Chapter 3: Managing a Customer Service Team
Chapter 3 Learning Outcomes
After reading this chapter, you should be able to do the following:
- Describe how to create a customer service philosophy for your company, department, or team.
- Explain the purpose of having service standards and goals.
- Describe why it is important to set SMART goals for customer service teams.
- Explain why it is important to measure service quality.
- Identify obstacles to outstanding service.
- Describe what service recovery looks, sounds, and feels like.
- Suggest ways in which to improve service quality.
- Identify the costs of poor customer service.
Customer Service Philosophy
“If you’re looking to improve your customer experience, start by creating a customer service philosophy for your support team. Having a shared philosophy keeps everyone focused on the same goal and helps them understand the holistic approach to achieving that goal.”[1]

In an environment in which front-line staff deal with an endless stream of unpredictable scenarios, having a strong philosophy helps empower team members, provides a coherent story to help employees understand company values, and sets the foundation for a customer-first strategy that’s proactive rather than reactive. No matter which employee a customer interacts with, they will experience the same delightful service that epitomizes the company’s values.
“A customer service philosophy is a shared mission for your support team, a set of guiding principles that ensure you’re upholding your core values with every customer interaction.”[2]
Generally, a customer service philosophy is composed of two parts: vision and values.
Customer Service Vision
The first section of a customer service philosophy is a customer service vision statement. A customer service vision statement provides meaning and direction for employees. It is the statement that outlines the type of service that agents are expected to provide to customers. It tends to be quite idealistic and ‘big picture’ thinking, needs to be clear and unambiguous, and it should be easily understood by both employees and customers alike.[3]
When your vision applies to everybody, it also embodies natural accountability and training opportunities for every person. New hires automatically understand what’s expected of them, leadership is expected to practice what it preaches, and agents can be coached on their customer-facing interactions using your statement as an observable benchmark.[4]
Customer Service Values
Your vision statement is followed by customer service values, which impact the experience the customer receives and help to define the personality and attitude the business is trying to put forth. Often, companies offer training to employees on how to uphold these values. The values can be conceptual, offering an explanation for why adhering to the vision is important, or more tactical, like Apple’s guidance for support representatives in their retail stores:[5]
Approach customers with a personalized, warm welcome.
Politely try to understand all the customer’s needs.
Present a solution for the customer to take home today.
Listen for and resolve any issues or concerns.
End with a fond farewell and an invitation to return.
Creating a Customer Service Philosophy for Your Team
Careful contemplation is the first step. Ask yourself some key questions. What is the purpose of your company? What is the role of customer service within your company? What experience should the customer have for your company to fulfill this role? What does this look like for your customer service representatives? What are your company’s core values, and how are they prioritized? What are the principles that should guide your employees who interact with customers daily? How will employees easily remember these principles?
There’s no fixed format to a customer service philosophy. But having it down on paper — preferably a digestible one-pager — will allow your service reps to reread and internalize it. Take your answers from above and integrate them into a coherent piece.[6]
Although good customer service philosophies have a few things in common, no two should be the same. For a philosophy to succeed, it needs to align with your team’s specific values, goals, and long-term vision for your relationship with customers.
Develop Service Standards
Service standards are guidelines for employees to follow when interacting with customers. Do not make them too rigid or strict as not all standards will apply to every customer situation. This gives employees the flexibility to adapt to each customer’s unique needs within a standard framework. Customer service guidelines should align with the company’s brand.
Standards may be as simple as:
- Make the customer feel welcome (e.g., greetings, body language)
- Efficiently serve customers’ needs (e.g., listen actively, ask probing questions, offer suggestions, take action)
- Look for additional ways to serve the customer (e.g., ask if there is anything else you can do, share promotions or new opportunities)
- End the customer interaction (e.g., thank the customer, follow up if needed, summarize what you have done if necessary)
As the Canada Revenue Agency puts it, “Service standards publicly state the level of performance that citizens can reasonably expect to encounter from the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) under normal circumstances. The CRA is committed to developing, monitoring, and reporting on a full suite of service standards in areas of importance to taxpayers and benefit recipients. Service standards support the CRA‘s commitment to Canadians for transparency, management accountability, and citizen-focused service.”[7]
“Starbucks strongly believes in meeting customer service standards. For example, employees are taught to put effort into the visual look of each drink. When you order a caramel macchiato at Starbucks, it has a precise pattern of caramel sauce. It has a lattice of seven vertical and horizontal lines with two full circles around it. They also pay attention to every detail in the store — from the lighting to the furniture, they’re on point!”[8]

The customer service team should be provided with clear documentation regarding how to handle common customer service complaints, what language to use and to avoid, how to document service issues, guidelines for escalation, the lengths employees can go for customers, and where to go with any questions or problems. Using documented processes and procedures will make it easier for the team to understand how to act in a given situation.[9] With that said, you do not want the company processes and procedures to be overly cumbersome or complicated; otherwise, employees may have difficulty following them.
Develop Customer Service Goals
Setting customer service goals can serve an important role in managing service teams. Set SMART goals as described in Table 3.1 below. Good goals focus attention on the right things, while poorly shaped goals focus attention on other things.
The service provided to customers, at every touchpoint, must be excellent and demand little effort from the customer in order to foster their loyalty. Customer service should make an extra effort to ensure customer happiness and satisfaction. Customer interactions need to be pleasant experiences, customer problems must be resolved quickly, and customers need to be totally confident in the services provided. Having a broad understanding of what excellent customer service looks like is a good step toward defining specific goals along with a plan that will lead to their attainment.[10]
| S = Specific | Make your goals specific and narrow for more effective planning |
|---|---|
| M = Measurable | Determine what evidence will prove you are making progress. Re-evaluate when necessary. |
| A = Attainable | Ensure you can reasonably accomplish your goal within a certain time frame given available resources. Stakeholders agree it is achievable. |
| R = Relevant | Goals should align with your values and long-term objectives. |
| T = Timebound | Set a realistic end date. This will help with task prioritization and motivation. |
For example, a manager may set a goal for the service team to “increase customer satisfaction”, but this goal does not inform the team of how to obtain this goal or the specific amount of increase the manager is expecting. We might do better by saying, “increase customer satisfaction by 10% over the next month”. The manager and staff should know how customer satisfaction is measured and that a 10% increase is a realistic expectation. The manager would then provide strategies on how this might be done. As well, incentives might be set for the service team to encourage their best performance.
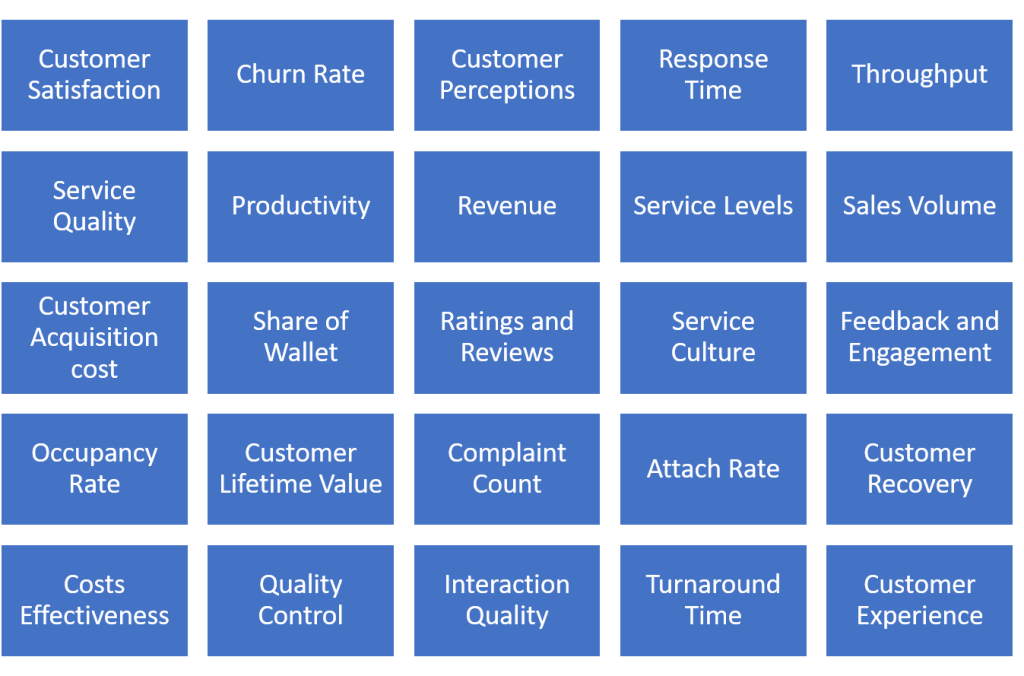
Customer service goals are targets for your customer experience and are part of strategic planning and performance management. Figure 3.1 below shows a list of 25 company goals for customer service.[11]
25 Goals for Customer Service
Watch the “What are SMART Goals? Quick Overview with 21 SMART Goals Examples” YouTube video below to learn about SMART goals.[12] Transcript for “What are SMART Goals? Quick Overview with 21 SMART Goals Examples” Video [PDF–New Tab]. Closed captioning is available on YouTube.
We cannot blame a wait staff who fails to increase the number of customers served in a given week if we later discover that, due to having live entertainment all week, customers were sitting longer at their tables, which resulted in fewer table changeovers, meaning staff were serving the existing customers longer rather than serving new ones. The goals managers set for staff will impact how the staff perform and what they choose to focus on. So if speed is the objective, then customer care may suffer as staff become obsessed with serving each customer quickly rather than serving each customer exceptionally. There must be a balance between efficient service and quality, effective service, and set goals that must drive employees in that performance direction.
“Profit-focused goals can hurt the customer relationship, and unrealistic goals demotivate and burn out employees. The goal structure should be set in a way that if your customer support representatives achieve their goals, it will propel the support manager closer to meeting his or her goals. Which in turn moves the director of support closer to meeting their goals. Typically, the goals of the director will be broad and align with specific company objectives. The customer support manager’s goals will be positioned more towards operational objectives – to make sure everything is running smoothly and efficiently. Customer support representatives will have more direct customer-centric goals like reducing response times and improving resolution rates.”[13]
Train Your Team
Investing time and money in customer service training can prove to be an invaluable investment for businesses of diverse sectors and sizes. Teaching members of staff the competencies, knowledge, and skills required to increase customer satisfaction and therefore customer retention is a shrewd way for businesses to ultimately increase their sales performance. Offering workplace training can provide staff with the necessary skills to strengthen their customer service skills, including communication, empathy, patience, and consistency, as well as adaptability. No matter the industry a business operates within, if it deals with customers, strong customer service skills are essential in ensuring customers remain loyal and a high level of customer retention is achieved. Workplace training that is focused on customer care will give employees valuable insight into how to develop and fine-tune customer service abilities. Such training will empower course participants to have the knowledge and confidence to provide effective solutions when they are faced with problems or difficult customers.[14]

First off, hire the right people. During an interview, tell potential employees what your customer service philosophy is and share your company’s missions, values, and goals. Then test applicants to see if they are a good fit.
Once hired, orient your new hire to the company and to the team of employees they will work with. Let them observe how things are done and how customer issues are resolved. Provide information on the company’s mission, vision, values, and goals, and explain how your department/area fits into the overall company goals.
Provide specific training on how to serve customers, even the difficult ones. Many service representatives do not know how to recover from a bad service situation with an upset or angry customer. A new employee can work alongside an experienced employee for a while and learn how to do things that will delight customers as well as support company goals. Such programs are often termed coaching, mentoring, on-the-job training, or job shadowing. Training may entail a more structured form such as classes teaching new employees how to use customer relationship management software, use phone systems; deal with service breakdown and service recovery; learn how to provide value to customers to encourage long-term loyalty, learn how to upsell or cross-sell in a way that customers will value; learn about the company vision, mission and goals; or manage social media platforms to serve and interact with customers.
Watch the “Service Recovery – Look, Sound, Feel” YouTube video below to learn about effective service recovery.[15] Transcript for “Service Recovery – Look, Sound, Feel” Video [PDF–New Tab]. Closed captioning is available on YouTube.
The Disney Institute does a great job at training Disney employees, so much so, that they offer on-demand online training to other companies that may wish to provide customer service training to their own employees. Disney’s website states, “In this on-demand course, our team will highlight how excellent service is the result of truly understanding your customer expectations and how to put the right service standards in place to exceed them. Begin to learn not only how to start to differentiate your organization from competitors, but also how to build customer loyalty through quality service. In this on-demand course, you will learn to:
- Assess and improve your organization’s commitment to quality service
- Differentiate and elevate your service to become a provider of choice
- Design standards for quality service and create a consistent service experience
- Gauge the needs, wants, stereotypes, and emotions of your customers at an individual level
- Understand the processes necessary to develop a workplace culture that consistently delivers exceptional service
- Recover effectively from a service failure and turn it into an opportunity to strengthen customer relations”[16]
Of course, there are many other training programs a company may utilize, such as those offered in LinkedIn Learning or those created in-house that are customized to the way your particular company goes about performing operations and serving customers.
Evaluate Service Quality
As a service manager, you continually need to be evaluating the quality of customer care your team provides. Key performance indicators (KPIs) measure how effectively a company is achieving its goals against a set of targets, objectives, or industry peers. Organizations use KPIs at multiple levels to evaluate their success in reaching targets.
Listed below are some of the ways in which you might measure service quality.
Net Promoter Score
The Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a customer loyalty metric that businesses use to gauge how their customers feel about them. It measures your customers’ willingness to recommend your company, product, or service to others. Companies with a high NPS are more likely to achieve long-term profitable growth.
Customer Retention Rate
Customer retention rate is another way to evaluate service quality. Why is it important to keep existing customers? Here are a few reasons:[17]
- Boosting customer retention by 5% increases profits by 25-95%.
- Companies have a 60-70% chance of selling to an existing customer vs. a 5-20% chance of selling to a new customer.
- 65% of a company’s business comes from existing customers.
- It costs 6x to 7x more to acquire new customers than to retain existing ones.
- 72% of customers switch to a competitor after one bad experience with a brand.
- Businesses lose over $75 billion each year to lost customers due to poor customer service.
Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
Obtaining customer feedback through customer satisfaction surveys is one way to gain customer insights. Surveying employees and asking for suggestions on customer service processes and procedures may lead to customer service improvements. Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) is a customer loyalty metric used by companies to gauge how satisfied a customer is with a particular interaction or overall experience.
Watch the “How to Use the Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) Metric” YouTube video below to learn how to use customer satisfaction scores.[18] Transcript for “How to Use the Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) Metric” Video [PDF–New Tab]. Closed captioning is available on YouTube.
Mystery Shoppers and Observation
Simply observing your team in action can help you identify common issues. Having a mystery shopper experience the service and processes your company provides and then reporting this experience back to you can help you understand where service breakdowns may occur.
Customer Engagement Metrics
Customer engagement starts from the first touch point and incorporates subsequent interactions, including the time customers spend with your brand and the actions they take throughout their journey. Customer engagement metrics are effective in measuring service accessibility and the quality of customer experience.[19]
Social Media Monitoring
Social media monitoring tools help understand what people are saying about you on social media. Insights like this paint a richer picture than simply relying on traditional media. Available in the market are the likes of Keyhole, Addict-o-Matic, CyberAlert, Sysomos among others.[20]
Identify Obstacles to Outstanding Service
There can be many obstacles creating barriers to your ability to provide excellent customer service. Some of these include the following.
Ineffective Employee Incentives
As a manager, you must ensure that incentives focus employees on the right performance. Incentives can be an obstacle to good performance when employees take action to gain incentives at the expense of doing what is right or good for the customer. Have you ever wondered about the motivation of an auto mechanic when they tell you your car needs more work than you anticipated? What about when the salesperson sounds very convincing as they try to sell you more than you think you need? Employees may be tempted to bend the rules, working against the concepts of good quality service, in order to win incentives. Ensure incentives are set up to encourage better service and not encourage unethical behaviour.
Inefficient or Ineffective Service Systems
Sometimes service systems, due to cumbersome processes customers must follow, unreliable service (works intermittently), poor quality products, or procedures, just don’t work! Often customer service representatives get blamed by customers for these things, but in reality, these things are beyond the scope of the service representatives’ control. With that said, certainly, service representatives should alert their managers when they observe such issues. For example, if several customers have complained about the same issue, then it might be time to fix the issue. As a manager, if your employees have informed you of processes that are not working you should examine them and consider how to make improvements.
Ineffective Policies, Processes, or Procedures
A lack of policies, processes, or procedures can also be an obstacle to providing great customer service. If these are missing or lacking in structure, customer service agents will not be guided in providing exceptional service. If the company does not clearly communicate its customer service vision and provide the tools for employees to do their job, then the lack of processes and procedures will become an obstacle. On the other hand, if there are too many policies, processes, or procedures, agents may be restricted in offering the best service they can. In either of these cases, customer service managers should work with the cross-functional management team to develop clear guidelines for policies, processes, and procedures and communicate those to employees.
Watch the “How to Avoid Roadblocks to Great Customer Service” YouTube video below to learn about avoiding roadblocks to great customer service.[21] Transcript for “How to Avoid Roadblocks to Great Customer Service” Video [PDF–New Tab]. Closed captioning is available on YouTube.
Lack of Communication
A lack of communication or support from other departments can be an obstacle to providing great customer service. Often, the front-line employees, those facing the customer, need support from other departments within an organization. This means depending on others within the company to do their jobs and to do a quality job; yet, not every employee is dedicated to the company or performs quality work. As a manager, if your employees are having difficulty getting what they need from other departments, you should step in and connect with the other department’s manager to discuss what can be done to make working together easier and more effective. Managers in other areas may not care about what is happening with your team, but they should care about fixing a problem that is costing the company money and customers.
Unanticipated Customer Demand
Customer demand can exceed what was expected or the number of customers can be far greater than anticipated, which can create an obstacle to providing excellent customer service. If customer demand is so great that your company runs out of products or not everyone can be served efficiently, then customers may become dissatisfied. If your company gets far more customers than anticipated, there may not be enough staff on hand to serve each customer; again, this can lead to customer loss and dissatisfaction. Managers need to schedule enough employees to serve all customers and serve them through various channels. Managers may forecast demand by reviewing past trends or patterns in sales and service. They may anticipate demand by analyzing the environment, for example, if there is an event in town bringing in vacationers, then maybe the company will require additional staff on hand that week. Managers may also hire contingent workers, or workers they can hire when short-staffed on an ad-hoc basis, but having them trained may be an issue.
Improve Service Quality
There is only one boss. The customer – and he can fire everybody in the company from the chairman on down, simply by spending his money somewhere else. –Sam Walton[22]
Great customer service is just the first stage, but by making sure you build in analytics and other ways of measuring this success, your customer support team’s hard work and effort can be quantified, and their progress can be measured.[23]
In the Future of CX report, PwC surveyed 15,000 consumers and found that 1 in 3 customers will leave a brand they love after just one bad experience, while 92% would completely abandon a company after two or three negative interactions.[24]
Companies should ensure that customers are able to find answers to their questions using a wide range of self-service options. Today, 67% of customers prefer self-service over speaking to a company representative. Furthermore, 91% of customers would use an online knowledge base if it were available and tailored to their needs.[25]
Do you know that 50% of customers will stop visiting a company’s website if it isn’t mobile-friendly?[26]
Forecast Customer Demand
Understanding and anticipating customer demand is critical for effective management. By forecasting demand, managers can plan staffing, order the right amount of supplies, and ensure consistent service during busy and slow periods. Accurate forecasting reduces costs, minimizes waste, maximizes revenue, and improves customer satisfaction. Without it, businesses risk overstaffing during slow times or running out of popular products or services during peak periods.
Managers typically rely on historical sales data, trend analysis, and observations of the business environment to forecast demand. For example, analyzing past sales patterns, seasonal trends, and local events helps predict when customer activity will rise. This information allows managers to align staff schedules, manage inventory, and plan promotions to meet anticipated demand.
Factors that can increase demand include promotions or loyalty programs, changes in the local environment such as new offices or schools, and emerging consumer trends. Conversely, demand may decrease due to price increases, negative reviews, poor product or service quality, increased competition, economic downturns, or seasonal lulls. Understanding these drivers enables managers to make proactive decisions that maintain service quality, optimize costs, and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
Practical Example: Forecasting in Action
Imagine a small retail store that sells a mix of groceries and household items. During the summer, the manager notices that sales of cold drinks, ice cream, and barbecue supplies spike, while other products remain steady. By analyzing historical sales data from previous summers, combined with observations of local events like festivals or nearby school holidays, the manager can forecast a rise in demand for these seasonal items.
Using this forecast, the manager increases staff during peak hours, orders extra inventory of high-demand products, and sets up promotions to attract more customers. At the same time, they avoid overstocking less popular items to reduce waste. Conversely, the manager also anticipates slower periods, such as early winter, and adjusts staffing and inventory accordingly. By proactively managing demand, the store maintains high customer satisfaction, reduces costs, and maximizes revenue throughout the year.
Make Doing Business Easy
Make it easy for customers to do business with your company by keeping processes simple, clear, and efficient. If interactions are too cumbersome or complicated, customers are likely to go elsewhere. Customers who feel they are wasting time standing in lines, being transferred between staff members, waiting for answers, or navigating confusing websites and paperwork for returns are likely to become frustrated—and may take both their business and their recommendations elsewhere.
To meet customer expectations, businesses should focus on removing barriers that make transactions difficult. This can include offering multiple delivery options, online ordering, self-service kiosks, and accepting a variety of payment methods. Clear, straightforward instructions for returns or exchanges, efficient and knowledgeable staff, and an easy-to-navigate website or app also contribute to a smooth customer experience.
Customers also value perks and conveniences that make interactions more rewarding. Loyalty programs that are simple to understand and redeem, personalized promotions, and fast checkout options enhance satisfaction. Automated updates, such as email or text notifications on order status, keep customers informed without extra effort. By anticipating customer needs and designing processes that reduce wait times and friction—whether online, in-store, or over the phone—businesses can improve customer satisfaction, encourage repeat purchases, and drive positive referrals. Ultimately, the easier it is for customers to engage with a business, the more likely they are to remain loyal and share positive recommendations.
Empower Your Employees

One way to improve service quality is to empower your employees. Empowering employees means giving them the authority to make certain decisions without needing approval from management. This allows front-line staff to resolve customer issues quickly, eliminating the “let me ask my boss” barrier and reducing wait times. To empower employees effectively, companies must provide access to the data, tools, and systems necessary to address customer problems. Boundaries should be clearly defined—for example, an employee might be authorized to correct a customer issue up to a certain dollar amount.
Supervisors play a critical role in this process. They need training to understand how much power to grant employees and in which areas, and they must coach their teams to make decisions that benefit both the customer and the company. When employees are empowered, customers receive faster, more efficient, and more effective service, which helps meet or exceed expectations. Satisfied customers are more likely to remain loyal and may even refer new business.
Employee empowerment can also have significant benefits for staff. It builds trust in leadership, boosts motivation, encourages creativity, and can improve employee retention. However, without proper training on company standards and guidelines, empowerment can increase business risks.
Some companies are hesitant to empower employees to handle customer service failures for valid reasons. Management may fear inconsistent decisions that confuse or frustrate customers if similar issues are handled differently. There may also be concerns about costs, as on-the-spot refunds, replacements, or complimentary services can become expensive. Additionally, companies may worry that employees lack the necessary training or experience to make sound decisions, potentially worsening customer issues. For example, an employee attempting to resolve a technical complaint without fully understanding the product could inadvertently create more frustration. While empowerment can greatly improve responsiveness and customer satisfaction, it requires careful planning, clear guidelines, and ongoing oversight to succeed.
Provide Employees with Feedback and Training
Train employees as needed and provide meaningful feedback in a constructive manner on a regular basis. Feedback should be thoughtful, whether you are providing encouragement on a job well done or providing constructive feedback for a performance correction. You may need to offer specialized training when you observe your team is lacking skills in a particular area, and this lack of skill is negatively affecting the quality of service being delivered. Orientation training or onboarding is not the only time you need to train your employees; when systems or procedures are updated, employees should be trained so they are able to offer the best customer service possible. Communication between management and employees is key in ensuring employees understand what is expected of them, what the company policies and procedures are, and how to serve customers in a way the company wants them to.
Implement an Effective Rewards System
Reward your team for providing excellent service. A customer service incentive program can improve employee morale and job satisfaction, but there are some drawbacks you need to steer clear of. Focusing on monetary rewards won’t necessarily have the results you expect. It might look good initially, but it often ends up creating a competitive environment and a team pitted against each other. Implementing a reward system that aligns with clearly defined goals is the best approach. For example, if you reward the person who sells the most product, then only one person on the team wins. This sets up the team to work against each other, which has negative effects on team collaboration. Instead, you might have a threshold that, when met, you reward your employees; in this type of system, several employees might meet the threshold. You also need to make the threshold attainable; something so difficult that no one can attain the reward will only have negative effects on employee motivation.
From 2020 onwards, there are officially 5 generations that have been working together in the workplace. This statistic is mind-boggling. Different age groups naturally desire different rewards- for example; senior executives may be looking at household-related items, whereas employees in their early 20s may value virtual learning experiences more. Besides, Generation Z- the latest one to enter the workforce- not only demand rewards for their hard work but also want a say in the ‘how’ and ‘what’ of rewards.[27]
In a consumerist world full of personalized experiences, rewards need to be tailored to an individual’s preference. Ideally, employees should be able to decide how they want to be recognized for their good work. Be it through a personal note or public recognition, through movie tickets, or shopping vouchers- top firms across the globe already offer an extensive range of rewards and experiences that can be redeemed instantly.[28]
“One reason that businesses cite not implementing a reward system for employee performance is temporary compliance. An employee-of-the-month program may increase productivity in the first month, but interest quickly dwindles. All the work of creating that program provides only short-term benefits. To avoid employees lapsing back into pre-reward productivity, it’s important for employers to keep the incentive programs new and exciting. Change up employee reward systems quarterly or yearly to reignite excitement about the plan.”[29]
Evaluate Your Personal Management Skills
You need to develop and improve your managerial skills on an ongoing basis as your career develops and as you meet new managerial challenges. Whether you manage a department or a project team, it is important to know how to get the work done right. You must develop not only your technical skills but your management skills as well. Delegating, motivating, communicating, and understanding team dynamics are some of the key skills needed. With those skills, along with patience and a strong sense of balance, you can become a very effective manager.[30]

A good manager sets their employees up for success. They provide the time and tools to accomplish tasks. They often have experience in the field of work they are supervising. They are capable of solving problems, managing time and money, and inspiring employees to perform optimally. A manager is responsible for the effective and efficient operations within a company, department, or team. A manager who is not able to create efficient schedules, keep employees motivated, or manage time and money will not perform optimally and may impede the ability of their subordinates to do the same. A poor manager may be someone who gives employees directives without any explanation, tools, or context. A good manager supports employees, chooses appropriate projects, and allocates resources (people, time, money, materials, and equipment) where needed and when needed in a reasonable manner to support the company’s goals. Management skills are important to lead a team and move the organization in the right direction. If the manager has weak management skills, customer service quality may suffer. To be a good manager, it is important to have skills such as planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. Managers need to create effective strategies, have good communication skills, be able to make decisions responsibly, be able to solve problems whenever they arise, be able to manage time effectively, be able to manage projects effectively, have conceptual skills, be able to motivate employees to lead their team, etc.
Some new managers are coached or mentored for the first few months on the job. Others take training courses in managing people and projects, negotiation, handling difficult people, sales, management, and emotional intelligence.
| People with High EQ |
|
|---|---|
| People with Low EQ |
|
Emotional intelligence is the ability to understand, interpret, and manage your emotions, as well as those of other people. If you have high EQ, you’re able to communicate with others, show empathy when needed, and overcome emotionally charged situations.[31] Emotional intelligence is widely recognized as a valuable skill that helps improve communication, management, problem-solving, and relationships within the workplace. It is also a skill that researchers believe can be improved with training and practice. Refer to Table 3.2 for a comparison of the traits people with high EQ have compared to those with low EQ.
Although emotional skills come naturally to some people, anyone can improve their ability to understand and reason. This can be particularly helpful in the workplace, where relationships and business decisions are often based on interpersonal understanding, teamwork, and communication.[32]
To be a manager who is great at their job, you will need to:
- Learn about the company’s vision, mission, goals, and values, and understand how your specific department/area supports the overall company goals.
- Learn what is expected of you and your department/area in terms of output, results, interactions with customers, and daily, weekly, and monthly reporting.
- Learn how to communicate well in all situations, including when you have to deliver negative information to an employee or customer, when you need to negotiate a contract, or when you need to persuade someone to do something. There are many books and courses on these subjects.
- Learn how to motivate others. What does it take to make employees want to work to their best ability? Often, recognition, rewards, involvement, and knowing that their manager cares about them and supports them in their jobs is enough.
- Learn how to manage projects. Everything that gets done in the workplace is a project, small or large.
Optimize Service Delivery
In a highly competitive market, service-based businesses need to set themselves apart from their competitors. Listed below are a few ways to drive growth in your company by committing to exceptional service delivery:
Communicate with Customers
When it comes to customers, there’s no such thing as over-communication — your clients feel more comfortable when they know what’s going on. That being said, the amount of communication is not as imperative as the timeliness, context, and ability to clearly identify the value added to the client. In a world of constant connectivity, your ability to cut through the flood of subpar information with quality and timely answers can go a long way.[33]
Set Customer Expectations
Define for customers what level of service they can expect from your company. Keep your message consistent across channels and train staff to deliver service to meet the expectations the company has set. One example might be turnaround time. If you promise to get back to a customer within 24 hours, make sure you do; even when you don’t have the answer, you can follow up to let the customer know you are still working on the problem. Under-promise and over-deliver is one way to exceed customer expectations. Do not promise to do something if you are not sure you can; this may result in a dissatisfied customer. You might say, “We will make every attempt to deliver by Friday, but I cannot promise it will arrive on time. I will try my best.” Then, if the package arrives on Thursday or Friday, you have delighted the customer.
Automate When Possible
Offer customers a choice of full-serve or self-serve processes. Today, we see online shopping, self-checkouts at retailers and grocery stores, and online accounts such as Amazon, which allow customers to customize their options and subscriptions. Automation, when working optimally, can increase customer satisfaction, streamline processes and services, and reduce the workload on employees. Ensure automated systems are not difficult to use and are working optimally, otherwise, your customers may become dissatisfied and may decide to do business with your competitor instead. Shipping processes may be automated as well, and it is important to ensure speedy delivery because if your customers can get the item from your competitor faster, they just might. Implementing automated systems may reduce costs for a company in the long run, but there will always be some customers who prefer personalized service provided by a real, live person. Automation comes with a high upfront cost but usually increases productivity, so in the long ru, itn saves money and increases revenue.[34]
Schedule Employees Effectively
Service organizations need to schedule employees in accordance with forecasted customer demand. For example, during holidays, stores might anticipate an influx of customers and plan to have additional cashiers and customer service employees on the schedule. The company does not want too many employees working at one time, as it leads to some employees standing around with nothing much to do. This is a waste of resources and costs the company money; it may also lower employee morale and motivation to do their best work. The company also does not want too few employees scheduled if they are so busy that customer service wanes due to being rushed, exhausted, and frustrated. Situations such as these may lead to higher turnover rates (employees quitting), increased customer dissatisfaction, lower employee morale, and a negative corporate culture. Managers should schedule resources (employees, equipment, raw materials) in accordance with current projects and sales forecasts, and ensure that no resource is over- or under-utilized.
Foster a Strong Culture
After establishing a feasible service concept, there is no other factor so instrumental to the success of a service organization as its culture. Employees should be aligned when it comes to a specific set of overarching principles — and, while methodology is crucial to service delivery, this should feel more like a philosophy. Don’t take it for granted that your culture is strictly internal — it shows up in your service delivery, your methodology, and your relationships and interactions with customers. The better employees understand the company’s service vision, the better it translates to customers. More often than not, your customers will know if you and your employees aren’t on the same page.[35]
Costs of Poor Customer Service
Bad customer service costs businesses $338 billion in revenue every year, globally. That’s the real cost of bad customer service.[36]
Not listening to customers is one of the biggest mistakes companies can make. It may lead to angry customers, lost business, and a damaged company reputation. In order to satisfy customers, companies must keep up with the latest technological advances and train their staff to meet or exceed customer expectations. Social media is growing in popularity, and customers increasingly use it to share their experiences—both positive and negative. Often, disgruntled customers do not communicate their complaints directly to a business. Instead, they voice concerns to friends, family, coworkers, or on social media platforms, which can amplify the negative impact.
Why Customers Might Not Voice Complaints
There are several reasons why customers may choose not to complain directly. Some may feel that their concerns will be ignored or dismissed, especially if they have experienced poor responses in the past. Others may not want to invest the time and effort required to contact the business, particularly if the complaint seems small or they perceive the process as cumbersome. Some customers may fear confrontation or feel uncomfortable speaking up, preferring to avoid conflict altogether. Additionally, in today’s digital age, it is often easier for customers to post a quick social media comment or review than to navigate customer service channels such as phone lines, email, or in-person visits.
Understanding why customers may withhold feedback is essential for businesses. By creating multiple, accessible channels for communication—such as online chat, social media messaging, feedback forms, and in-store kiosks—companies can make it easier for customers to voice concerns. Prompt, empathetic responses demonstrate that the business values customer input, increasing the likelihood that dissatisfied customers will share their concerns directly rather than venting elsewhere. Proactively listening to and addressing complaints helps businesses resolve issues quickly, maintain customer loyalty, and protect their reputation.
Why Employees Might Not Share Customer Complaints
Employees are often the first point of contact with customers, yet they may hesitate to relay complaints to management. One common reason is fear of blame or reprisal. If employees feel that reporting a customer issue will result in criticism, disciplinary action, or a negative performance review, they may choose to keep the complaint to themselves. Additionally, some employees may perceive management as unresponsive or unsupportive, believing that raising concerns will not lead to meaningful change. This perception can discourage employees from escalating issues, even when they recognize that doing so could benefit the customer and the company.
Another factor is workload and time pressure. Frontline employees often handle multiple tasks simultaneously, from serving customers to completing administrative duties. In the midst of a busy shift, taking extra time to document and communicate a complaint may feel burdensome. Some employees may also assume that minor complaints are not worth reporting, or that management already knows about recurring issues. Without clear processes, support, and encouragement from leadership, valuable feedback can be lost, leaving customer problems unresolved and opportunities for improvement unrealized.
Watch the “How Poor Customer Service Can Lead to Big Losses!” YouTube video below to learn how bad customer service can cost a company money.[37] Transcript for “How Poor Customer Service Can Lead to Big Losses!” Video [PDF–New Tab]. Closed captioning is available on YouTube.
Key Takeaways
- A customer service philosophy is a shared mission for your support team, a set of guiding principles that ensure you’re upholding your core values with every customer interaction.
- The first section of a customer service philosophy is a customer service vision statement, which Jeff Toister defines as “a statement that clearly defines the type of customer service employees are expected to provide”.
- Your vision statement is followed by your team’s values. Customer service values impact the experience the customer receives, and they help to define the personality and attitude the business is trying to put forth. Often, companies offer training to employees on how to uphold these values.
- Service standards are guidelines for employees to follow when interacting with customers. Do not make them too rigid or strict, as not all standards will apply to every customer situation. This gives employees the flexibility to adapt to each customer’s unique needs within a standard framework. Customer service guidelines should align with the company’s brand.
- Setting customer service goals can serve an important role in managing service teams. Set SMART goals. Good goals focus attention on the right things, while poorly shaped goals focus attention on other things.
- Investing time and money in customer service training can prove to be an invaluable investment for businesses of diverse sectors and sizes.
- Key performance indicators (KPIs) measure how effectively a company is achieving its goals against a set of targets, objectives, or industry peers. Some indicators include Net Promoter Score, Customer Retention Rate, Customer Satisfaction Score, Mystery Shoppers, Observation, Customer Engagement Metrics, and Social Media Monitoring.
- Obstacles to outstanding service include employee incentives; inefficient or ineffective service systems; ineffective policies, processes, or procedures; lack of communication; and, unanticipated customer demand.
- Improve service quality by forecasting customer demand, making doing business easy for your customers, empowering employees, providing employees with feedback and training, implementing an effective rewards system, and evaluating your personal management skills.
- Optimize service delivery by communicating with customers, setting customer expectations, automating when possible, scheduling employees effectively, and fostering a strong culture.
- Bad customer service costs businesses $338 billion in revenue every year, globally.
End-of-Chapter Exercises
- Service Philosophy. Search the Internet for “customer service philosophy” or “Examples of customer service philosophy” or visit a specific company website and locate their customer service philosophy. Compare a few examples and identify things they may have in common. What are three of the most prevalent concepts in organizations’ customer service philosophies? Share your findings with the class and/or your professor.
- SMART Goals. Practice setting a SMART goal. Maybe you want to lose weight, quit smoking, get a part-time job, or make the people close to you happier. Set a SMART goal to help you get started.
- Management Skills Quiz. Take a quiz from MindTools to see if you have good management skills.
- Emotional Intelligence Quiz. How emotionally intelligent are you? Take this quiz to find out.
- Jobs. Visit Best Job Interview to learn more about the tasks, duties, responsibilities, education, experience, skills, and competencies one must have in order to obtain a customer service management position. Consider how you might grow and develop your own skills so that one day you may become a team manager. Are you taking courses currently in college or university that may help you develop some of the required skills and abilities to be a team manager? Where else might you develop some of these skills?
- Obstacles. Consider the obstacles to outstanding customer service discussed in this chapter. Can you think of, or research, three additional service obstacles you might encounter? What could a service manager do to overcome those obstacles? Discuss with the class and/or professor.
- Training. Assume you are the customer service manager in a large retail store such as Walmart or Loblaws. You will be developing a training program for your customer service employees. Conduct a bit of research about employee training methods and jot down some notes on how you will train your team. Will you offer in-person training? If so, how many days? Will you offer online courses? Will you offer mentoring or coaching programs? What are three concepts you will teach your team? Discuss with the class and/or your professor.
- Incentive Programs. Search the Internet for “employee incentive program” and review a few. Assume you are a manager for a mobile phone service provider, Koodo, Fido, or such. What type of employee incentive program would you set up? Why? Discuss your rationale with the class and/or your professor.
- Write a Customer Service Vision. Assume you are managing a customer service team within a Gym similar to Fit4Life, Planet Fitness, or GoodLife, and you need to create a customer service vision statement. Use the Internet to gather some tips, advice, and examples for writing this statement, then create one. Share it with your class and/or professor. Discuss the considerations you made while developing your company’s customer service vision.
Additional Resources
- LinkedIn Learning Customer Service Training
- I was Seduced by Exceptional Customer Service
- 7 Management Practices That Can Improve Employee Productivity
- 10 Barriers to Outstanding Customer Service
- How to Write a Customer Service Vision Statement
- How to Evaluate Customer Service
- 10 Phrases to Avoid in Customer Service, YouTube Video
- 7 Customer Service KPIs to Evaluate Your Team
- 22 Goals for Customer Service Teams to Strive for in 2022
- Improve Your Customer Experience with Customer Journey Mapping, YouTube Video
References
(Note: This reference list was produced using the auto-footnote and media citation features of Pressbooks; therefore, the in-text citations are not displayed in APA style).
Media Attributions
- A customer at Checkout © Photo by Blake Wisz from UnSplash is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- Restaurant server taking an order © Photo by Andrea Piacquadio from Pexels is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- 25goals © Simplicable adapted by Kerri Shields is licensed under a All Rights Reserved license
- A person being hired © Photo by Sora Shimazaki from Pexels is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- Employee Empowerment © Igor Link | Pixabay
- A team meeting in the office © Photo by Smartworks Coworking from UnSplash is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- Wellington, E. (2022, July 14). How to create an inspiring customer service philosophy. Help Scout. https://www.helpscout.com/blog/customer-service-philosophy/ ↵
- Wellington, E. (2022, July 14). How to create an inspiring customer service philosophy. Help Scout. https://www.helpscout.com/blog/customer-service-philosophy/ ↵
- Callcenter Helper. (n.d.). What should you put in a customer service vision statement?https://www.callcentrehelper.com/what-should-you-put-in-a-customer-service-vision-statement-204455.htm ↵
- Callcenter Helper. (n.d.). What should you put in a customer service vision statement?https://www.callcentrehelper.com/what-should-you-put-in-a-customer-service-vision-statement-204455.htm ↵
- Wellington, E. (2022, July 14). How to create an inspiring customer service philosophy. https://www.helpscout.com/blog/customer-service-philosophy/ ↵
- Pascal (2016, October 20). How to create a strong customer service philosophy. Userlike. https://www.userlike.com/en/blog/customer-service-philosophy ↵
- Government of Canada. (n.d.) Service standards in the CRA. CRA. https://www.canada.ca/en/revenue-agency/services/about-canada-revenue-agency-cra/service-standards-cra.html ↵
- Dinardi, G. (2020). The 10 best customer service examples for 2020. nextiva. https://www.nextiva.com/blog/customer-service-examples.html ↵
- Landsman, I. (2021, August 24). How to create realistic customer service guidelines. helpspot. https://www.helpspot.com/blog/customer-service-guidelines ↵
- Customer Thermometer. (n.d.). Measurable customer service goals with examples. https://www.customerthermometer.com/customer-service/measurable-customer-service-goals-with-examples/ ↵
- Spacey, J. (2020, January 19). 25 examples of customer service goals. https://simplicable.com/en/customer-service-goals ↵
- Develop Good Habits. (2020, October 5). SMART goals quick overview with 21 SMART goals examples. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/elJcG83m-qg ↵
- Richards, R. (2020, August 7). How to set measurable customer support goals that drive growth. Jitbit. https://www.jitbit.com/news/customer-support-goals/ ↵
- Luke, H. (2016, August 1). How customer service training can improve customer service skills and ultimately sales performance. [Blog]. https://www.mycustomer.com/community/blogs/hadyn-luke/how-workplace-training-can-improve-customer-service-skills-and-ultimately ↵
- Gilbert-Jamison, T. (2020, July 28). Service recovery - Look, sound, feel. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/AeC5nNYhlA8 ↵
- Disney Institute. (n.d.). On-Demand: Disney's approach to quality service. https://www.disneyinstitute.com/disneys-approach-quality-service-online/?ef_id=eff625c563ad159d6b7b7a600e68d939:G:s&s_kwcid=AL!5052!10!80745491051194!80745603288295&CMP=KNC-FY21_DI_INS_CAN_PDI_LGN_DIQS_Course_QualityService%7CB%7C1165729.DI.SM.01.04%7CMALWT9Z%7CNB%7C80745491051194&msclkid=eff625c563ad159d6b7b7a600e68d939 ↵
- McCain, A. (2023, January 16). 28 critical customer retention statistics [2023]: Average customer retention rate by industry. https://www.zippia.com/advice/customer-retention-statistics/ ↵
- SurveyMonkey. (2020, June 26). How to use the customer satisfaction score (CSAT) metric. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/8ANkDCHkjew ↵
- Dhangal, A. (2020, June 19). How do you measure customer service performance and success? With 10 useful KPIs. Acquire. https://acquire.io/blog/measure-customer-service-success/ ↵
- Dhangal, A. (2020, June 19). How do you measure customer service performance and success? With 10 useful KPIs. Acquire. https://acquire.io/blog/measure-customer-service-success/ ↵
- Hyken, S. (2020, September 17). How to avoid roadblocks to great customer service. [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/A5YhrLnxOTQ[/ ↵
- commbox. (n.d.). Best customer support strategies, evaluate and reward your team. https://www.commbox.io/best-customer-support-strategies-evaluate-and-reward-your-team/ ↵
- commbox. (2019, October 21). Best customer support strategies, evaluate and reward your team. https://www.commbox.io/best-customer-support-strategies-evaluate-and-reward-your-team/ ↵
- SuperOffice. (2023, September 1). 32 customer experience statistics you need to know for 2024. https://www.superoffice.com/blog/customer-experience-statistics/ ↵
- SuperOffice. (2023, September 1). 32 customer experience statistics you need to know for 2024. https://www.superoffice.com/blog/customer-experience-statistics/ ↵
- SuperOffice. (2023, September 1). 32 customer experience statistics you need to know for 2024. https://www.superoffice.com/blog/customer-experience-statistics/ ↵
- Gratifi. (2021, September 14). Why a one-size-fits-all employee rewards program won’t work. https://www.gratifi.com/blog/importance-of-a-flexible-employee-rewards-program/ ↵
- Gratifi. (2021, September 14). Why a one-size-fits-all employee rewards program won’t work. https://www.gratifi.com/blog/importance-of-a-flexible-employee-rewards-program/ ↵
- Team Synerion. (2015, April 3). Building a reward system for employee performance. Synerion. https://blog.synerion.com/building-a-reward-system-for-employee-performance ↵
- Mindtools. (n.d.). How good are your management skills? https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newTMM_28.htm ↵
- PsychCentral. (n.d.). Emotional intelligence test. https://psychcentral.com/quizzes/emotional-intelligence-test ↵
- Cherry, K. (2022, December 11). Utilizing emotional intelligence in the workplace. https://www.verywellmind.com/utilizing-emotional-intelligence-in-the-workplace-4164713 ↵
- Mullen, R. (2022, June 7). 5 ways to improve service quality in your organization. https://www.replicon.com/blog/5-ways-improve-service-delivery-organization/ ↵
- Mullen, R. (2022, June 7). 5 ways to improve service quality in your organization. https://www.replicon.com/blog/5-ways-improve-service-delivery-organization/ ↵
- Mullen, R. (2022, June 7). 5 ways to improve service quality in your organization. https://www.replicon.com/blog/5-ways-improve-service-delivery-organization/ ↵
- Widmer, B. (2022, June 7). The real cost of bad customer service (and how to avoid it). formilla. https://www.formilla.com/blog/the-real-cost-of-bad-customer-service-and-how-to-avoid-it/ ↵
- Hyken, S. (2018, July 5). How poor customer service can lead to big losses! [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/5T_Wme6pres ↵
is a shared mission for your support team, a set of guiding principles that ensure you’re upholding your core values with every customer interaction
A customer service vision statement provides meaning and direction for employees. It is the statement that outlines the type of service that agents are expected to provide to customers. It tends to be quite idealistic and ‘big picture’ thinking, needs to be clear and unambiguous, and it should be easily understood by both employees and customers alike.
impact the experience the customer receives and they help to define the personality and attitude the business is trying to put forth. Often companies offer training to employees on how to uphold these values.
are guidelines for employees to follow when interacting with customers.
Setting customer service goals can serve an important role in managing service teams. Set SMART goals. Good goals focus attention on the right things, while poorly shaped goals focus attention on other things.
Investing the time and money in customer service training can prove to be an invaluable investment for businesses of diverse sectors and sizes. Teaching members of staff the competencies, knowledge and skills required to increase customer satisfaction and therefore customer retention is a shrewd way for businesses to ultimately increase their sales performance.
measure how effectively a company is achieving its goals against a set of targets, objectives, or industry peers.
is a customer loyalty metric that businesses use to gauge how their customers feel about them. It measures your customers' willingness to recommend your company, product, or service to others. Companies with high a NPS are more likely to achieve long-term profitable growth.
are effective in measuring service accessibility and the quality of customer experience.
is the practice of tracking notified brand mentions, comments, and tags on digital channels and responding as appropriate, often focusing on customer service and reputation management. It allows businesses to quickly address questions, praise, or complaints one-on-one, providing timely support and engagement.

