9.5 Chapter Summary
Real Life Example: Close-up: Democratic Decline in America?
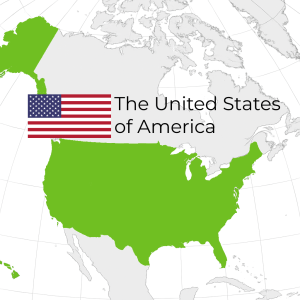
- V-Dem Regime Type: Liberal Democracy
- Transparency International Corruption Rank: 28\180
- Economist Democracy Score & Category: 7.85/10 – Flawed Democracy
- Freedom in the World Score: 84/100
In the 2024 Democracy Index from the Economist Intelligence Unit, the United States was downgraded from a Full Democracy to a Flawed Democracy. There are several factors that could be contributing to this decline. For one, the V-Dem project has documented instances of political violence and threats against election workers (Klarhoefer, 2024). Second, since taking office for a second time, President Trump has wielded executive power to bar specific journalists from press availabilities; to stop enforcing the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA), which prevents American companies from paying bribes; and to deport individuals without due process (Global State of Democracy Initiative, n.d.).

What do you think?
- Does this justify categorizing the US as a flawed democracy?
- How would you categorize the American political system?
Chapter Summary
In this chapter,
- The chapter examines global threats to election integrity, including high-profile fraud allegations and foreign interference, and their impact on public trust in democratic systems.
- It differentiates between procedural and substantive definitions of democracy, highlighting the need for free competition, legal participation, and voting rights beyond simply holding elections.
- Tools like V-Dem, Freedom House, and the Electoral Integrity Project assess the quality of democracies, with examples such as Russia illustrating “facade democracies” where elections exist but lack fairness.
- In 2024, despite record voter turnout across 74 countries, data showed a global decline in democracy quality, with increasing autocratization and only a few nations strengthening democratic institutions.
- Elections are increasingly threatened by both physical violence—especially in emerging democracies like Chad—and digital threats, including AI-generated deepfakes and social media manipulation.
- Foreign interference is growing, with documented cases in Canada, Romania, and elsewhere, prompting inquiries and initiatives like the European Democracy Shield to counteract external manipulation.
- Election fraud is categorized into voter fraud (e.g., multiple voting) and institutional fraud (e.g., ballot tampering), though in stable democracies like the U.S. and Canada, such cases are rare and often overstated.
- Trust in elections depends on both institutional transparency and individual factors such as media influence and partisan bias, and is further shaped by anti-corruption measures, observer missions, and electoral integrity safeguards.
OpenAI. (2025, June 30th). ChatGPT. [Large language model]. https://www.chatgpt.com Prompt: Can you please summarize the passage into 8 key points with no additional bullets. Edited & Reviewed by author.
Key Terms
- Adjudication –The process of fairly resolving disputes and enforcing rules during elections, ensuring procedural fairness and legal compliance.
- Autocracy – A system of government in which supreme power is concentrated in the hands of one person, often with limited political freedoms or checks on authority.
- Autocratizing – A term for countries becoming more autocratic, where democratic practices and freedoms are being eroded or dismantled.
- Birthday Problem – A statistical phenomenon where people with similar names and birthdates may be mistakenly flagged as the same individual, leading to false positives in fraud detection systems.
- Contestation –A measure of whether elections allow meaningful competition between candidates or political parties.
- Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) – A global ranking by Transparency International that scores countries based on perceived levels of public sector corruption.
- Deliberation – The quality of public debate and information available to voters, including whether choices are meaningful and based on unbiased facts.
- Democratization – The transition process through which a country adopts democratic systems of governance, including free and fair elections, rule of law, and civil liberties.
- Democratizing –A term used to describe countries that are becoming more democratic through institutional reforms and increased political freedoms.
- Election Observers – Independent individuals or groups—often international—who monitor elections to ensure they are conducted freely and fairly.
- Electoral Integrity – The adherence to democratic principles in the conduct of elections, ensuring they are free, fair, transparent, and conducted without fraud or manipulation.
- Electoral Management Bodies (EMB) –Official organizations or agencies responsible for administering elections, including registering voters, overseeing voting, and counting ballots.
- Facade Democracy –A regime that appears to follow democratic procedures, such as holding elections, but lacks genuine democratic substance due to corruption, repression, or manipulation.
- International Election Observers are independent individuals or organizations from outside a country who monitor electoral processes to assess their fairness, transparency, and adherence to international democratic standards.
- Plural Voting – The illegal act of casting more than one vote in the same election, often by exploiting weaknesses in the voter registration system.
- Procedural Approach to defining a democracy- if democratic procedures are present, such as elections, then the country must be a democracy.
- Satisfaction With Democracy (SWD) – A survey-based metric that assesses how satisfied citizens are with the way democracy functions in their country.
- Substantive Approach to defining democracy is based on the realization of core principles rather than on the presence of formal procedures like elections.
- Universal Suffrage – The right of almost all adult citizens to vote, regardless of race, gender, income, or social status.
- Voter Fraud – Illegal actions by individual voters or candidates aimed at influencing the outcome of an election, such as voting more than once or impersonating another voter.

