Note-Taking

You’ve got the PowerPoint slides for your lecture, and the information in your textbook. Do you need to take notes as well?
Despite the vast amount of information available in electronic formats, taking notes is an important learning strategy. In addition, the way that you take notes matters, and not all note-taking strategies lead to equal results. By considering your note-taking strategies carefully, you will be able to create a set of notes that will help retain the most important concepts from lectures and tests, which will assist you in your exam preparation.
Two Purposes for Taking Notes
People take notes for two main reasons:
- To keep a record of the information they heard. This is also called the external storage function of note-taking.
- To facilitate learning material they are currently studying.
The availability of information on the internet may reduce the importance of the external storage function of note-taking. When the information is available online, it may seem logical to stop taking notes. However, by neglecting to take notes, you lose the benefits of note-taking as a learning tool.
How Note-Taking Supports Learning
Taking notes during class supports your learning in several important ways:
- Taking notes helps you to focus your attention and avoid distractions.
- As you take notes in class, you will be engaging your mind in identifying and organizing the main ideas. Rather than passively listening, you will be doing the work of active learning while in class, making the most of your time.
- Creating good notes means that you will have a record for later review. Reviewing a set of condensed and well-organized notes is more efficient than re-reading longer texts and articles.
Everybody takes notes, or at least everybody claims to. But if you take a close look, many who are claiming to take notes on their laptops are actually surfing the Web, and paper notebooks are filled with doodles interrupted by a couple of random words with an asterisk next to them reminding you that “This is important!” In college and university, these approaches will not work. Your instructors expect you to make connections between class lectures and reading assignments; they expect you to create an opinion about the material presented; they expect you to make connections between the material and life beyond school. Your notes are your road maps for these thoughts. Do you take good notes? Actively listening and note-taking are key strategies to ensure your student success.
Effective note-taking is important because it:
- supports your listening efforts.
- allows you to test your understanding of the material.
- helps you remember the material better when you write key ideas down.
- gives you a sense of what the instructor thinks is important.
- creates your “ultimate study guide.”
There are various forms of taking notes, and which one you choose depends on both your personal style and the instructor’s approach to the material. Each can be used in a notebook, index cards, or in a digital form on your laptop. No specific type is good for all students and all situations, so we recommend that you develop your own style, but you should also be ready to modify it to fit the needs of a specific class or instructor. To be effective, all of these methods require you to listen actively and to think; merely jotting down words the instructor is saying will be of little use to you.
| Method | Description | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| Lists | A sequential listing of ideas as they are presented. Lists may be short phrases or complete paragraphs describing ideas in more detail. | This method is what most students use as a fallback if they haven’t learned other methods. This method typically requires a lot of writing, and you may find that you are not keeping up with the professor. It is not easy for students to prioritize ideas in this method. |
| Outlines | The outline method places most important ideas along the left margin, which are numbered with roman numerals. Supporting ideas to these main concepts are indented and are noted with capital letters. Under each of these ideas, further detail can be added, designated with an Arabic number, a lowercase letter, and so forth. | A good method to use when material presented by the instructor is well organized. Easy to use when taking notes on your computer. |
| Concept Maps | When designing a concept map, place a central idea in the centre of the page and then add lines and new circles in the page for new ideas. Use arrows and lines to connect the various ideas. | Great method to show relationships among ideas. Also good if the instructor tends to hop from one idea to another and back. |
| Cornell Method | The Cornell method uses a two-column approach. The left column takes up no more than a third of the page and is often referred to as the “cue” or “recall” column. The right column (about two-thirds of the page) is used for taking notes using any of the methods described above or a combination of them. After class or completing the reading, review your notes and write the key ideas and concepts or questions in the left column. You may also include a summary box at the bottom of the page, in which to write a summary of the class or reading in your own words. | The Cornell method can include any of the methods above and provides a useful format for calling out key concepts, prioritizing ideas, and organizing review work. Most universities recommend using some form of the Cornell method. |
The List Method
Example: The List Method of Note-taking
Learning Cycle
September 3
Prof. Jones
The learning cycle is an approach to gathering and retaining info that can help students be successful in Col. The cycle consists of 4 steps which should all be app’d. They are preparing, which sets the foundation for learning, absorbing, which exposes us to new knowledge, capturing, which sets the information into our knowledge base and finally reviewing and applying which lets us set the know. into our memory and use it.
Preparing for learning can involve mental preparation, physical prep, and oper. prep. Mental prep includes setting learning goals for self based on what we know the class w/ cover (see syllabus)/ Also it is very important to do any assignments for the class to be able to learn w/ confidence and…. ______________
Physical Prep means having enough rest and eating well. Its hard to study when you are hungry and you won’t listen well in class if you doze off.
Operation Prep means bringing all supplies to class, or having them at hand when studying… this includes pens, paper, computer, textbook, etc. Also means setting to school on time and getting a good seat (near the front).
Absorbing new knowledge is a combination of listening and reading. These are two of the most important learning skills you can have.
The list method is usually not the best choice because it is focused exclusively on capturing as much of what the instructor says as possible, not on processing the information. Most students who have not learned effective study skills use this method, because it’s easy to think that this is what note-taking is all about. Even if you are skilled in some form of shorthand, you should probably also learn one of the other methods described here, because they are all better at helping you process and remember the material. You may want to take notes in class using the list method, but transcribe your notes to an outline or concept map method after class as a part of your review process. It is always important to review your notes as soon as possible after class and write a summary of the class in your own words.
The Outline Method
Example: The Outline Method of Note-taking
Learning Cycle
September 3
Prof Jones
Learning is a cycle made up of 4 steps:
- Preparing: setting the foundation for learning.
- Absorbing: (data input) exposure to new knowledge.
- Capturing: taking ownership of the knowledge.
- Review & Apply: putting new knowledge to work.
- Preparing
- Mental Prep.
- Do assignments—new knowledge is built on prior knowledge.
- assignments from prior classes.
- Readings! (May not have been assigned in class – see syllabus!)
- Review Syllabus
- Know what instructor expects to cover
- Know what assignments you need to do
- Set yr. own obj.
- Do assignments—new knowledge is built on prior knowledge.
- Physical Prep
- Get right amount of rest. Don’t zzz in class.
- Eat right. Hard to focus when you are hungry.
- Arrive on time.
- Practical Prep (Organizational Prep):
- Bring right supplies – (Notebooks, Texts, Pens, etc.)
- Arrive on time
- Get organized and ready to listen
- Don’t interrupt the focus of others
- Get a good seat
- Sit in the front of the class.
- Mental Prep.
The advantage of the outline method is that it allows you to prioritize the material. Key ideas are written to the left of the page, subordinate ideas are then indented, and details of the subordinate ideas can be indented further. To further organize your ideas, you can use the typical outlining numbering scheme (starting with roman numerals for key ideas, moving to capital letters on the first subordinate level, Arabic numbers for the next level, and lowercase letters following.) At first you may have trouble identifying when the instructor moves from one idea to another. This takes practice and experience with each instructor, so don’t give up! In the early stages you should use your syllabus to determine what key ideas the instructor plans to present. Your reading assignments before class can also give you guidance in identifying the key ideas.
If you’re using your computer to take notes, a basic word processing application (like Microsoft Word or Works) is very effective. Format your document by selecting the outline format from the format bullets menu. Use the increase or decrease indent buttons to navigate the level of importance you want to give each item. The software will take care of the numbering for you!
After class be sure to review your notes and then summarize the class in one or two short paragraphs using your own words. This summary will significantly affect your recall and will help you prepare for the next class.
The Concept Map Method
Example: The Concept Map Method of Note-taking
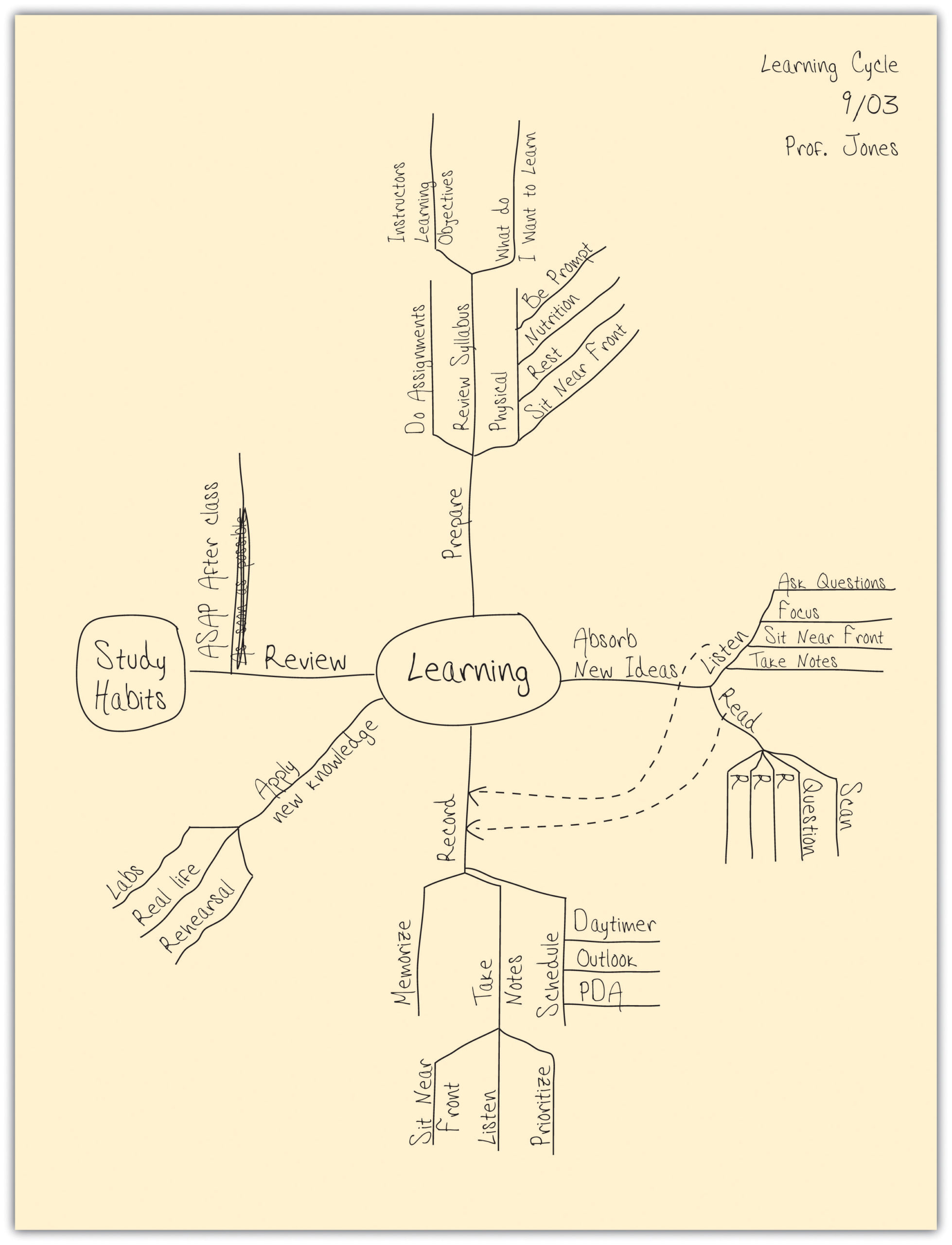
This is a very graphic method of note-taking that is especially good at capturing the relationships among ideas. Concept maps harness your visual sense to understand complex material “at a glance.” They also give you the flexibility to move from one idea to another and back easily (so they are helpful if your instructor moves freely through the material).
To develop a concept map, start by using your syllabus to rank the ideas you will listen to by level of detail (from high-level or abstract ideas to detailed facts). Select an overriding idea (high level or abstract) from the instructor’s lecture and place it in a circle in the middle of the page. Then create branches off that circle to record the more detailed information, creating additional limbs as you need them. Arrange the branches with others that interrelate closely. When a new high-level idea is presented, create a new circle with its own branches. Link together circles or concepts that are related. Use arrows and symbols to capture the relationship between the ideas. For example, an arrow may be used to illustrate cause or effect, a double-pointed arrow to illustrate dependence, or a dotted arrow to illustrate impact or effect.
As with all note-taking methods, you should summarize the chart in one or two paragraphs of your own words after class.
The Cornell Method
Example: The Cornell Method of Note-taking

The Cornell method was developed in the 1950s by Professor Walter Pauk at Cornell University [1]. It is recommended by many universities because of its usefulness and flexibility. This method is simple to use for capturing notes, is helpful for defining priorities, and is a very helpful study tool.
The Cornell method follows a very specific format that consists of four boxes: a header, two columns, and a footer.
The header is a small box across the top of the page. In it you write identification information like the course name and the date of the class. Underneath the header are two columns: a narrow one on the left (no more than one-third of the page) and a wide one on the right. The wide column, called the “notes” column, takes up most of the page and is used to capture your notes using any of the methods outlined earlier. The left column, known as the “cue” or “recall” column, is used to jot down main ideas, keywords, questions, clarifications, and other notes. It should be used both during the class and when reviewing your notes after class. Finally, use the box in the footer to write a summary of the class in your own words. This will help you make sense of your notes in the future and is a valuable tool to aid with recall and studying.
Using Index Cards for the Cornell Method
Some students like to use index cards to take notes. They actually lend themselves quite well to the Cornell method. Use the “back” or lined side of the card to write your notes in class. Use one card per key concept. The “front” unlined side of the card replaces the left hand “cue” column. Use it after class to write keywords, comments, or questions. When you study, the cards become flash cards with questions on one side and answers on the other. Write a summary of the class on a separate card and place it on the top of the deck as an introduction to what was covered in the class.
“I used to tape my lecture classes so I could fill in my sketchy notes afterwards. Now that I’m using the Cornell system, my notes are complete and organized in much less time. And my regular five-minute reviews make learning almost painless. No more taping and listening twice.”
— A student at Southern Methodist University
You will have noticed that all methods end with the same step: reviewing your notes as soon as possible after class. Any review of your notes is helpful (reading them, copying them into your computer, or even recasting them using another note-taking method). But THINK! Make your review of notes a thoughtful activity, not a mindless process. When you review your notes, think about questions you still have and determine how you will get the answers. (From the next class? Studying with a friend? Looking up material in your text or on the net?) Examine how the material applies to the course; make connections with notes from other class sessions, with material in your text, and with concepts covered in class discussions. Finally, it’s fun to think about how the material in your notes applies to real life. Consider this both at the very strategic level (as in “What does this material mean to me in relation to what I want to do with my life?”) as well as at a very mundane level (as in, “Is there anything cool here I can work into a conversation with my friends?”).
Instructor Handouts
Some instructors hand out or post their notes or their PowerPoint slides from their lectures. These handouts should never be considered a substitute for taking notes in class. They are a very useful complement and will help you confirm the accuracy of your notes, but they do not involve you in the process of learning as well as your own notes do. After class, review your notes with highlighter in hand and mark keywords and ideas in your notes. This will help you write a summary of the class in your own words.
General Tips on Note-Taking
Regardless of what note-taking method you choose, there are some note-taking habits you should get into for all circumstances and all courses:
- Be prepared. Make sure you have the tools you need to do the job. If you are using a notebook, be sure you have it with you and that you have enough paper. Also be sure to have your pen (and a spare) and perhaps a pen with different-coloured ink to use for emphasis. If you are taking notes on your laptop, make sure the battery is charged! Select the application that lends itself best to your style of note-taking. Microsoft Word works very well for outline notes, but you might find taking notes in Excel to work best if you are working within the Cornell method. (It’s easier to align your thoughts in the cue or recall column to your notes in the right column. Just be sure you keep one idea per row!)
- Write on only one side of the paper. This will allow you to integrate your reading notes with your class notes.
- Label, number, and date all notes at the top of each page. This will help you keep organized.
- When using a laptop, position it such that you can see the instructor and white board right over your screen. This will keep the instructor in your field of vision even if you have to glance at your screen or keyboard from time to time. Make sure your focus remains with the instructor and not on your laptop. A word of caution about laptops for note-taking: use them if you are very adept at keyboarding, but remember that not all note-taking methods work well on laptops because they do not easily allow you to draw diagrams and use special notations (scientific and math formulas, for example).
- Don’t try to capture everything that is said. Listen for the big ideas and write them down. Make sure you can recognize the instructor’s emphasis cues and write down all ideas and keywords the instructor emphasizes. Listen for clues like “the four causes were…” or “to sum up.…”
- Copy anything the instructor writes on the board. It’s likely to be important.
- Leave space between ideas. This allows you to add additional notes later (e.g., notes on the answer to a question you or one of your classmates asked).
- Use signals and abbreviations. The ones you use are up to you, but be consistent so you will know exactly what you mean by “att.” when you review your notes. You may find it useful to keep a key to your abbreviations in all your notebooks.
- Use some method for identifying your own thoughts and questions to keep them separate from what the instructor or textbook author is saying. Some students use different colour ink; others box or underline their own thoughts. Do whatever works for you.
- Create a symbol to use when you fall behind or get lost in your note-taking. Jot down the symbol, leave some space, and focus on what the instructor is covering now. Later you can ask a classmate or the professor to help you fill in what you missed, or you can find it in your textbook.
- Review your notes as soon after class as possible (the same day is best). This is the secret to making your notes work! Use the recall column to call out the key ideas and organize facts. Fill in any gaps in your notes and clean up or redraw hastily drawn diagrams.
- Write a summary of the main ideas of the class in your own words. This process is a great aid to recall. Be sure to include any conclusions from the lecture or discussion.
- Use notes when preparing for a test or doing an assignment. Your notes usually have a summary of the most important points and are useful for making sure you incorporate important concepts in your assignments and for focusing on the main concepts when studying for tests and exams.
Watch It: Note Taking
These videos provide some great tips for note-taking as well.
Note Taking (Text Version)
Watch How to take great notes (5:08 minutes) on YouTube
Watch Taking notes: Crash Course study skills #1, (8:50 minutes) on YouTube
Activity source: “Note Taking” H5P activity by Jessica Jones and oeratgc licensed under CC BY NC SA 4.0, except where otherwise noted.
What If You Miss Class?
Clearly the best way to learn class material is to be at the class and to take your own notes. In university, regular attendance is expected. But life happens. On occasion, you may have to miss a class or lecture. When this happens, here are some strategies you can use to make up for it:
- Check with the instructor to see if there is another section of the class you can attend. Never ask the instructor “Did I miss anything important?” (Think about what that’s saying and you’ll see it’s rather insulting.)
- If the instructor posts their lectures as a podcast, listen to the lecture online and take notes. If the instructor uses PowerPoint slides, request a copy (or download them if posted) and review them carefully, jotting down your own notes and questions. Review your notes with a classmate who did attend.
- You may want to borrow class notes from a classmate. If you do, don’t just copy them and insert them in your notebook. They will not be very helpful. When you borrow notes from a classmate, you should photocopy them and then review them carefully and mark your copy with your own notes and questions. Use your textbook to try to fill in the gaps. Finally, schedule a study session with the person who gave you the notes to review the material and confirm your understanding.
- If none of these options is available for you, use the course syllabus to determine what was covered in the class, then write a short paper (two pages or so) on the material using the class readings and reliable online sources. See your instructor during office hours to review your key findings and to answer any questions you still may have.
Group Notes: A Collaborative Approach
Groups within a class can take notes together using file-sharing software on the cloud such as Google Docs. The individuals in the group can add to the document in real time as different individuals are adding themselves. This creates a collaborative document that all can use, download, or adapt. This won’t work for all situations but can be very useful especially in a fast-moving classroom.
Keeping Your Notes
Class is over, and you have a beautiful set of notes in your spiral notebook or saved in your laptop. You have written the summary of the class in your own words. Now what?
Start by organizing your notes. We recommend you use a three-ring binder for each of your subjects. Print your notes if you used a computer. If you used note cards, insert them in plastic photo holders for binders. Group all notes from a class or unit together in a section; this includes class notes, reading notes, and instructor handouts. You might also want to copy the instructor’s syllabus for the unit on the first page of the section.
Next, spend some time linking the information across the various notes. Use the recall column in your notes to link to related information in other notes (e.g. “See class notes date/page”).
If you have had a quiz or test on the unit, add it to your binder, too, but be sure to write out the correct answer for any item you missed. Link those corrections to your notes, too.
Use this opportunity to write “notes on your notes.” Review your summary to see if it still is valid in light of your notes on the reading and any handouts you may have added to your notes package.
You don’t need to become a pack rat with your notes. It is fairly safe to toss them after the end of a course except in the following cases:
- If the course you took is a prerequisite for another course, or when the course is part of a standard progression of courses that build upon each other (this is very common in math and science courses), you should keep them as a reference and review for the follow-up course.
- If the course may pertain to your future major, keep your notes. You may not realize it now that they may have future value when you study similar topics or even the same topics in more depth.
- If you are very interested in the course subject and would like to get into the material through a more advanced course, independent study, or even research, keep your notes as a prep tool for further work.
Summary
Congratulations on finishing the second part of this module! In this module, you learned about the following:
- How note-taking supports learning, and can be used as an additional learning tool while you read
- A variety of note-taking techniques, including the list, outline, Cornell and mind mapping methods
Attribution & References
Except where otherwise noted, this section is adapted from “5.6 Note-Taking” In Student Success by Mary Shier, licensed under CC BY 4.0./An adaptation of:
- This chapter was adapted from “Got Notes?” in University Success by N. Mahoney, B. Klassen, and M. D’Eon. Adapted by Mary Shier. CC BY-NC-SA.
- The first two paragraphs and text under the “Two Purposes for Taking Notes” heading are from “Take Notes from Lectures – That You’ll Actually Use” in University 101: Study, Strategize and Succeed by Kwantlen Polytechnic University. CC BY-SA.
- Alterations include removing exercises.
- Pauk, W. & Owens, R.J.Q. (2013). How to Study in College. Boston, MA: Wadsworth, Cengage Learning. ↵

