Chapter 9: Building Strong Customer Relationships
Chapter 9 Learning Outcomes
After reading this chapter, you should be able to do the following:
- Explain how “customer relations” differs from “customer service.”
- Explain how offering an exceptional customer experience requires team collaboration.
- List three benefits companies receive from developing positive customer relationships.
- List three ways companies can build customer loyalty.
- Describe two key trends currently shaping the field of customer service.
- Describe how companies can use Artificial Intelligence (AI) to personalize customers’ experiences.
- Explain how journey mapping can help a business improve the customer experience.
- Discuss how social listening and social monitoring help companies build customer relationships.
- Explain how customer relationship management (CRM) software might be used across business departments to build positive customer relationships.
Customer Relations Versus Customer Service
Customer relations refers to the different methods and strategies that a business can use to forge, improve, and manage all interactions with its customers.[1] Customer service refers to the support and assistance given to a customer before, during, and after a sale. Both are critical and work together to create positive customer experiences (CX).
The customer service team plays a key role in growing customer relationships, as they are usually the first point of contact for customers. In customer service, agents help customers in real time to solve issues and deliver a positive journey through the sales funnel. Companies can use the valuable data gathered from customer service interactions to foster customer relations and proactively strive to improve the customer experience and address problems before they impact customers.[2] With that said, building customer relationships is not just a job for a single customer service team. It is every employee’s responsibility to ensure customers receive the best service and a positive experience when interacting with the company.
Some department employees are considered customer-facing and actually interact very directly with customers as part of their daily jobs. This includes groups like customer support, sales, and service representatives, but these are not the only teams that directly impact the customer experience and overall journey. Every team has an important role to play, and product development teams, human resources staff, supply chain managers, and maintenance crews (to name a few) need to understand how their daily efforts are connected to the overall customer experience.
High-performing companies view customer service as their primary revenue driver, and seventy-three percent of business leaders say there is a direct link between customer service and business performance.[3]
A customer experience vision or mission statement and leaders who support and communicate the vision can help every department see their value and role in providing exceptional customer experiences that build positive customer relationships. For example, if the customer service team needs to provide information to a customer on their account balance, the employee interacting with the customer may require assistance from the Accounting department personnel. If the assistance is slow or the information provided is inaccurate, the service the customer receives will be below their expectations and result in an unhappy customer. It is critical that all department personnel understand that each has a responsibility to contribute to an overall excellent customer experience.
Every touchpoint a customer has with an organization should leave them feeling satisfied, valued, and impressed with the company. Customers want to feel that they made the right choice when purchasing from a company; therefore, they have certain expectations around product performance, service levels, warranties, employee interactions, social media and website interactions, brand, image, community, and more. Businesses need to ensure that they are supporting what they are promoting. If a product is marketed with a lifetime guarantee, then you can believe that customers will expect that to be true.
Below are a few customer relations activities.
- Tracking customer behavior and providing personalized customer experiences.
- Automating customer feedback collection (e.g., surveys).
- Analyzing customer feedback provided during customer interactions.
- Making data-driven decisions and marketing strategies.
- Proposing solutions to frequent issues.
- Utilizing the right sales and marketing software.
- Providing omnichannel service and social media presence.
- Ensuring the customer service experience is consistent across customer touchpoints.
- Delivering live assistance and boosting customer engagement.
- Working with IT and technical teams to streamline customer interactions and decrease wait times.
Importance of Building Customer Relationships

It’s more important than ever for businesses to create strong customer relationships. Building any long-lasting relationship requires nurturing and personalized experiences. Customers don’t want to feel like their interactions are transactional. Transactional relationships often attract customers based on price alone who are looking to fill a short-term need without building a long-term relationship with a brand. Businesses that seek to create long-term, repeat business focus on providing excellent customer experiences because they understand that retaining customers is less expensive than obtaining new ones.
A critical step in establishing these long-term relationships is building trust. Customers are more likely to remain loyal and engage with a brand when they feel confident that the company is honest, transparent, and reliable. Trust is earned through consistent, high-quality experiences, clear communication, and by demonstrating that the business genuinely values the customer’s needs and feedback. Without trust, even the most personalized interactions may fail to create a meaningful connection, as customers are unlikely to commit to a brand they perceive as unreliable or indifferent.
By prioritizing trust, businesses lay the foundation for deeper engagement and long-term loyalty. Trusted brands are better positioned to encourage repeat purchases, receive candid feedback, and foster advocacy, where satisfied customers actively recommend the business to others.
Below are a few of the benefits companies gain from creating positive customer relationships, supported by trust and long-term engagement:
- Higher Customer Retention. Loyal customers continue to return when they trust the brand.
- More Customer Loyalty. Trust encourages customers to stick with a company even if competitors offer lower prices.
- Better Business Reputation and Brand Credibility. Trusted businesses are viewed more favorably and attract new customers through positive word-of-mouth.
- Ability to Maintain Prices. Customers who value the relationship and trust the brand are less price-sensitive.
- Increased Competitive Advantage. Strong relationships and trust differentiate the business in a crowded market.
- Improved Employee Morale and Attitude. Employees take pride in working for a trusted brand and are motivated to provide better customer experiences.
Explore the Concept: Customer Relations Statistics
Check out these statistics gathered by Zendesk that strongly show customer relationships are the way of the future for company growth and longevity.[4]
- The top reason customers leave brands is that they feel unappreciated.
- Eighty percent of consumers are more likely to do business with a company if it offers personalized experiences.
- Offering high-quality experiences can lower the cost of serving customers by up to thirty-three percent.
- The average cost of customers switching to other companies due to poor service is $1.6 trillion.
- Companies that earn $1 billion a year will see an average gain of $700 million within three years of investing in the customer experience.
Explore the Internet to locate additional statistics that support the claim that companies need to ensure positive customer relationships in order to thrive and secure business longevity. Can you locate statistics for Canada (or the country in which you reside)? Share your findings with your class and/or professor.
Enhance Customer Retention by Building Loyalty
Customer loyalty happens when customers give a company repeat business over time. When a company provides great value in its products and services, and the customer experience stays consistently good, then the business will reap the benefits of customer retention.[5]
Listed below are eight ways businesses can develop meaningful customer relationships and create long-lasting customer loyalty:[6]
1. Communicate Company Values
Share values with employees and customers. Create more effective marketing strategies for new products and services.
2. Know the Customer Journey
Create journey maps to assess the gaps in the current service offerings. Recognize how each customer persona’s service experience differs. Mapping the customer journey for the personas, or target segments, a company wishes to reach can help the business better understand customers’ expectations, and then the business can tailor customer experiences to fit the customer’s needs. Mapping helps businesses measure the progress of optimizing processes against the customer experience desired by customers. The mapping process brings together sales, marketing, and customer support to define what customers need to know before they buy, what they need after they buy, and how these interactions can be enhanced. [7]

Not only can journey mapping help businesses identify issues that may be negatively affecting a positive customer journey, but it can also help businesses identify new growth opportunities. During the mapping process, auditing content can reveal areas where the company may be losing customers so that the business can strengthen those areas. A journey map can help steer the team toward company priorities. A journey map that expresses the needs of the target audience helps to ensure that the team stays true to what customers need and want.
When should journey mapping be done? Customer journey mapping can be done whenever the business wants to do any of the following tasks.[8]
- Assess the gaps in the current service offering.
- Increase the personalization of customer interactions for each customer profile or segment.
- Create a more effective marketing strategy for new products and services.
- Recognize how each customer persona’s service experience differs.
- Develop a new experience while keeping the important moments in mind.
- Compare competitors’ journeys to the company’s and create better differentiators.
3. Provide Exceptional Customer Service
Train and support employees. Use AI Chatbots to improve service. Have meaningful conversations with customers so that each interaction is not purely transactional.
4. Activate Loyalists
Ask brand ambassadors to help spread the word. Connect with brand ambassadors as these are the most ardent supporters of the company’s brand and its values, and are the customers the company should seek out. These consumers are the ones who mention the company and/or its products and services on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), Instagram, and other social media platforms and tell everyone how much they like your brand. These highly satisfied customers help a company understand who is connecting with the brand and why. It’s up to the company to find these supporters and learn about them, so the company can find others who fit the same profile. These people will become the company’s brand ambassadors out in the world. The business should engage with them often – and possibly surprise an existing customer with special gifts to thank them for their loyalty, a strategy known as “surprise and delight” that can help increase retention and cultivate customer loyalty.[9]
5. Show Customer Appreciation
Develop a Loyalty Program.
6. Connect in a Deeper Way
Create a Community. Increase the personalization of customer interactions for each customer profile or segment. Offer personalized service. Use video chats and co-browsing (the agent and customer are browsing at the same time) to engage customers.
7. Ask for Feedback
Conduct Customer Satisfaction Surveys (CSAT) as well as employee surveys, then use analytics to improve service.
8. Continually Improve
Businesses should continually strive to improve the customer experience by monitoring customer trends and preferences, comparing competitor company journeys, and leveraging these insights to develop stronger differentiators. This proactive approach enables companies to stay ahead of market demands, personalize offerings, and create unique value that strengthens customer loyalty and drives sustainable growth.
Customer Experience Trends
In the Zendesk Customer Experience (CX) Trends Report, the following customer experience trends appear. Companies need to embrace these trends to meet customer needs and expectations in order to build relationships. There are five trends discussed below.
Trend 1: AI is becoming more evolved and seamless
The retail sector has been experiencing a significant digital transformation over the past few years. One of the greatest drivers of this transformation is the combination of the Internet of Things and Artificial Intelligence. Amazon widely uses AI in its retail operations, while Walmart and Target follow closely behind. Retailers are seeking the help of AI-based digital solutions to tackle challenges like changing consumer behavior, labour shortages, supply chain disruptions, and rising costs. AI is a powerful tool for retailers, enabling them to quickly analyze large amounts of data and make customer-focused decisions.[10]
Using artificial intelligence retail solutions, retailers can provide smooth customer support in different scenarios – starting from automated checkouts to customer mood tracking. AI-based retail solutions also provide customers with personalized and immersive shopping experiences. Several reports suggest that customers would be a lot more loyal to the brands that added personalization features in their outlets. With retail transactional data, AI, and machine learning, brands can easily track and analyze past purchases, customer behavior, and loyalty cards to deliver more customized offerings. Customers can now take a photo of an item or product they like in reality and then utilize the image to search for a retailer selling it online. Utilizing AI calculations, retail organizations can run focused marketing and advertising campaigns based on customers’ location, preferences, gender, and buying habits.[11]
Here are a few examples of companies that are using AI (artificial intelligence) and ML (machine learning) in retail to improve the overall user experience and increase sales.[12]
- Sephora’s Color IQ scans faces to recommend personalized foundation and concealer shades, while Lip IQ helps find the perfect lipstick shade, making way for a seamless makeup shopping experience.
- Lowe’s leverages LoweBot, a robot that assists customers in navigating stores. LoweBot asks questions to help customers find products, offers directions, shares expertise, and keeps track of inventory.
- Starbucks streamlines ordering through the My Starbucks Barista app, which enables voice and text-based orders, allowing customers to skip lines and pick up orders upon arrival. AI analyzes purchase history and preferences via the app and loyalty program, enabling Starbucks to send personalized offers and recommendations that enhance the customer experience.
- Amazon uses AI to personalize product recommendations by analyzing purchase history, browsing data, and customer behavior, helping shoppers discover items tailored to their interests.
- Disney enhances the theme park experience with AI-powered virtual assistants through the My Disney Experience app and MagicBand, helping guests plan visits, manage reservations, and receive real-time updates.
- Spotify leverages AI to analyze listening patterns and preferences. Features like Discover Weekly and Release Radar provide tailored playlists, keeping users engaged with both new and familiar music.
- Domino’s employs AI-powered chatbots, such as Dom, to simplify ordering via voice or text. AI also optimizes delivery routes, ensuring faster and more efficient service.
- Netflix creates a personalized experience for each subscriber. New users select favorite movies and shows, and AI generates recommendations for similar programming. The system continually adapts based on viewing habits, watch duration, and device usage to offer a highly tailored experience.[13]
Play the YouTube video below to learn how businesses can use AI to personalize customers’ experiences.[14] Transcript for “How to use AI to personalize your customer’s experience” Video [PDF–New Tab]. Closed captioning is available on YouTube.
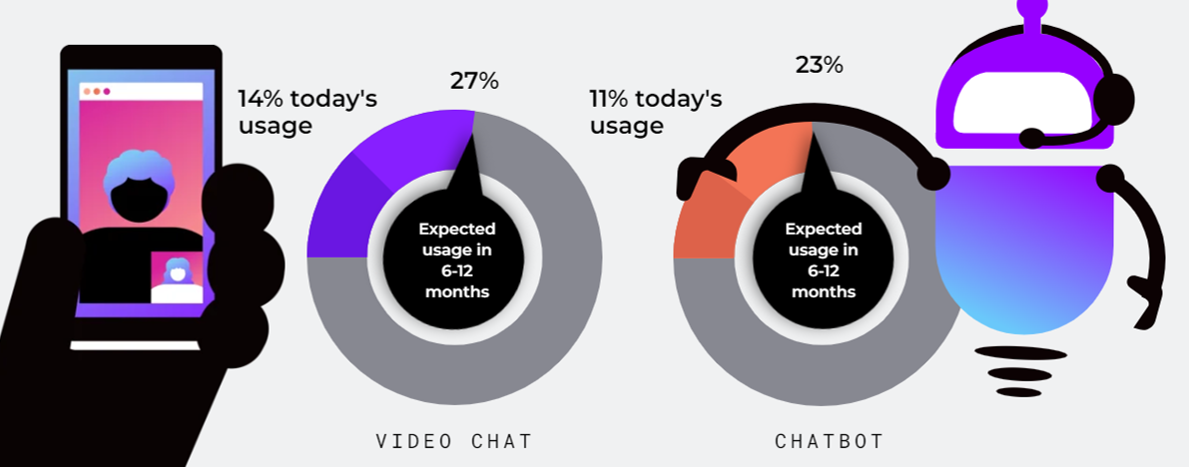
According to Vonage’s Global Customer Engagement Report 2022 omnichannel, commerce that integrates the different methods of interaction available to customers (e.g., online, mobile device, physical store), enhanced by artificial intelligence, will help meet the expectations of customers. Customers expect an efficient customer experience in the first channel they choose. As seen below in Figure 9.1, the two channels set to explode the most are video chat and chatbot.[15]
Trend 2: Consumers want conversational experiences
Customers want to receive immediate assistance, and it does not matter if it comes from an AI-powered bot or a real human agent. What does matter is that those interactions feel natural, friendly, and personal. As those conversations unfold, consumers expect anyone they interact with at the company to have the full context of their purchase history, previous interactions, and so on. Should a customer decide to stop an interaction and resume it later, they want a new support representative to be able to pick up the conversation seamlessly. Seventy percent of consumers purchase more from companies that offer seamless conversational experiences.[16]
Trend 3: Customers are eager for deeper personalization
Most customers don’t want to be lumped into some demographic bucket—they crave experiences in which they are a segment of one, not thousands. For example, consider the barista who greets you by your name, starts whipping up your normal order, and then asks a follow-up question about something you talked about during your last visit. Consumers want that experience, whether it’s in a brick-and-mortar store or on an ecommerce site. Fifty-nine percent of consumers believe businesses should use the data they collect about them to personalize their experiences.[17] How do you feel about that? Do you agree?
In the Spotlight: Airbnb Customer Experience
Airbnb has revolutionized short-stay accommodation since it was founded in August 2008 and has disrupted the hospitality industry. When it first began, people might have thought that an idea based on inviting strangers to stay in your home would be doomed. However, it isn’t doomed, and quite the contrary. Per USA Today, Airbnb has more than seven million listings in 100,000 cities as of early September 2019, and they plan to go public in 2020. They also reported revenues of over one billion dollars in the second quarter of 2019, although there is no report on the profits.[18]
Airbnb observed that consumers were looking for ways to travel differently and find better deals. They wanted to use their mobile technology to explore the world around them. Airbnb took advantage of these wants and positioned a solution that is high-tech.[19]

Airbnb offers exceptional experiences by providing a platform for hosts to offer a wide range of activities. These activities can include sharing a personal hobby, teaching a language or cooking class, hosting an art or dance workshop, or organizing sports or pub crawls.[20] Airbnb also offers a wide range of accommodation options, from cozy cottages to elegant penthouses.[21] Airbnb has also improved the user experience for guests and hosts by providing flexibility, easier hosting, and improved service support.[22]The company collects customer data to make better recommendations and match the right people together. Airbnb personalization is the adjustment of search results based on each guest’s unique profile. This includes what they clicked on, what they booked, and more.[23]
Here’s how Airbnb is shaping the future of the travel industry:[24]
- It’s aspirational.
- It’s built on pure trust.
- It’s price sensible.
- It’s personable.
- It’s innovative.
- It’s memorable.
- It’s responsive.
- It’s beautiful.
- It’s relevant.
- It’s human.
Airbnb is one of the most inspirational and progressive brands in the world, regardless of industry. This is mainly due to its forward-thinking and absolute focus on the customer experience. The question is, will the Airbnb experience become the future of the travel industry? And what can travel agents do to start offering their current customers some of what Airbnb has made central to their overall customer experience?[25]
Trend 4: Consumers’ well-being and sentiment are reshaping CX

Sixty-six percent of consumers who often interact with support said a bad interaction with a business can ruin their day. Sixty percent of consumers have purchased something from one brand over another based on the service they expect to receive. On the frontlines of support, agents know all too well how their company’s customer experience affects consumers. Thirty-seven percent of agents say that when a customer cannot complete tasks on their own, they often become noticeably angry, frustrated, or stressed. Fifty-three percent of agents say that how their organization approaches service leads directly to negative customer behavior, and because leaders aren’t formally tracking sentiment, their organizations fail to remedy these persistent issues—what’s out of sight ends up being out of mind.[26]
Trend 5: CX teams are breaking down silos
For too long, leaders have viewed their customer service organizations as cost centers, not drivers of revenue. As a result, that mindset has created siloed teams with little connection to their wider organizations, leading to disastrous side effects: agents lack relevant customer data, which then hampers efforts to provide exceptional (or even satisfactory) experiences. But as business leaders have begun to discover, customers expect data to be widely shared so their experiences can be personalized and immersive. Leaders now realize that silos must be broken down, with true integration between customer service, sales, and marketing. Doing so promises great returns: increased efficiency, better customer experiences, and finally, more revenue.[27]
Social Listening, Monitoring, and Selling for Improved Customer Relationships
Social listening is the process of actively tracking and analyzing online conversations, mentions, and discussions about a brand, competitors, products, or industry to gain valuable insights into customer sentiment, trends, and emerging issues. Social monitoring, while closely related, focuses more on observing and responding to specific brand mentions, comments, or queries in real time, often aiming for immediate engagement or support.[28]
What is Social Listening?
- Social listening involves gathering and analyzing real-time data from social media platforms, websites, forums, and blogs to understand broader public opinion and sentiment.
- It uncovers patterns, trends, and audience feelings, providing businesses with a strategic overview of what people are saying and why they feel that way.
- The main goal is to inform decision-making by integrating customer feedback and market insights into product development, marketing, and customer service strategies.
What is Social Monitoring?
- Social monitoring is the practice of tracking notified brand mentions, comments, and tags on digital channels and responding as appropriate, often focusing on customer service and reputation management.
- It allows businesses to quickly address questions, praise, or complaints one-on-one, providing timely support and engagement.
What is Social Selling?
- Social selling uses social media to build relationships with potential customers rather than relying on cold calls or mass advertising. It emphasizes listening to customer needs, sharing relevant content, and providing value, leading to stronger connections and higher conversion rates.
- Platforms like LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, TikTok, Pinterest, WhatsApp, and YouTube each offer unique ways to engage audiences, from professional networking and B2B lead generation to visual storytelling and direct product sales.
Why Do Companies Use Social Listening and Monitoring?
-
Social Media Listening and Monitoring Customer Understanding: Gain deep insight into what customers truly think, want, or dislike, helping to align offerings with audience needs.
- Trend Identification: Detect early trends and shifts in public sentiment, allowing brands to stay ahead of competitors and adapt strategies quickly.
- Crisis Management: Spot potential issues or negative sentiment before they escalate into brand crises, and act proactively to manage problems and protect reputation.
- Product/Service Improvement: Use customer feedback for continuous improvement, innovation, and evolving offerings that better match market expectations.
- Competitive Analysis: Monitor competitor performance and public opinion to identify business opportunities and strategic threats.
- Stronger Engagement: Build better customer relationships through fast, targeted responses and authentic engagement, increasing loyalty and advocacy.
- Personalized Service: By analyzing social conversations, businesses gain data for personalized proposals, marketing campaigns, and support responses, fostering loyalty and repeat business.
- Comprehensive Customer Profiles: Social CRM platforms enrich customer profiles with social data for more informed decisions and improved relationships.
The difference between social listening and social monitoring can be summarized as follows:
Social monitoring is the reactive process of tracking direct mentions, comments, and interactions about a brand to respond quickly to customer queries or issues. It focuses on immediate engagement and crisis management by observing specific keywords and tagged mentions in real time.
In contrast, social listening is proactive and analytical, involving the broader analysis of online conversations, including those about competitors and industry trends. It seeks to understand customer sentiment, behaviors, and emerging patterns to inform long-term business strategies, product development, and marketing plans.
While social monitoring answers “what is happening right now” on a micro level, social listening provides insights into “why it is happening” on a macro level. Both are essential but serve different purposes within a comprehensive social media strategy.
In summary, social listening and social monitoring significantly enhance customer relationships by enabling businesses to understand customer sentiment, respond promptly to feedback, and offer personalized experiences tailored to customer needs. Both practices can be integrated within Salesforce CRM and are supported by dedicated software tools designed for these tasks. By leveraging social listening and monitoring, companies can make informed decisions, improve their customer experience, and enhance brand reputation in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.[29]
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is both a business strategy and a technology for managing interactions with customers and prospects. Its primary purpose is to strengthen relationships, improve service delivery, and drive growth. A CRM system centralizes customer information, streamlines processes, and enhances profitability by enabling better communication across departments. These systems support customer contact management, sales tracking, marketing campaigns, and customer service—providing a unified view of the customer lifecycle from marketing and sales through digital commerce and service interactions.[30]
A key function of CRM is building stronger customer relationships. By consolidating customer data, CRM systems allow companies to better understand customer preferences, track purchase history, and record service interactions. This insight enables personalization, proactive communication, and more consistent service delivery—all of which help create trust and loyalty. For example, sales representatives can recommend products that align with past purchases, while service agents can review previous interactions and address issues with empathy and context. Over time, this consistency and personalization help transform one-time buyers into long-term customers.
An enterprise-wide approach to CRM allows every department—sales, marketing, customer service, operations, and beyond—to share information in one system. This collaboration prevents miscommunication and creates a smoother customer experience. Consider the following scenario: a customer receives an order missing a part and contacts customer service. The first agent assures them the part will be shipped quickly. Weeks later, the customer calls back and speaks to a second agent, who apologizes but cannot provide a clear update. Later that day, a third agent calls with the same information the customer has already received. This repetition leaves the customer frustrated and doubting the company’s reliability.
CRM software eliminates this type of breakdown. With shared access to records, agents can see all prior interactions, check shipping status, and even leave notes for colleagues. In this case, the second agent could have verified the shipment details, expedited delivery, and scheduled a follow-up call to reassure the customer. CRM systems can also generate automatic alerts for delays, prompting proactive communication or sending automated updates with the option to connect to a live representative.
The importance of CRM is underscored by customer expectations. Research shows that 48% of customers have switched brands due to poor service, while 94% say good service makes them more likely to purchase again. Many customers now value the experience a company provides as highly as its products or services. To meet these expectations, service professionals need visibility into the entire customer journey. Sixty-two percent of service professionals report that all departments in their organization use the same CRM system, enabling teams to collaborate effectively and respond empathetically. As customer interactions increasingly shift to digital channels, CRM-enabled contact centers remain vital for delivering seamless, relationship-focused service.[31]
Social Listening and Monitoring in Salesforce Social Studio
Salesforce CRM uses Social Studio (part of Salesforce Marketing Cloud) for social listening and monitoring, offering businesses a unified, data-driven approach to understand, engage, and respond to their audiences on social media.[32]
Salesforce: Social Listening
-

Social Media Social CRM in Salesforce enables teams to respond to social inquiries in real time, track sentiment, manage leads, and analyze campaign effectiveness through built-in dashboards and connectors.
- Many enterprise-grade tools (Sprinklr, Sprout Social, Hootsuite, Salesforce Social Studio) integrate directly with Salesforce CRM, while other affordable options (Metricool, Agorapulse, Statusbrew) are available for standalone monitoring and listening needs.[33]
- Social Studio provides real-time tracking of keywords, hashtags, brand mentions, competitor names, and industry terms across multiple social platforms.
- Built-in sentiment analysis tools allow teams to assess the mood around the brand, helping quickly identify and react to negative sentiment or capitalize on positive trends.
- The system identifies trends and emerging topics, offering insights so organizations can adapt their strategy and remain relevant to customer conversations.
- Social Studio facilitates seamless data sharing between CRM and social platforms, linking social interactions with customer records for unified management and personalized follow-ups.
Salesforce: Social Monitoring and Engagement
- Salesforce Social Studio consolidates social interactions, enabling organizations to monitor and respond promptly to customer mentions, inquiries, and feedback, all from one integrated dashboard.
- Users can organize and tag interactions, creating workflows that allow teams (marketing, sales, service) to follow up efficiently and ensure that no customer engagement goes unnoticed.
- Engagement activities, such as responding to social posts and tracking conversation history, are automatically recorded in the CRM, giving full visibility into each customer’s social engagement journey.
Salesforce: Analytics, Reporting, and Integration
- Analytics dashboards provide detailed reports on engagement, brand sentiment, key metrics, and campaign performance for continuous improvement.
- Seamless integration between Social Studio and Salesforce CRM enables unified customer records, allowing social engagement data to enhance contact and lead profiles for more targeted sales and service actions.
- Social media insights can be combined with other marketing, sales, and service data, providing a complete 360-degree view of the customer and supporting personalized outreach.
Salesforce CRM, through Social Studio, empowers organizations to listen, monitor, and react to social conversations in ways that drive better relationships and business outcomes. In summary, using social listening and monitoring — especially with powerful integrations in Salesforce CRM — allows brands to deliver more personalized, empathetic, and effective customer experiences, thereby strengthening customer relationships and brand loyalty.
Social Listening and Monitoring in Hootsuite Insights
Hootsuite Insights is the analytics and social listening component built into the Hootsuite platform. It enables users to track, measure, and analyze social media conversations across multiple networks from a single dashboard. Hootsuite supports real-time monitoring, reporting, and analysis of online mentions and social interactions, helping organizations manage brand reputation, uncover customer insights, and respond proactively to strengthen customer relationships. Both Hootsuite and Hootsuite Insights can integrate with other platforms, such as Salesforce, to enhance social media management, analytics, and overall customer engagement.[34]
Hootsuite: Social Listening
- Hootsuite enables real-time monitoring of brand mentions, competitor activities, and industry keywords across 30+ social channels, news sites, blogs, forums, and more.
- It uses AI-powered tools (like Blue Silk™ AI and integration with Talkwalker) for advanced sentiment analysis, trend detection, and identification of emerging topics, providing deep insights that help organizations understand audience mood and behavior.
- Custom dashboards, widgets, and summarized analytics let users visualize important metrics such as sentiment, demographics, and engagement, making it easier to recognize recurring themes and adapt strategy accordingly.
- Hootsuite offers historical data analysis, allowing users to benchmark metrics, compare periods, and forecast social trends to guide future decisions.
Hootsuite: Social Monitoring Capabilities
- Users can create and customize streams to follow mentions, conversations, reviews, and hashtags in real time, enabling quick responses and active engagement with audiences.
- Instant alerts and notifications are provided for significant shifts in sentiment or conversation spikes, allowing brands to react quickly to both opportunities and crises.
- All plans come with basic listening and monitoring capabilities, but advanced tools (like Hootsuite Listening powered by Talkwalker) are available for enterprise users, offering broader coverage, deeper analytics, and longer historical data access.
Hootsuite: Integration and Accessibility
- Hootsuite integrates with a wide range of additional social listening platforms and third-party analytics tools, providing flexibility for users to extend their listening capabilities as needed.
- Permissions and roles allow teams to manage, organize, and tag mentions for workflow efficiency and accurate reporting.
Hootsuite’s robust toolset allows businesses to monitor, analyze, and act on social media data efficiently, creating a competitive advantage through rapid, data-driven responses and improved customer understanding.
Social Media Strategy
A strategy ensures social media efforts align with business goals and customer expectations. Key steps include:
- Research: Understand target customers, behaviors, and preferences.
- Customer Personas: Represent the ideal audience to guide messaging.
- Brand Positioning: Communicate brand identity consistently across platforms.
- Content Planning: Share content that builds trust, provides value, and engages your audience.
- Standards and Monitoring: Use quality standards and social monitoring to maintain a positive brand image.
Social media is not just for marketing—it’s a powerful ecosystem for building relationships, monitoring sentiment, and driving sales. Tools like Hootsuite, Salesforce, LinkedIn, and AI-powered analytics help businesses listen, engage, and act strategically, creating stronger customer connections and measurable business growth.
Key Takeaways
- Customer relations refers to the different methods and strategies that a business can use to forge, improve, and manage all interactions with its customers. Building customer relationships is not just a job for a single team. It is every employee’s responsibility to ensure customers receive the best service and a positive experience when interacting with the company.
- High-performing companies view customer service as their primary revenue driver, and seventy-three percent of business leaders say there is a direct link between customer service and business performance.
- A few of the benefits companies gain from creating positive customer relationships include the following:
- Higher customer retention
- More customer loyalty
- Better business reputation and brand credibility
- Ability to maintain prices
- Increased competitive advantage
- Improved employee morale and attitude
- Businesses can develop meaningful customer relationships and create long-lasting customer loyalty by doing the following:
- Communicate company values
- Know your company journey
- Provide exceptional customer service
- Activate loyalists
- Show customer appreciation
- Connect in a deeper way
- Ask for feedback
- Continually improve the customer experience
- The journey mapping process brings together sales, marketing, and customer support to define what customers need to know before they buy, what they need after they buy, and how these interactions can be enhanced.
- Customer experience trends include the following:
- AI is becoming more evolved and seamless
- Consumers want conversational experiences
- Customers are eager for deeper personalization
- Consumers well-being and sentiment are reshaping CX
- CX teams are breaking down silos
- Social listening is the process of actively tracking and analyzing online conversations, mentions, and discussions about a brand, competitors, products, or industry to gain valuable insights into customer sentiment, trends, and emerging issues.
- Social monitoring, while closely related, focuses more on observing and responding to specific brand mentions, comments, or queries in real time, often aiming for immediate engagement or support.
- Social selling uses social media to build relationships with potential customers rather than relying on cold calls or mass advertising. It emphasizes listening to customer needs, sharing relevant content, and providing value, leading to stronger connections and higher conversion rates.
- According to Vonage’s Global Customer Engagement Report 2022 omnichannel, commerce that integrates the different methods of interaction available to customers (e.g., online, mobile device, physical store), enhanced by artificial intelligence will help meet the expectations of customers. Customers expect an efficient customer experience in the first channel they choose. The two channels set to explode the most are video chat and chatbot.
- Customer relationship management (CRM) is a technology for managing all company relationships and interactions with customers and potential customers. A CRM system helps companies stay connected to customers, streamline processes, and improve profitability.
- Salesforce CRM uses Social Studio (part of Salesforce Marketing Cloud) for social listening and monitoring, offering businesses a unified, data-driven approach to understand, engage, and respond to their audiences on social media
- Hootsuite CRM is widely used for social listening and monitoring by providing real-time tracking, analysis, and reporting of social media conversations and online mentions across various platforms. Its integrated features help organizations monitor brand reputation, uncover customer insights, and respond proactively to develop stronger customer relationships.
End-of-Chapter Exercises
- Departments Responsible for Building Relationships. As stated in the chapter, it is every employee’s responsibility to ensure customers have a positive experience interacting with the company. Search the Internet, speak with company employees, or hold a class discussion (as assigned by your professor) in order to determine how four of the following departments participate in building positive customer relationships: Marketing/Promoting, Accounting, Sales, Human Resources, Information Technology, Operations/Delivery, Product/Service Development, Administration/Management, Purchasing/Acquiring Raw Materials. Make a list and share that list with your class and professor.
- Artificial Intelligence for Improved CX. One of the CX trends listed in the chapter is “AI is becoming more evolved and seamless.” Use the Internet to research how businesses use AI to improve customer experiences. In which ways is AI becoming more involved and seamless? How do you envision AI for CX evolving in the next 10 years? Share your findings with your class and/or professor.
- Consumers Emotions Reshaping CX. One of the CX trends listed in the chapter is “Consumer well-being and sentiments are reshaping CX.” Use the Internet to research what this means, and provide a specific customer example. How are companies using customer emotions to improve CX? Discuss your findings with your class and/or professor.
- Loyalty Programs. Use the Internet (or visit a business) to research a specific loyalty program from a specific company (e.g. Tim Hortons, Starbucks, Petro-Canada, Loblaws Super Store). Your professor may prefer to assign a specific company. Learn about how customers use the loyalty program to gain value. What about the loyalty program do you think is most valuable to customers? Why? How can the company afford to offer this loyalty program? What might happen if they did not offer the loyalty program? Do you feel this loyalty program is the best way for the company to gain customer loyalty? Why or why not? Share your research and thoughts with your class and/or professor.
- Brand Ambassadors. Use the Internet to research how companies connect with loyal customers and turn them into brand ambassadors. How do companies get these loyal customers to promote their products/services and become brand ambassadors? Locate a brand ambassador online. What is the brand ambassador getting from the relationship with the company? Share your findings with your class and/or professor.
- Creating a Community. Use the Internet, your personal experience, or speak with someone, to discover how a specific company creates a community of customers. What is this community all about? What benefit are the customers getting? How does this help the company build customer relationships that foster loyalty? Share your findings with your class and/or professor.
- Sharing Economy Companies. Use the Internet to research how sharing economy companies build customer relationships. Your professor may assign a company for you to research or you can research one of the following: Airbnb, Uber, LIme, JustPark, ZipCar, Fon, Spotahome, Stashbee, Hubble, Omni, Fiverr, Snap, Couchsurfing, BlaBlaCar, or Silvernest. What is it about these types of businesses that customers like? What value are customers receiving? What type of customer experiences are they having? How are these companies building positive customer relationships? Share your findings with your class and/or professor.
- Personalized Customer Experiences. Use the Internet to research how companies personalize customer experiences. Locate a specific company example and share your findings with your class and/or professor.
- CRM Comparison. Use the Internet to research several CRM systems. Determine which systems would work for small businesses and which would be best for larger organizations. What are the pros and cons of each? Which are the most popular? Share your findings with your class and/or professor.
- Co-Creation Examples. Use the Internet to research which companies are co-creating with their customers. Locate specific examples of co-creating experiences or services (rather than products). What are a few of the successful projects companies have had when co-creating with customers? Share your findings with your class and/or professor.
- Create a Journey Map. Watch the YouTube video, Customer Journey Mapping 101, and then create a journey map for a specific customer segment that would shop at Canadian Tire (or other company) on a fairly regular basis. Did you identify pain points? How might the company do better? Share your map with your class and/or professor.
- Trailhead Training. Visit Trailhead at Trailhead | The fun way to learn (salesforce.com) and complete the Customer Service with Salesforce: Quick Look learning module for free. It should only take you about 10 minutes to complete. Scan through the learning modules for Salesforce and select three you think would be important training to offer employees of any organization. Share your suggested learning modules with your class and/or professor.
Additional Resources
- 7 Types of Customer Relationship
- 5 Customer Service Trends to Watch in 2023
- Salesforce State of Service Report
- Hubspot Free CRM Software
- Customer Relationship Management Free Course (1 hour)
- An Introduction to Customer Relationship Management Free Course (3 hours)
- Customer Relationship Management in Business Services Free Course (4 hours)
- Customer Relationship Management Free Course (6 weeks, 3-5 hours per week)
References
(Note: This reference list was produced using the auto-footnote and media citation features of Pressbooks; therefore, the in-text citations are not displayed in APA style).
Media Attributions
- pexels-ketut-subiyanto-4350104 is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- ux-indonesia-w00FkE6e8zE-unsplash © UX Indonesia is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- Vonage Expected Usage of Video Chat and Chatbot © Vonage is licensed under a All Rights Reserved license
- Airbnb Kitchen of Rental Property © Peggy is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- feedback-3709752_1280 © Mohamed Hassan is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- Social Media Monitoring © Mudassar Iqbal | Pixabay
- Mobile Phone Social Media © Gerd Altmann | Pixabay
- Sapardic, J. (2023, August 30). What is customer relations? Definition, benefits & tips. https://www.tidio.com/blog/customer-relationship/ ↵
- Zendesk Blog. (n.d.). Customer relations 101: Beginner's guide to building relationships. https://www.zendesk.com/blog/customer-relations/ ↵
- Zendesk Blog. (n.d.). Customer relations 101: Beginner's guide to building relationships. https://www.zendesk.com/blog/customer-relations/ ↵
- Zendesk Blog. (n.d.). Customer relations 101: Beginner's guide to building relationships. https://www.zendesk.com/blog/customer-relations/ ↵
- Zendesk Blog. (n.d.). 7 ways to build customer loyalty (and why it's important). https://www.zendesk.com/blog/build-customer-loyalty/ ↵
- Zendesk Blog. (n.d.). 7 ways to build customer loyalty (and why it's important). https://www.zendesk.com/blog/build-customer-loyalty/ ↵
- windmill. (n.d.). Customer journey mapping: The Windmill guide to design thinking. https://www.windmill.digital/customer-journey-mapping-the-windmill-guide-to-design-thinking/ ↵
- windmill. (n.d.). Customer journey mapping: The Windmill guide to design thinking. https://www.windmill.digital/customer-journey-mapping-the-windmill-guide-to-design-thinking/ ↵
- Oson, S. (2022, June 2). 7 ways to build customer loyalty (and why it’s important). https://www.zendesk.com/blog/build-customer-loyalty/ ↵
- Srivastava, S. (2023, November 3). AI in retail - How artificial intelligence is improving the retail shopping experiences. https://appinventiv.com/blog/impact-of-ai-in-retail/ ↵
- Srivastava, S. (2023, November 3). AI in retail - How artificial intelligence is improving the retail shopping experiences. https://appinventiv.com/blog/impact-of-ai-in-retail/ ↵
- Srivastava, S. (2023, November 3). AI in retail - How artificial intelligence is improving the retail shopping experiences. https://appinventiv.com/blog/impact-of-ai-in-retail/ ↵
- Eyo, I. (2023, January 4). 10 ways AI will improve the customer experience in 2023. https://www.zendesk.com/blog/ai-customer-experience/ ↵
- Salesforce. (2021, April 23). How to use AI to personalize your customer's experience. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/BVMDz6FUzxc?si=YakhaQ_eA609SUDz ↵
- Vonage. (2022). The global customer engagement report 2022: Maximizing the omnichannel CX with AI. https://www.vonage.com/resources/publications/global-customer-engagement-report/ ↵
- Zendesk. (2023). Empowering consumers with conversational experiences. https://cxtrends.zendesk.com/trends/trend-2 ↵
- Zendesk. (2023). Customers are eager for deeper personalization. https://cxtrends.zendesk.com/trends/trend-3 ↵
- Shaw, C. (2019, December 13). Four customer experience lessons from The Airbnb Way. https://www.mycustomer.com/customer-experience/loyalty/four-customer-experience-lessons-from-the-airbnb-way ↵
- Shaw, C. (2019, December 13). Four customer experience lessons from The Airbnb Way. https://www.mycustomer.com/customer-experience/loyalty/four-customer-experience-lessons-from-the-airbnb-way ↵
- Zaidi, T. (n.d.). Airbnb Experiences explained [Plus how to book, examples]. https://trvlguides.com/articles/airbnb-experiences ↵
- Airbnb Help Center. (n.d.). About Airbnb: What it is and how it works. https://www.airbnb.ca/help/article/2503?locale=en&_set_bev_on_new_domain=1696777926_ODlmYmE5MTQzMGZk ↵
- Ruiz, J. (2021, May 25). 3 major ways Airbnb is improving the user experience for guests and hosts. https://thepointsguy.com/news/airbnb-improved-user-experience/ ↵
- Mah, K. (n.d.). How Airbnb personalization really affects rankings (14 Major Takeaways). https://higherbookings.com/airbnb-personalization/ ↵
- Rouke, P (2016, October 5). Airbnb: How its customer experience is revolutionising the travel industry. https://econsultancy.com/airbnb-how-its-customer-experience-is-revolutionising-the-travel-industry/ ↵
- Rouke, P (2016, October 5). https://econsultancy.com/airbnb-how-its-customer-experience-is-revolutionising-the-travel-industry/ ↵
- Zendesk. (2023). Consumer well-being and sentiment are reshaping CX. https://cxtrends.zendesk.com/trends/trend-4 ↵
- Zendesk. (2023). CX teams are breaking down silos. https://cxtrends.zendesk.com/trends/trend-5 ↵
- Lama, D., Debayan, P. (2025, July 7). What is social listening? All you need to know. https://www.sprinklr.com/blog/social-listening/ ↵
- Oliver, E. (2025, February 20). The new age of social listening—8 ways it helps increase your brand’s value to consumers. https://www.agilitypr.com/pr-news/content-media-relations/the-new-age-of-social-listening-8-ways-it-helps-increase-your-brands-value-to-consumers/ ↵
- Salesforce. (n.d.). CRM 101: What is CRM? https://www.salesforce.com/ca/crm/what-is-crm/?d=cta-resources-1-what-is-crmhttps://www.salesforce.com/ca/form/contact/crm-starter-pack/?d=cta-mustache-1-crm-starter-formhttps://www.salesforce.com/ca/?ir=1 ↵
- Afshar, V. (2022, September 8). 10 key customer service trends for 2022 and beyond. https://www.zdnet.com/article/10-key-customer-service-trends-for-2022-and-beyond/ ↵
- Salesforce. (n.d.) What is social CRM? https://www.salesforce.com/ca/crm/social-crm/ ↵
- Pennings, E. (2025, September 15). I tested the 7 best free social media monitoring tools — here’s how they stack up. https://blog.hubspot.com/blog/tabid/6307/bid/29437/20-free-social-media-and-brand-monitoring-tools-that-rock.aspx ↵
- Hootsuite. (n.d.). Protect your brand, outpace the competition, and stand out across all media. https://www.hootsuite.com/platform/listening ↵
refers to the different methods and strategies that a business can use to forge, improve, and manage all interactions with its customers.
involves gathering and analyzing real-time data from social media platforms, websites, forums, and blogs to understand broader public opinion and sentiment. In contact centers, social listening allows agents to listen to customer issues online using predefined keywords and hashtags on social media. Social media posts can be immediately routed to agents and prioritized so that they can provide immediate resolution to customers.
is the practice of tracking notified brand mentions, comments, and tags on digital channels and responding as appropriate, often focusing on customer service and reputation management. It allows businesses to quickly address questions, praise, or complaints one-on-one, providing timely support and engagement.
uses social media to build relationships with potential customers rather than relying on cold calls or mass advertising. It emphasizes listening to customer needs, sharing relevant content, and providing value, leading to stronger connections and higher conversion rates.

