9.2 The Chain of Infection
The chain of infection explains how infections can spread. The chain has six links: the infectious agent (germs), reservoir, portal of exit, mode of transmission, portal of entry, and susceptible host. The chain can be broken at each link to prevent the spread of infection.
 Infectious Agent
Infectious Agent
Infectious agents are germs, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
 Reservoir
Reservoir
Reservoirs are where germs live. Germs can live on people, animals, food, soil, and water.
 Portal of Exit
Portal of Exit
The portal of exit is how germs get out of the current host where they have been living. Germs exit their human hosts via the mouth and nose (sneeze), breaks or cuts in the skin (blood), and through toileting activities, such as urination and defecation.
 Mode of Transmission
Mode of Transmission
The mode of transmission is how germs travel around. Germs can live outside the reservoir for a few hours and up to a couple of months. For example, the common cold virus can live on hard surfaces for 24 to 48 hours. Clostridium Difficile (C. diff) can survive on surfaces for upwards of five months.
 Portal of Entry
Portal of Entry
The portal of entry is how germs get into the new host. Germs sneak into humans by way of the mouth, eyes, and openings in the skin. The average human touches their face twenty-three times every hour. This action brings germs from the hands to the mouth and eyes 184 times in an eight-hour shift in the workplace (Kwok et al., 2015).
 Susceptible Host
Susceptible Host
A susceptible host is the next person who gets sick. Germs have found their way into an environment that supports growth and reproduction. Sometimes, the human immune system will defend against germs and kill them before they can grow and reproduce.
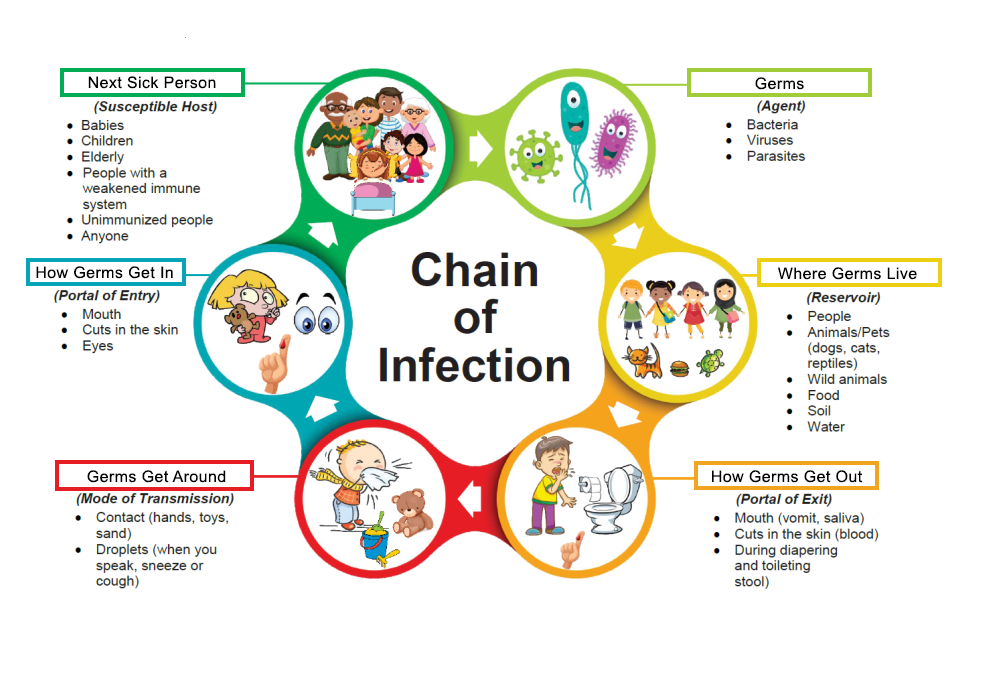
Image Description
The Chain of Infection
Germs (Agent) – Bacteria, Viruses, Parasites
Where Germs Live (Reservoir) – People, Animals/Pets (dogs, cats, reptiles), Wild animals, Food, Soil, Water
How Germs Get Out (Portal of Exit) – Mouth (vomit, saliva), Cuts in the skin (blood), During diapering and toileting (stool)
Germs Get Around (Mode of Transmission) – Contact (hands, toys, sand), Droplets (when you speak, sneeze, or cough)
How Germs Get In (Portal of Entry) – Mouth, Cuts in the Skin, Eyes
Next Sick Person (Susceptible Host) – Babies, Children, Elderly, People with a weakened immune system, Unimmunized people, Anyone
Watch: AHE: The Chain of Infection
Video: “AHE: The Chain of Infection” by AHEofAHA [3:02] is licensed under the Standard YouTube License. Transcript.
“Virus“, “Poultry“, “Cough“, “Hands“, “Clean“, “Infected” by Umeicon, Flaticon License.

