue called perineurium. Finally, individual axons are surrounded by loose connective tissue called the endoneurium (Figure 13.2.3). These three layers are similar to the connective tissue sheaths for muscles. Because peripheral axons are surrounded by an endoneurium it is possible for severed axons to regenerated. After they are cut the proximal severed end of the axon sprouts and one of the sprouts will find the endoneurium which is, essentially, an empty tube leading to (or near) the original target. The endoneurim is empty because the distal portion of the severed axon degenerates, a process called Wallerian (anterograde or orthograde) degeneration. Nerves are associated with the region of the CNS to which they are connected, either as cranial nerves connected to the brain or spinal nerves connected to the spinal cord.
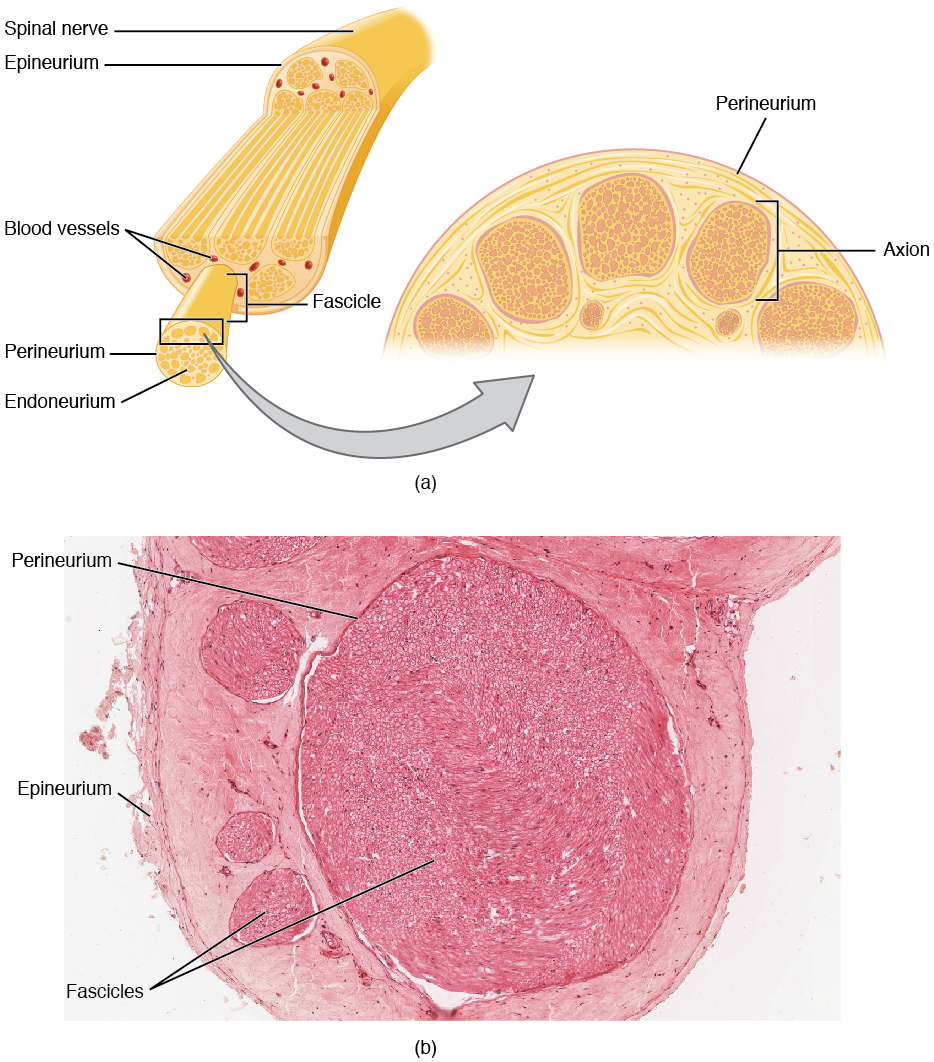
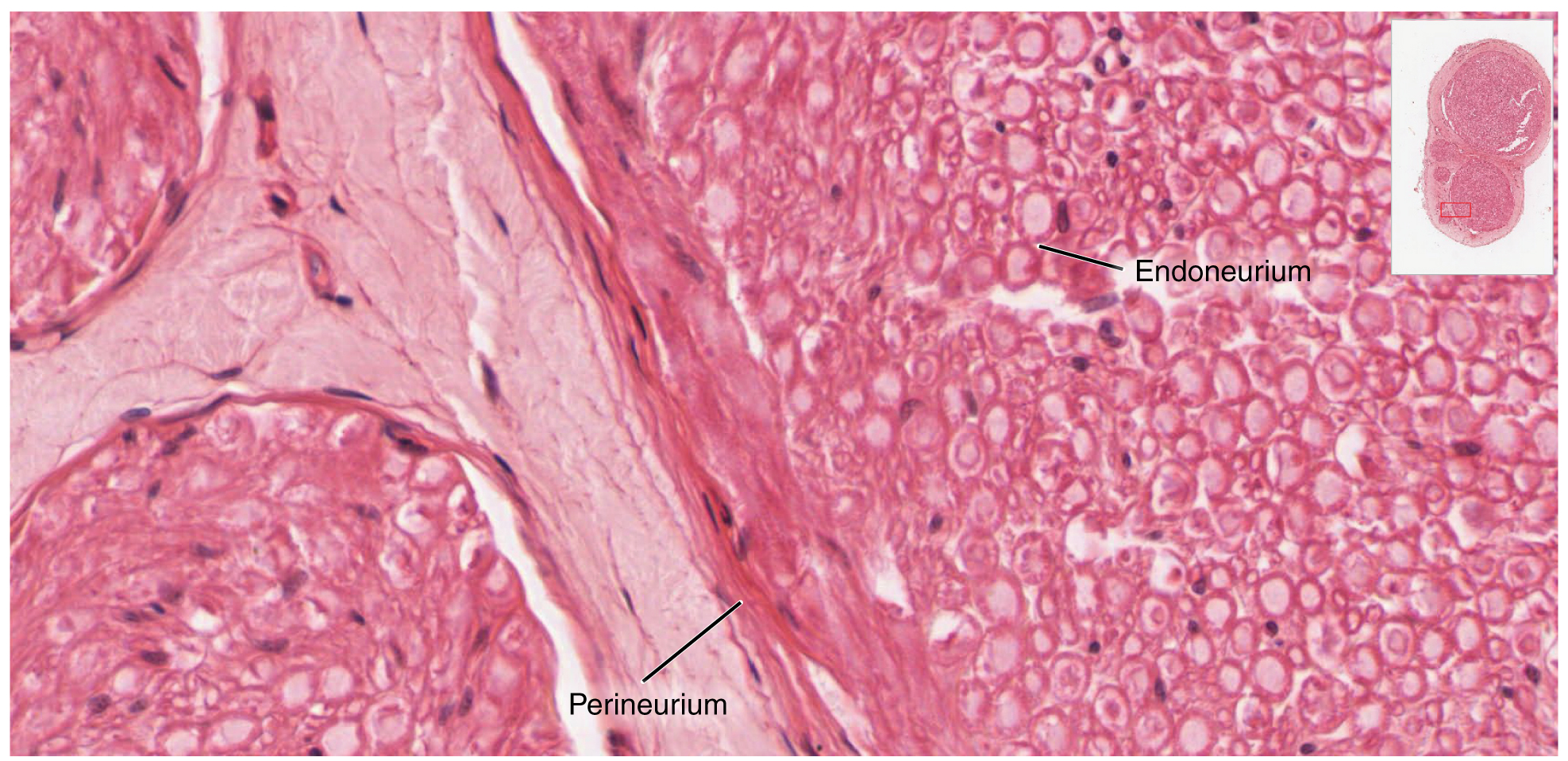
External Website

View the University of Michigan WebScope at http://virtualslides.med.umich.edu/Histology/Basic%20Tissues/Nervous%20Tissue/068_HISTO_40X.svs/view.apml to explore the tissue sample in greater detail. With what structures in a skeletal muscle are the endoneurium, perineurium, and epineurium comparable?
Chapter Review
The PNS is composed of the groups of neurons (ganglia) and bundles of axons (nerves) that are outside of the brain and spinal cord. Ganglia are of two types, sensory or autonomic. Sensory ganglia contain unipolar sensory neurons and are found on the dorsal root of all spinal nerves as well as associated with many of the cranial nerves. Autonomic ganglia are in the sympathetic chain, the associated paravertebral or prevertebral ganglia, or in terminal ganglia near or within the organs controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
Review Questions
Critical Thinking Questions
- Why are ganglia and nerves not surrounded by protective structures like the meninges of the CNS?
Glossary
- cranial nerve ganglion
- sensory ganglion of cranial nerves
- cranial nerve
- one of twelve nerves connected to the brain that are responsible for sensory or motor functions of the head and neck
- dorsal (posterior) root ganglion
- sensory ganglion attached to the posterior nerve root of a spinal nerve
- endoneurium
- innermost layer of connective tissue that surrounds individual axons within a nerve
- enteric plexus
- neuronal plexus in the wall of the intestines, which is part of the enteric nervous system
- epineurium
- outermost layer of connective tissue that surrounds an entire nerve
- esophageal plexus
- neuronal plexus in the wall of the esophagus that is part of the enteric nervous system
- fascicle
- small bundles of nerve or muscle fibers enclosed by connective tissue
- gastric plexuses
- neuronal networks in the wall of the stomach that are part of the enteric nervous system
- paravertebral ganglia
- autonomic ganglia superior to the sympathetic chain ganglia
- perineurium
- layer of connective tissue surrounding fascicles within a nerve
- plexus
- network of nerves or nervous tissue
- prevertebral ganglia
- autonomic ganglia that are anterior to the vertebral column and functionally related to the sympathetic chain ganglia
- spinal nerve
- one of 31 nerves connected to the spinal cord
- sympathetic chain ganglia
- autonomic ganglia in a chain along the anterolateral aspect of the vertebral column that are responsible for contributing to homeostatic mechanisms of the autonomic nervous system
- trigeminal ganglion
- sensory ganglion that contributes sensory fibers to the trigeminal nerve
This work, Anatomy & Physiology, is adapted from Anatomy & Physiology by OpenStax, licensed under CC BY. This edition, with revised content and artwork, is licensed under CC BY-SA except where otherwise noted.
Images, from Anatomy & Physiology by OpenStax, are licensed under CC BY except where otherwise noted.
Access the original for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction.

