21.1
Bite-wing technique is a method used to examine the interproximal surfaces of teeth and is useful to monitor the progression of dental caries, assess existing restorations, and examine the crestal bone levels between teeth.
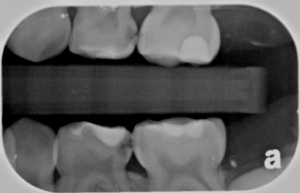
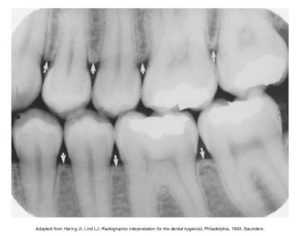
An understanding of these basic terms is necessary for learning about the bite-wing technique.
Term |
Definition |
| Interproximal | Between two adjacent surfaces |
| Interproximal Examination | Used to inspect the crowns of both maxillary and mandibular teeth on a single image |
| Bite-Wing Receptor (BW) | Receptor used in interproximal examination. Has a “wing” or tab, and the patient “bites” on the wing to stabilize the |
| Alveolar Bone | Bone that supports and encases the roots of the teeth |
| Crestal Bone | The most coronal portion of alveolar bone found between teeth; composed of cortical bone; appears radiopaque (also known as the alveolar crest) |
| Contact Areas | The area where adjacent tooth surfaces contact each other. |
| Horizontal Bite-Wing | The bite-wing receptor is placed in the mouth with the long portion of the receptor in a horizontal direction. |
| Opened Contacts | On a dental image, open contacts appear as a thin radiolucent line between adjacent tooth surfaces. |
| Overlapped Contacts | On a dental image, the area where the contact area of one tooth is superimposed over the contact area of an adjacent tooth. |
| Vertical Bite-Wing | The bite-wing receptor is placed in the mouth with the long portion of the receptor in a vertical direction. |
Alveolar & Crestal Bone
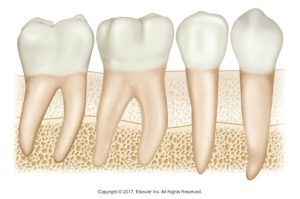
Alveolar bone is the bone of the maxilla and the mandible that supports and encases the roots of teeth; appears radiopaque.
 |
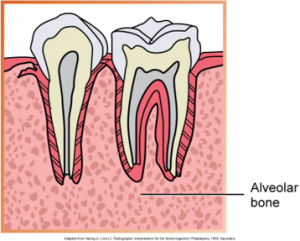 |
| Illustration of three types of human teeth (molar, premolar, and canine) embedded in the alveolar bone. | Illustration showing a cross-section of two teeth with their internal structures and surrounding alveolar bone. |
The crestal bone is the most coronal portion of alveolar bone found between teeth, also known as an alveolar crest.
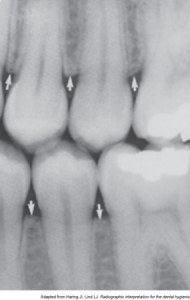
Contact Areas
See the slides below that talk about the different contact areas.
Principles of Bite-Wing Technique
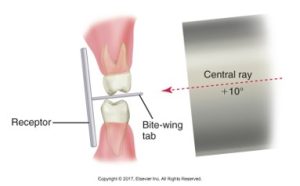
A principle is that the receptor is placed in the mouth parallel to the crowns of both the upper and lower teeth. Another principle is that the receptor is stabilized when the patient bites on the bite-wing tab or beam alignment device. And lastly, the central ray is directed through the contacts of the teeth, using a +10 degree vertical angulation.
Vertical Angulation
Positions of the receptor, bite-wing tab, and central ray in the bite-wing technique. The receptor is parallel to the crowns in the maxillary and mandibular teeth. The central ray is directed downward (+10 degrees of vertical angulation).
The diagram below displays the setup for a dental x-ray using the bite-wing technique with vertical angulation.
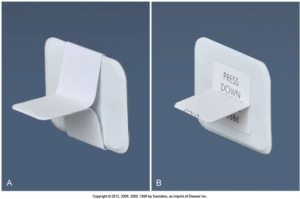
Beam Alignment Device and Bite-Wing Tab
A bite-wing beam alignment device is a device used to position an intraoral receptor in the mouth and maintain the receptor in position during the imaging procedure.
A bite-wing tab is an alternative to a beam alignment device. It is a heavy paperboard tab or loop fitted around a periapical receptor and used to stabilize the receptor during exposure.
Below is a hotspot image highlights a bite-wing tab holder, a beam alignment device, the use of bite-wing exposure.
Here is an image of a bite-wing tab and an adhesive bite-wing tab.
Media Attributions
- Iannuci: Dental Radiography, 6th Edition, Chapter 21, CC BY-NC-ND

