7.5.1- Limitations of NAP
The effect of NAP on Amyloid β proteins.
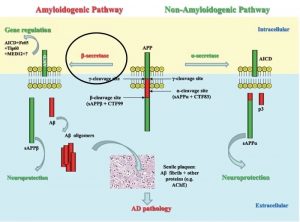
The deposition of amyloid plaques in the brains of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) patients is one of the pathological hallmarks of the disease. These amyloid plaques come from the processing of Amyloid precursor protein (APP). APP can be cleaved by either a-secretase or b-secretase enzymes resulting into APP-CTF83 or APP-CTF99 respective. It is subsequent cleavage of APP-CTF99 by g-secretase that results in the production of amyloid β1-42 or β1-40. These products aggregate and form the plagues seen in AD brains. In AD models like the aluminum ion neurotoxicity model, both Aβ1-40/42 are observed to be increased upon aluminum treatment. The subsequent administration of NAP, however, results in the alleviation of the increase in Aβ1-42 but not Aβ1-40. On the contrary, it actually results in a small increase of Aβ1-40 and other peptide fragments. These findings are problematic since both Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 form the plagues that are associated with the pathogenesis of AD.
Effect of NAP on Tauopathies
On a similar note the presence of hyperphosphorylated tau protein decreases upon the administration of NAP. Tau is a microtubule associated protein that comes in two isoforms or flavours. These are the tau isoform 3 (Tau3R) and tau isoform 4 (Tau4R). Neurodegenerative diseases like AD affect the ratio of these isoforms and result in the ultimate hyperphosphorylation of the protein. These hyperphosphorylated protein aggregate to form tangles known as neurofibrillary tangles that are associated with the cognitive deficits caused by the disease. Research on tauopathies shows that NAP has a preference for Tau3R compared to Tau4R. This would explain why tau deposition decreases in AD patients upon NAP treatment since AD leads to a high Tau3R/Tau4R ratio. This, however, would mean that NAP would not be as effect against neurodegenerative diseases such as progressive supranuclear palsy in which patients have increased Tau4R. Moreover, the mechanism of interaction of NAP with Tau and its preference for Tau3R are not yet fully understood and need to be studied further.
