28.4
Normal Tooth Anatomy
Supporting Structures: Alveolar Bone
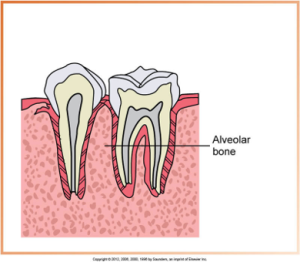 |
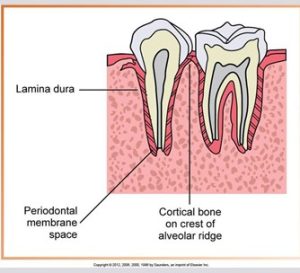
Anatomic landmarks of the alveolar process include the lamina dura, alveolar crest and the periodontal ligament space.
The shape and density of alveolar bone include both anterior and posterior regions |
Lamina Dura
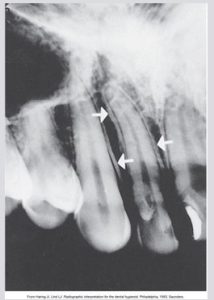
The lamina dura is the wall of the tooth socket, made of dense cortical bone. The lamina dura appears as a dense, thin radiopaque line that surrounds the root of a tooth.
 |
|
Alveolar Crest
Periodontal Ligament Space
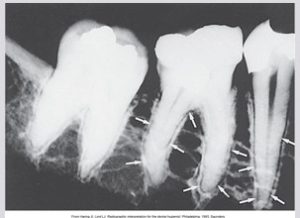
Shape and Density of Alveolar Bone: Anterior regions
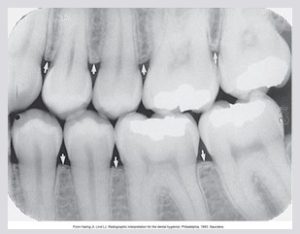
Normal alveolar crest appears pointed and sharp between the teeth. The alveolar crest appears as a dense radiopaque line in the anterior region. Alveolar crest fibers run from the crest of the alveolar bone to the cementum in the region of the CEJ. The anterior alveolar crest normally appears pointed and sharp.
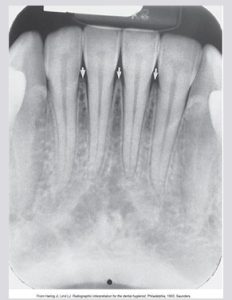
Shape and Density of Alveolar Bone: Posterior regions
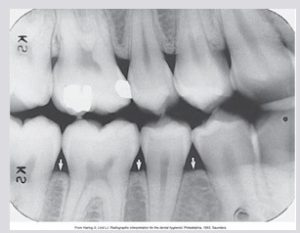
Exercise: Identify Normal Tooth Anatomy
Media Attributions
- Images courtesy of Iannucci & Howerton, Dental Radiography: Principles and Techniques, 6th Edition, (2022), Chapter 28.