3.2
Radiation Effects on Cells
A cell that is sensitive to radiation is termed radiosensitive; one that is resistant is termed radioresistant.
The response is determined by mitotic activity and cell differentiation.
Mitotic activity refers to cells that divide frequently and are more sensitive to radiation. Cell differentiation refers to cells that are immature or are not highly specialized and are more sensitive to radiation. Cell metabolism refers to cells that have higher metabolism and are more sensitive to radiation.
Radiation Effects on Tissues and Organs
Radiosensitive organs are:
- Lymphoid tissue
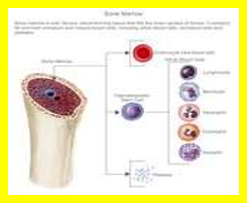
- Bone marrow
- Testes
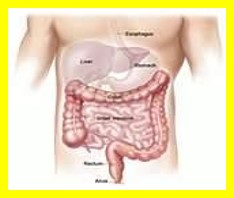
- Intestines
 |
 |
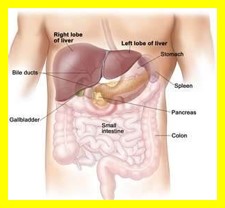
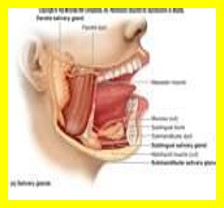
Lymphocytes (immune system) and oocytes (female reproductive cells) are nondividing cells that are very radiosensitive. The salivary glands, kidneys, and liver are all radioresistant tissues.
 |
 |
A critical organ is an organ that, if damaged, diminishes the quality of a person’s life. Critical organs exposed during dental radiographic procedures include skin, thyroid gland, lens of the eye and bone marrow.
Radiation Measurements
Measurements that dental radiographers will have to deal with very often are:
- Units of measurement
- Exposure measurement
- Dose measurement
- Dose equivalent measurement
| Traditional (older) units of radiation measurement: | SI (newer) units of radiation measurement: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exposure Measurements
Roentgen measures radiation by determining the amount of ionization that occurs in the air. It does not describe the amount of radiation absorbed.
No SI equivalent (International Systems of Units) exposure is stated in coulombs per kilogram.
| Radiation exposure equivalents | -1 roentgen (R) = 1 coulomb per kilogram (C/kg) |
| Radiation absorbed dose equivalents | -100 radiation absorbed doses (rad) = 1 gray (Gy) |
| Radiation dose equivalence | -100 roentgen equivalents in [hu]man (rem) = 1 sievert (Sv) |
Dose Measurement
The amount of energy absorbed by the tissue. The traditional unit is the rad (radiation absorbed dose).
SI equivalent is the gray: 1 Gy = 100 rads
Dose Equivalent Measurement
Dose equivalent measurement is used to compare the biological effects of different kinds of radiation. The traditional unit is the rem (roentgen equivalent man).
SI equivalent is the sievert: 1 Sv = 100 rems
Measurements Used in Dental Radiography
Milli means 1/1000, which is used to express the small doses used in dental radiography. The gray and sievert are equal in dental radiography, and the roentgen, rad, and rem are considered approximately equal.
Radiation Risks
Radiation Risks are:
Media Attributions
- Iannucci & Howerton: Dental Radiography Principles and Techniques, 6th Edition, Chapter 3, CC BY-NC-ND

