Week 13: Optometry Office
During the final content week of the semester, we will be examining the processes involved in working in an optometry office!
Eye Anatomy Review
Visual Acuity
Match the definition with the visual acuity term:
Optometry Office Professionals
- Ophthalmologist: A medical doctor specialist who diagnoses diseases of the eye, performs surgery, dispenses lenses, and prescribes medications. Regulated by the College of Physicians and Surgeons of Ontario.
- Optometrist: Graduated with a science degree plus 4 years of optometry schooling. Passed national board exam. Performs eye exams, and minor procedures, prescribes medications, and dispenses lenses. Regulated by the College of Optometrists of Ontario.
- Optician: Completed a college diploma program and passed the provincial licensing exam. Tests vision and dispenses lenses. Regulated by the College of Opticians.
- Optometric Assistant: Completed certificate from the Canadian Association of Optometrists. Adjusts and measures frames, completes contact lens consultations, and facilitates vision pre-testing. Regulated by the College of Optometrists of Ontario.
Interested in a career as an optometric assistant? After completion of your HOA diploma, you are eligible to enrol in the online CCOA program. Learn more at the Canadian Association of Optometrists website.
Optometric Assistant Duties
- Greets clients, verifies information, helps complete necessary forms, book appointments
- Answer phone, return emails and voicemails
- Update client EMR profile
- Manage schedule and triage appointments
- Order office supplies including frames, lenses, and equipment
- Billing: OHIP, private insurance, out-of-pocket
- Help clients select frames
Preliminary Vision Testing
Common visual assessments:
Autorefractor
- A machine that gives a quick estimate of the patient’s prescription, giving a starting point
Lensometer
- A machine that measures the strength of a pair of eyeglasses
Fundus Camera
- Captures an image of the retina
Colour vision test
- Measures the ability to differentiate between colours
Air puff tonometry:
- Uses a small puff of air to measure intraocular pressure
Key Optic Terms
Select the correct optic term for the provided description.
Understanding a Prescription Notation
Sample Prescription Notation:
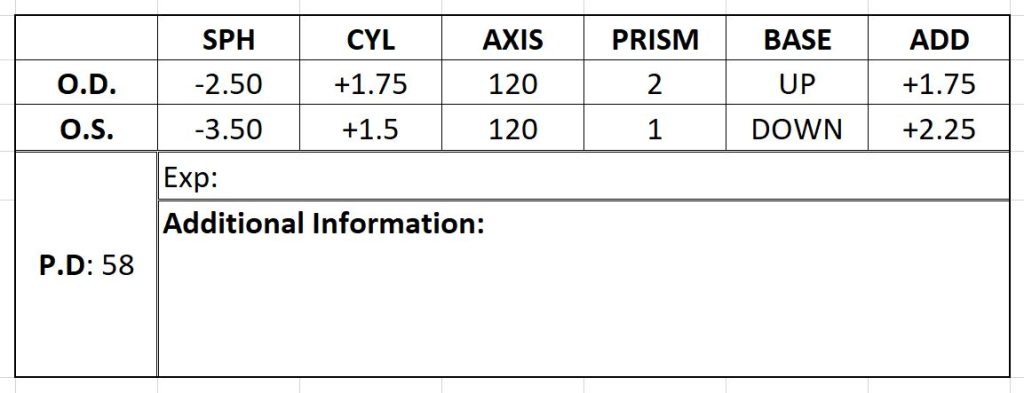
| Notation | Description |
| O.D. | Right eye |
| O.S. | Left eye |
| P.D. | Pupillary distance – how far apart the two pupils are from each other. |
| SPH | Sphere of the eye – indicates the level of lens power required to correct nearsightedness or farsightedness. A minus sign (–) means you are nearsighted, and a plus sign (+) means you are farsighted. |
| CYL | Cylinder of the eye – indicates the level of power required to correct an astigmatism. A minus sign (–) means your astigmatism causes nearsightedness, and a plus sign (+) means your astigmatism causes farsightedness. |
| AXIS | The axis confirms which way and degree the astigmatism is oriented. |
| PRISM | A special type of lens used to correct eye alignment issues such as double vision. |
| BASE | Indicates the direction of the prism (either up, down, or out). |
| ADD | Added magnifying power – used for multifocal lenses such as bifocals or trifocals. |
Optometry Office Billing
An HOA working in an optometry office will need to understand OHIP billing, and private insurance, and process out-of-pocket transactions.
OHIP
- Clients who are 19 and younger or 65 and older are eligible for an eye exam every 12 months under OHIP.
- Clients receiving ODSP or OW are covered for an eye exam every 2 years under OHIP.
- Clients of any age with certain medication conditions are eligible for an eye exam every 12 months. E.g. glaucoma, retinal disease, diabetes mellitus
- Click here to review the MOHLTC fact sheet on OHIP billing and eye care
Private Insurance
- Some clients will have coverage for eye care under their private insurance plans.
- You will be required to either bill directly to their insurance company or assist your client in completing a manual insurance claim form.
- We will be learning more about private insurance in our next unit!
Out of Pocket:
- If a client does not qualify for OHIP billing and does not have private insurance, they will be responsible for paying the required fees associated with their exams, lenses, or procedures.
- An HOA would create an invoice, process payment, and provide the client with a receipt.
References:
CCOA. (2023). Canadian Certified Optometric Assistant: About the program. Retrieved November 7, 2023 from https://opto.ca/ccoa
Depisteo. (2022). Tools used by an optometrist. Retrieved November 7, 2023 from https://depisteo.com/blog/tools-used-by-optometrist/
Heiting, G. (2022). All about vision: How to read your eyeglasses prescription. Retrieved November 7, 2023 from https://www.allaboutvision.com/eyeglasses/eyeglass-prescription.htm
Seltman, W. (2022). Eye Doctors: Optometrists and Ophthalmologists. Retrieved November 7, 2023 from https://www.webmd.com/eye-health/eye-doctors-optometrists-ophthalmologists

