5.1 Rotation Angle and Angular Velocity
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Define arc length, rotation angle, radius of curvature and angular velocity.
- Calculate the angular velocity of a car wheel spin.
In Kinematics, we studied motion along a straight line and introduced such concepts as displacement, velocity, and acceleration. Two-Dimensional Kinematics dealt with motion in two dimensions. Projectile motion is a special case of two-dimensional kinematics in which the object is projected into the air, while being subject to the gravitational force, and lands a distance away. In this chapter, we consider situations where the object does not land but moves in a curve. We begin the study of uniform circular motion by defining two angular quantities needed to describe rotational motion.
Rotation Angle
When objects rotate about some axis—for example, when the CD (compact disc) in Figure 5.2 rotates about its center—each point in the object follows a circular arc. Consider a line from the center of the CD to its edge. Each pit used to record sound along this line moves through the same angle in the same amount of time. The rotation angle is the amount of rotation and is analogous to linear distance. We define the rotation angle [latex]\Delta \theta[/latex] to be the ratio of the arc length to the radius of curvature:
[latex]\Delta \theta = \frac{\Delta s}{r} .[/latex]
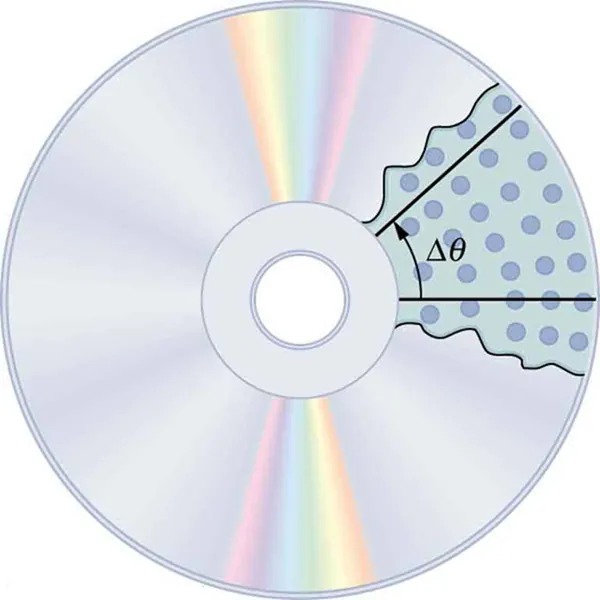
Figure 5.2 All points on a CD travel in circular arcs. The pits along a line from the center to the edge all move through the same angle [latex]\Delta \theta[/latex] in a time [latex]\Delta t[/latex]. Image from OpenStax College Physics 2e, CC-BY 4.0
Image Description
The image shows a graphic representation of a CD (compact disc). The CD displays its typical circular shape with a reflective surface that exhibits a rainbow-like spectrum. Part of the CD is removed to reveal an internal section which is illustrated with a dotted pattern.
Within this cutaway section, there are angular lines meeting at a point creating a small triangular angle marked with the symbol Δθ (Delta Theta). This symbol represents a change in the angle. The diagram appears to be illustrating a concept related to angular measurement or perhaps data encoding on a CD.
The reflective surface gives off a rainbow effect due to the light diffraction, a characteristic of CDs. The center contains the familiar circular hole typical in all CDs for placement onto a drive spindle.
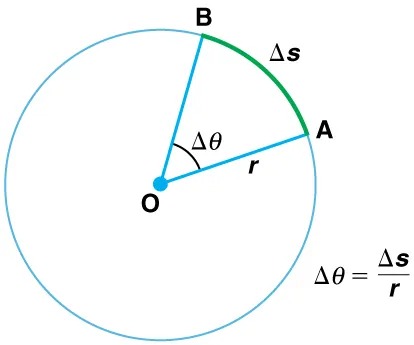
Figure 5.3 The radius of a circle is rotated through an angle [latex]\Delta \theta[/latex]. The arc length [latex]\Delta\text{s}[/latex] is described on the circumference. Image from OpenStax College Physics 2e, CC-BY 4.0
Image Description
The image depicts a circle with center labeled as O. A sector of the circle is highlighted with an arc between points A and B. The following details describe the elements in the image:
- O is the center of the circle.
- The radius of the circle from O to A is labeled as r.
- The arc length between points A and B is labeled as Δs, highlighted in green.
- The angle at O subtended by the arc AB is labeled as Δθ.
- A formula is provided: Δθ = Δs / r.
This image illustrates the relationship between the arc length, the radius, and the angle measured in radians.
The arc length[latex]\Delta s[/latex] is the distance traveled along a circular path as shown in Figure 6.3. Note that [latex]r[/latex] is the radius of curvature of the circular path.
We know that for one complete revolution, the arc length is the circumference of a circle of radius [latex]r[/latex]. The circumference of a circle is [latex]2π r[/latex]. Thus for one complete revolution the rotation angle is
[latex]\Delta \theta = \frac{2π r}{r} = 2π .[/latex]
This result is the basis for defining the units used to measure rotation angles, [latex]\Delta \theta[/latex] to be radians (rad), defined so that
[latex]2π \text{rad } = \text{ 1 revolution}.[/latex]
A comparison of some useful angles expressed in both degrees and radians is shown in Table 5.1.
| Degree Measures | Radian Measure |
|---|---|
| [latex]\text{30}º[/latex] | [latex]\frac{\pi}{6}[/latex] |
| [latex]\text{60}º[/latex] | [latex]\frac{\pi}{3}[/latex] |
| [latex]\text{90}º[/latex] | [latex]\frac{\pi}{2}[/latex] |
| [latex]\text{120}º[/latex] | [latex]\frac{2π}{3}[/latex] |
| [latex]\text{135}º[/latex] | [latex]\frac{3π}{4}[/latex] |
| [latex]\text{180}º[/latex] | [latex]\pi[/latex] |
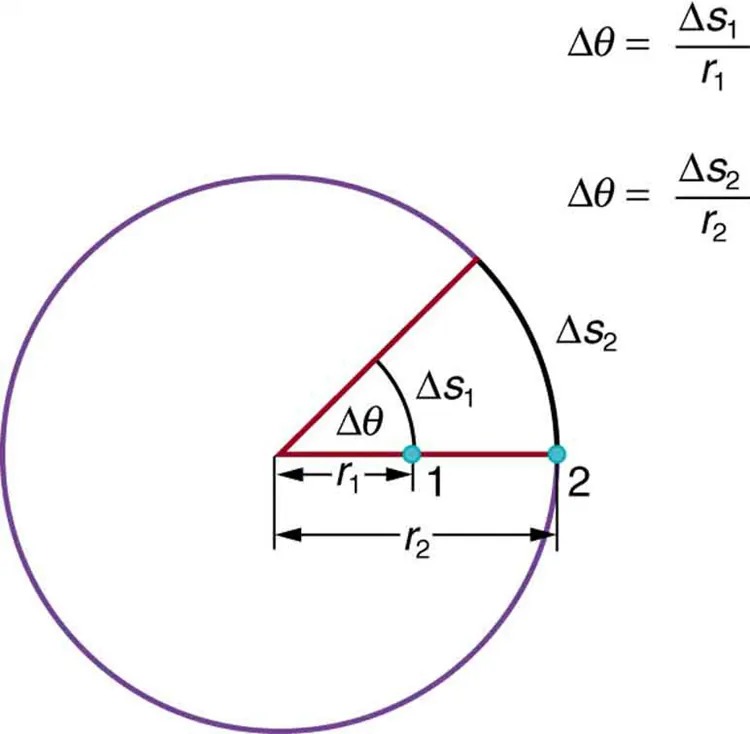
Figure 5.4 Points 1 and 2 rotate through the same angle ([latex]\Delta \theta[/latex]), but point 2 moves through a greater arc length [latex]\left(\Delta s\right)[/latex] because it is at a greater distance from the center of rotation [latex]\left(\right. r \left.\right)[/latex]. Image from OpenStax College Physics 2e, CC-BY 4.0
Image Description
The image is a diagram of a circle with two radii and arcs, illustrating angular displacement.
– The circle is outlined in purple, containing a sector highlighted in red.
– Inside the sector, there are two points labeled “1” and “2” along the arcs.
– The angle at the center of the circle, denoted as Δθ (delta theta), is formed between two radii.
– The radius extending to point “1” is labeled as \( r_1 \), and the arc segment associated with it is labeled as \( \Delta s_1 \).
– Similarly, the radius extending to point “2” is labeled as \( r_2 \), and the corresponding arc segment is \( \Delta s_2 \).
– Two formulae are shown on the right side of the image:
– \( \Delta \theta = \frac{\Delta s_1}{r_1} \)
– \( \Delta \theta = \frac{\Delta s_2}{r_2} \)
This diagram is likely illustrating the relationship between arc length, radius, and angular displacement in radians.
If [latex]\Delta \theta = 2 \pi[/latex] rad, then the CD has made one complete revolution, and every point on the CD is back at its original position. Because there are [latex]\text{360}º[/latex] in a circle or one revolution, the relationship between radians and degrees is thus
[latex]2 \pi \text{rad} = \text{360}º[/latex]
so that
[latex]1 \text{rad} = \frac{\text{360}º}{2π} \approx \text{57}. 3º .[/latex]
Angular Velocity
How fast is an object rotating? We define angular velocity [latex]\omega[/latex] as the rate of change of an angle. In symbols, this is
[latex]\omega = \frac{\Delta \theta}{\Delta t} ,[/latex]
where an angular rotation [latex]\Delta \theta[/latex] takes place in a time [latex]\Delta t[/latex]. The greater the rotation angle in a given amount of time, the greater the angular velocity. The units for angular velocity are radians per second (rad/s).
Angular velocity [latex]\omega[/latex] is analogous to linear velocity [latex]v[/latex]. To get the precise relationship between angular and linear velocity, we again consider a pit on the rotating CD. This pit moves an arc length [latex]\Delta s[/latex] in a time [latex]\Delta t[/latex], and so it has a linear velocity
[latex]v = \frac{\Delta s}{\Delta t} .[/latex]
From [latex]\Delta \theta = \frac{\Delta s}{r}[/latex] we see that [latex]\Delta s = r \Delta \theta[/latex]. Substituting this into the expression for [latex]v[/latex] gives
[latex]v = \frac{r \Delta \theta}{\Delta t} = rω .[/latex]
We write this relationship in two different ways and gain two different insights:
[latex]v = rω \textrm{ }\text{or}\textrm{ } \omega = \frac{v}{r} .[/latex]
The first relationship in [latex]v = rω \textrm{ }\text{or}\textrm{ } \omega = \frac{v}{r}[/latex] states that the linear velocity [latex]v[/latex] is proportional to the distance from the center of rotation, thus, it is largest for a point on the rim (largest [latex]r[/latex]), as you might expect. We can also call this linear speed [latex]v[/latex] of a point on the rim the tangential speed. The second relationship in [latex]v = rω \textrm{ }\text{or}\textrm{ } \omega = \frac{v}{r}[/latex] can be illustrated by considering the tire of a moving car. Note that the speed of a point on the rim of the tire is the same as the speed [latex]v[/latex] of the car. See Figure 5.5. So the faster the car moves, the faster the tire spins—large [latex]v[/latex] means a large [latex]\omega[/latex], because [latex]v = rω[/latex]. Similarly, a larger-radius tire rotating at the same angular velocity ([latex]\omega[/latex]) will produce a greater linear speed ([latex]v[/latex]) for the car.
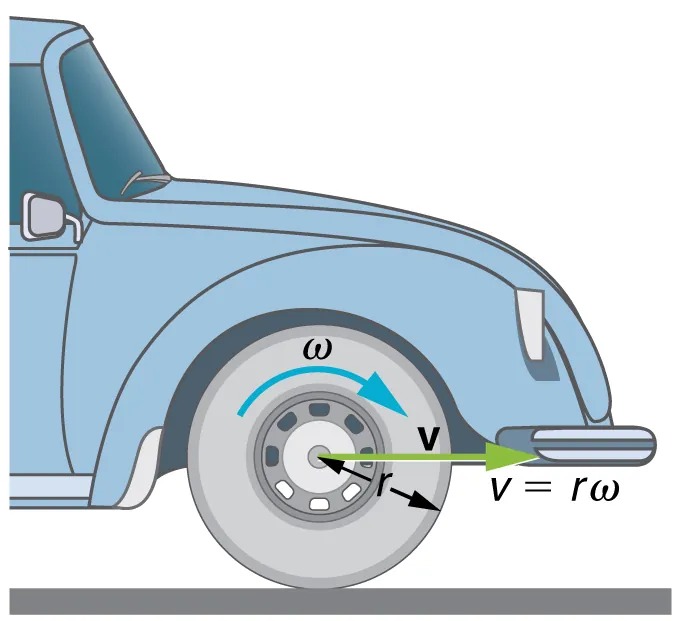
Figure 5.5 A car moving at a velocity [latex]v[/latex] to the right has a tire rotating with an angular velocity [latex]\omega[/latex].The speed of the tread of the tire relative to the axle is [latex]v[/latex], the same as if the car were jacked up. Thus the car moves forward at linear velocity [latex]v = rω[/latex], where [latex]r[/latex] is the tire radius. A larger angular velocity for the tire means a greater velocity for the car. Image from OpenStax College Physics 2e, CC-BY 4.0
Image Description
The image is an illustration of the front left side of a blue car, focusing on the wheel. The car is facing to the right. The main elements depicted in the image are:
– Car Body: A simplistic, partial side view of a blue car, showing details like the front bumper, a side mirror, and part of the front wheel well.
– Wheel: The wheel of the car is prominently featured. An arrow labeled with the Greek letter ω (omega) indicates the angular velocity or rotational speed of the wheel, shown in a counterclockwise direction.
– Radius: A line labeled ‘r’ is shown from the center of the wheel to its edge, representing the radius of the wheel.
– Velocity Vector: An arrow labeled ‘v’ extends horizontally from the center of the wheel toward the right, indicating linear velocity. Another arrow from outside the wheel to the right is labeled with the formula ‘v = rω’, relating linear velocity, radius, and angular velocity.
The illustration visually explains the relationship between angular velocity, linear velocity, and radius in a rotating wheel of a car.
Example 5.1
How Fast Does a Car Tire Spin?
Calculate the angular velocity of a 0.300 m radius car tire when the car travels at [latex]\text{15} . 0 \text{m}/\text{s}[/latex] (about [latex]\text{54} \text{km}/\text{h}[/latex]). See Figure 5.5.
Strategy
Because the linear speed of the tire rim is the same as the speed of the car, we have
[latex]v = \text{15}.\text{0 m}/\text{s} .[/latex]
The radius of the tire is given to be
[latex]r = \text{0}.\text{300 m} .[/latex] Knowing
[latex]v[/latex] and [latex]r[/latex], we can use the second relationship in [latex]v = rω , \omega = \frac{v}{r}[/latex] to calculate the angular velocity.
Solution
To calculate the angular velocity, we will use the following relationship:
[latex]\omega = \frac{v}{r} .[/latex]
Substituting the knowns,
[latex]\omega = \frac{\text{15} . 0 \text{m}/\text{s}}{0 . \text{300} \text{m}} = \text{50} . 0 \text{rad}/\text{s}.[/latex]
Discussion
When we cancel units in the above calculation, we get 50.0/s. But the angular velocity must have units of rad/s. Because radians are actually unitless (radians are defined as a ratio of distance), we can simply insert them into the answer for the angular velocity. Also note that if an earth mover with much larger tires, say 1.20 m in radius, were moving at the same speed of 15.0 m/s, its tires would rotate more slowly. They would have an angular velocity
[latex]\omega = \left(\right. \text{15} . 0 \text{m}/\text{s} \left.\right) / \left(\right. 1 . \text{20} \text{m} \left.\right) = \text{12} . 5 \text{rad}/\text{s}.[/latex]
Both [latex]\omega[/latex] and [latex]v[/latex] have directions (hence they are angular and linear velocities, respectively). Angular velocity has only two directions with respect to the axis of rotation—it is either clockwise or counterclockwise. Linear velocity is tangent to the path, as illustrated in Figure 5.6.
Take-Home Experiment
Tie an object to the end of a string and swing it around in a horizontal circle above your head (swing at your wrist). Maintain uniform speed as the object swings and measure the angular velocity of the motion. What is the approximate speed of the object? Identify a point close to your hand and take appropriate measurements to calculate the linear speed at this point. Identify other circular motions and measure their angular velocities.
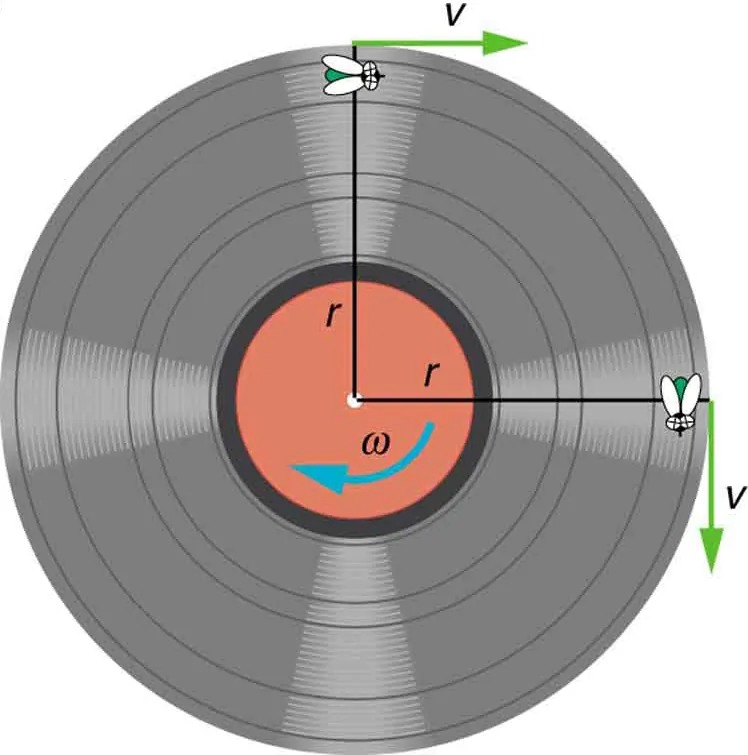
Figure 5.6 As an object moves in a circle, here a fly on the edge of an old-fashioned vinyl record, its instantaneous velocity is always tangent to the circle. The direction of the angular velocity is clockwise in this case. Image from OpenStax College Physics 2e, CC-BY 4.0
Image Description
The image depicts a diagram of a vinyl record with two cartoon flies positioned on opposite sides of the record’s surface. The record is shown from a top view and contains the following elements:
– The vinyl record is circular, with alternating light and dark gray stripes indicating grooves.
– At the center is an orange circular label area.
– A blue arrow within the orange section indicates rotation in a counterclockwise direction, labeled with the Greek letter “ω” (omega), signifying angular velocity.
– Two straight black lines extend from the center to the edges of the record, each labeled with “r” for radius.
– At the end of each radial line is a cartoon fly, each positioned on the outer edge of the record.
– Each fly has an associated green arrow pointing tangentially along the edge of the record, representing linear velocity, labeled “v”.
– The fly at the top of the image has an arrow pointing to the right, while the fly on the right side of the image has an arrow pointing downward.
Ladybug Revolution
Join the ladybug in an exploration of rotational motion. Rotate the merry-go-round to change its angle, or choose a constant angular velocity or angular acceleration. Explore how circular motion relates to the bug’s x,y position, velocity, and acceleration using vectors or graphs.

