14.2 Speed of Sound, Frequency, and Wavelength
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Define pitch.
- Describe the relationship between the speed of sound, its frequency, and its wavelength.
- Describe the effects on the speed of sound as it travels through various media.
- Describe the effects of temperature on the speed of sound.

Figure 14.7 When a firework explodes, the light energy is perceived before the sound energy. Sound travels more slowly than light does. Image from OpenStax College Physics 2e, CC-BY 4.0
Sound, like all waves, travels at a certain speed and has the properties of frequency and wavelength. You can observe direct evidence of the speed of sound while watching a fireworks display. The flash of an explosion is seen well before its sound is heard, implying both that sound travels at a finite speed and that it is much slower than light. You can also directly sense the frequency of a sound. Perception of frequency is called pitch. The wavelength of sound is not directly sensed, but indirect evidence is found in the correlation of the size of musical instruments with their pitch. Small instruments, such as a piccolo, typically make high-pitch sounds, while large instruments, such as a tuba, typically make low-pitch sounds. High pitch means small wavelength, and the size of a musical instrument is directly related to the wavelengths of sound it produces. So a small instrument creates short-wavelength sounds. Similar arguments hold that a large instrument creates long-wavelength sounds.
The relationship of the speed of sound, its frequency, and wavelength is the same as for all waves:
[latex]v_{\text{w}} = fλ,[/latex]
where [latex]v_{w}[/latex] is the speed of sound, [latex]f[/latex] is its frequency, and [latex]\lambda[/latex] is its wavelength. The wavelength of a sound is the distance between adjacent identical parts of a wave—for example, between adjacent compressions as illustrated in Figure 14.8. The frequency is the same as that of the source and is the number of waves that pass a point per unit time.
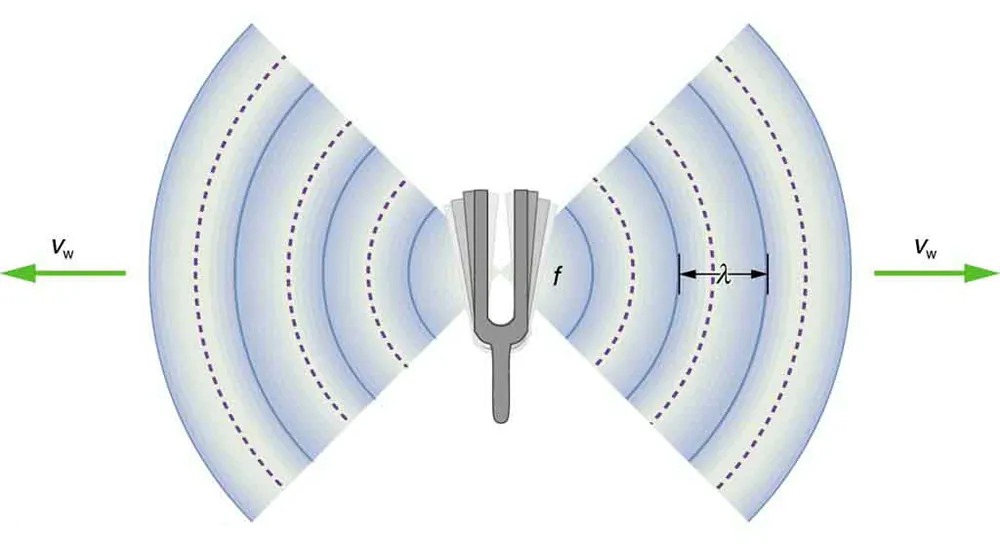
Figure 14.8 A sound wave emanates from a source vibrating at a frequency [latex]f[/latex], propagates at[latex]v_{\text{w}}[/latex], and has a wavelength [latex]\lambda[/latex]. Image from OpenStax College Physics 2e, CC-BY 4.0
Image Description
The image depicts a diagram illustrating wave propagation from a tuning fork. The tuning fork is placed in the center, with wavefronts emanating from it. The waves are shown as concentric arcs on both sides of the fork, indicating the direction of sound wave travel. There are arrows labeled “Vw” on both sides, pointing in opposite directions, representing wave velocity. The distance between two consecutive wavefronts on the right side is marked as “λ,” indicating the wavelength. The tuning fork is labeled “f,” denoting frequency. The background of the wavefronts is shaded with a gradient of blue, becoming lighter as the distance from the tuning fork increases.
Table 14.1 makes it apparent that the speed of sound varies greatly in different media. The speed of sound in a medium is determined by a combination of the medium’s rigidity (or compressibility in gases) and its density. The more rigid (or less compressible) the medium, the faster the speed of sound. For materials that have similar rigidities, sound will travel faster through the one with the lower density because the sound energy is more easily transferred from particle to particle. The speed of sound in air is low, because air is compressible. Because liquids and solids are relatively rigid and very difficult to compress, the speed of sound in such media is generally greater than in gases.
The speed of sound is affected by temperature in a given medium. For air at sea level, the speed of sound is given by
[latex]v_{\text{w}} = \left(\text{331} \text{ m}/\text{s}\right) \sqrt{\frac{T}{\text{273} \text{K}}} ,[/latex]
where the temperature (denoted as [latex]T[/latex]) is in units of kelvin. The speed of sound in gases is related to the average speed of particles in the gas, [latex]v_{\text{rms}}[/latex], and that
[latex]v_{\text{rms}} = \sqrt{\frac{\text{3} kT}{m}} ,[/latex]
where [latex]k[/latex] is the Boltzmann constant ([latex]1.38 \times \text{10}^{−\text{23}} \text{J}/\text{K}[/latex]) and [latex]m[/latex] is the mass of each (identical) particle in the gas. So, it is reasonable that the speed of sound in air and other gases should depend on the square root of temperature. While not negligible, this is not a strong dependence. At [latex]\text{0}º\text{C}[/latex], the speed of sound is 331 m/s, whereas at [latex]\text{20}.\text{0}º\text{C}[/latex] it is 343 m/s, less than a 4% increase. Figure 14.9 shows a use of the speed of sound by a bat to sense distances. Echoes are also used in medical imaging.
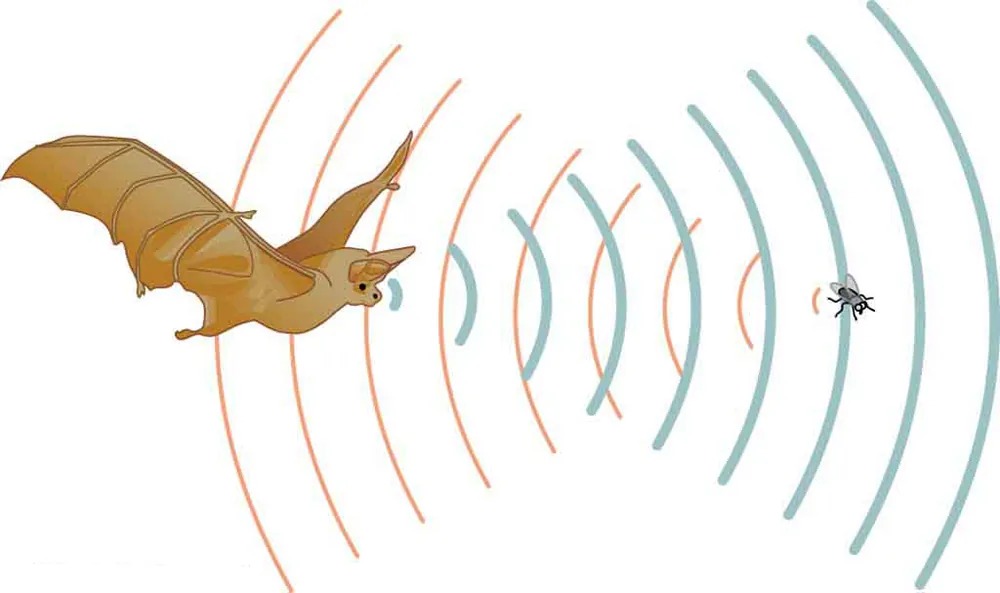
Figure 14.9 A bat uses sound echoes to find its way about and to catch prey. The time for the echo to return is directly proportional to the distance. Image from OpenStax College Physics 2e, CC-BY 4.0
Image Description
An illustration depicting a bat using echolocation to locate an insect. The bat is shown flying on the left side of the image. Sound waves are emanating from the bat in the form of curved lines, colored in orange, moving outward towards an insect on the right. The insect, drawn as a small black creature with wings, is on the far right. The sound waves that reflect back from the insect to the bat are represented by blue curved lines, illustrating the process of echo detection.
One of the more important properties of sound is that its speed is nearly independent of frequency. This independence is certainly true in open air for sounds in the audible range of 20 to 20,000 Hz. If this independence were not true, you would certainly notice it for music played by a marching band in a football stadium, for example. Suppose that high-frequency sounds traveled faster—then the farther you were from the band, the more the sound from the low-pitch instruments would lag that from the high-pitch ones. But the music from all instruments arrives in cadence independent of distance, and so all frequencies must travel at nearly the same speed. Recall that
[latex]v_{\text{w}} = fλ.[/latex]
In a given medium under fixed conditions, [latex]v_{\text{w}}[/latex] is constant, so that there is a relationship between [latex]f[/latex] and [latex]\lambda[/latex]; the higher the frequency, the smaller the wavelength. See Figure 17.10 and consider the following example.
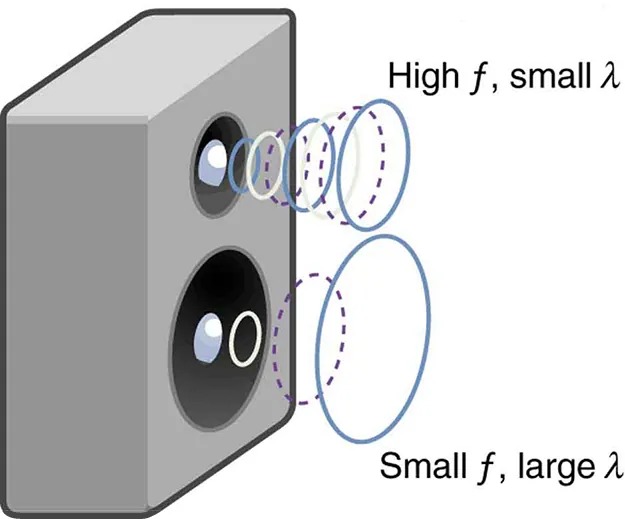
Figure 14.10 Because they travel at the same speed in a given medium, low-frequency sounds must have a greater wavelength than high-frequency sounds. Here, the lower-frequency sounds are emitted by the large speaker, called a woofer, while the higher-frequency sounds are emitted by the small speaker, called a tweeter. Image from OpenStax College Physics 2e, CC-BY 4.0
Image Description
The image shows a speaker-like object with two circular components on its front face, each resembling a speaker driver. The upper driver is labeled “High f, small λ,” indicating high frequency and small wavelength. The lower driver is labeled “Small f, large λ,” indicating low frequency and large wavelength. Concentric circles, emanating from each driver, represent sound waves. The circles for the high frequency (upper) driver are smaller and closer together, while those for the low frequency (lower) driver are larger and spaced further apart.
Example 14.1
Calculating Wavelengths: What Are the Wavelengths of Audible Sounds?
Calculate the wavelengths of sounds at the extremes of the audible range, 20 and 20,000 Hz, in [latex]\text{30}.\text{0}º\text{C}[/latex] air. (Assume that the frequency values are accurate to two significant figures.)
Strategy
To find wavelength from frequency, we can use [latex]v_{\text{w}} = fλ[/latex].
Solution
- Identify knowns. The value for [latex]v_{\text{w}}[/latex], is given by
[latex]v_{\text{w}} = \left(\text{331} \text{m}/\text{s}\right) \sqrt{\frac{T}{\text{273} \text{K}}} .[/latex]
14.5 - Convert the temperature into kelvin and then enter the temperature into the equation
[latex]v_{\text{w}} = \left(\text{331} \text{m}/\text{s}\right) \sqrt{\frac{\text{303 K}}{\text{273} \text{K}}} = \text{348} . 7 \text{m}/\text{s} .[/latex]
14.6 - Solve the relationship between speed and wavelength for [latex]\lambda[/latex]:
[latex]\lambda = \frac{v_{w}}{f} .[/latex]
14.7 - Enter the speed and the minimum frequency to give the maximum wavelength:
[latex]\lambda_{\text{max}} = \frac{\text{348} . 7 \text{m}/\text{s}}{\text{20 Hz}} = \text{17} \text{m} .[/latex]
14.8 - Enter the speed and the maximum frequency to give the minimum wavelength:
[latex]\lambda_{\text{min}} = \frac{\text{348} . 7 \text{m}/\text{s}}{\text{20} , \text{000 Hz}} = 0 . \text{017} \text{m} = 1 . \text{7 cm} .[/latex]
14.9
Discussion
Because the product of [latex]f[/latex] multiplied by [latex]\lambda[/latex] equals a constant, the smaller [latex]f[/latex] is, the larger [latex]\lambda[/latex] must be, and vice versa.
The speed of sound can change when sound travels from one medium to another. However, the frequency usually remains the same because it is like a driven oscillation and has the frequency of the original source. If [latex]v_{\text{w}}[/latex] changes and [latex]f[/latex] remains the same, then the wavelength [latex]\lambda[/latex] must change. That is, because [latex]v_{\text{w}} = fλ[/latex], the higher the speed of a sound, the greater its wavelength for a given frequency.
Making Connections: Take-Home Investigation—Voice as a Sound Wave
Suspend a sheet of paper so that the top edge of the paper is fixed and the bottom edge is free to move. You could tape the top edge of the paper to the edge of a table. Gently blow near the edge of the bottom of the sheet and note how the sheet moves. Speak softly and then louder such that the sounds hit the edge of the bottom of the paper, and note how the sheet moves. Explain the effects.
Check Your Understanding
Imagine you observe two fireworks explode. You hear the explosion of one as soon as you see it. However, you see the other firework for several milliseconds before you hear the explosion. Explain why this is so.
Click for Solution
Solution
Sound and light both travel at definite speeds. The speed of sound is slower than the speed of light. The first firework is probably very close by, so the speed difference is not noticeable. The second firework is farther away, so the light arrives at your eyes noticeably sooner than the sound wave arrives at your ears.
Check Your Understanding
You observe two musical instruments that you cannot identify. One plays high-pitch sounds and the other plays low-pitch sounds. How could you determine which is which without hearing either of them play?
Click for Solution
Solution
Compare their sizes. High-pitch instruments are generally smaller than low-pitch instruments because they generate a smaller wavelength.

