5.1 What is Sustainability?
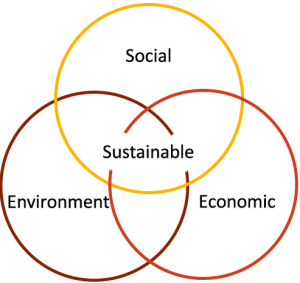
The definition of sustainability development by the Brundtland Commission (1987) states sustainability means meeting our own needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. The commission outlined three pillars of sustainability: social, economic and environmental.
Social sustainability identifies that universal human rights and necessities are attainable by all people who have enough resources to keep their families and communities healthy and secure.
Economic sustainability means that human communities across the globe are able to maintain their independence and have access to the resources that they require, financial and other to meet their needs.
Environmental states that ecological integrity is maintained, all of the earth’s environmental systems are kept in balance, while natural resources are consumed by humans at a rate where they are able to replenish themselves (Brundtland Commission, 1987).
As a Nutrition and Food Service manager, it is important to consider the impact of work on the pillars of sustainability, which are social, economic and environmental.
How does the work that is happening now affect the people, costs, and the environment? Can any of the pillars of sustainability be improved by using new processes? When implementing or maintaining a sustainability program, think about how the program impacts the people in your community the finances, which could be additional cost or cost savings of the program and the environment.

