28.1
Types of Bone
Cortical bone
The cortical bone, also referred to as compact bone, is a dense outer layer of bone that appears radiopaque on a radiograph. The inferior border radiopaque of the mandible is composed of cortical bone.
Cancellous bone
The cancellous bone is a soft, spongy bone located between two layers of dense cortical bone. It appears primarily radiolucent. Trabeculae (bony spicules) appear Trabeculae Radiopaque, while marrow spaces appear Bone marrow Radiolucent
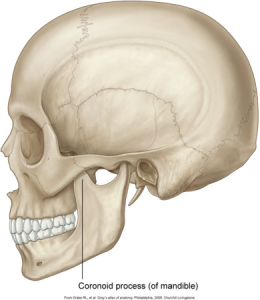
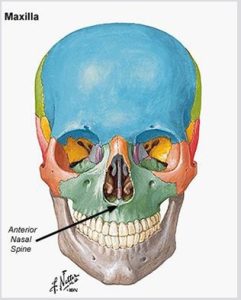
Prominences of Bone
Prominences of bone appear radiopaque on dental images. There are five types of prominences: process, ridge, spine, tubercle, and tuberosity.
Spaces and Depressions in Bone
Spaces and depressions in bone do not resist the passage of the x-ray beam and appear radiolucent on dental images. There are four spaces and depressions in bones: canal, foramen, fossa and sinus.
Spaces and Depressions in Bone |
|
Canal: tubelike passageway through bone that contains nerves and blood vesselsExample: Mandibular canal |
 |
Foramen: opening or hole that permits the passage of nerves and blood vesselsExample: Mental foramen of the mandible |
 |
Fossa: broad, shallow, scooped-out, or depressed areaExample: Submandibular fossa of the mandible |
 |
Sinus: hollow space, cavity, or recess in boneExample: Maxillary sinus |
 |
Miscellaneous Terms
Septum
A bony wall or partition that divides two spaces or cavities. A septum may be present within the space of a fossa or sinus. Appears radiopaque on a radiograph.
- Example: Nasal Septum

Suture
An immovable joint representing a line of union between adjoining bones of the skull. This thin line appears radiolucent.
- Example: Median palatine suture of the maxilla

Practice Makes Perfect