1.3 AI Prompting Skills
Prompting means giving clear instructions and requests to an AI system to get desirable responses. Good prompting skills can help teachers and students to support their work, get precise answers, and learn independently. Good prompting skills can also ensure AI is used ethically and responsibly.
Guides to Basic AI Prompting
The guides below provide information and practice activities to help you learn more about AI prompting.
Teaching and Learning Resources
Teaching and Learning has shortlisted a set of prompting techniques: Generative AI Prompting Techniques. The page provides ideas and examples of various uses of AI in your teaching practice.
Open AI and Microsoft Resources
OpenAI’s Prompt Engineering Guide provides ideas for getting better results from chatbots. The guide emphasizes the importance of clear instructions, providing reference text, breaking down complex tasks, allowing the model time to “think,” and using external tools to enhance accuracy and efficiency. Access the full guide, then return for these practice activities: Open AI’s Prompt Engineering (General Strategies and Specific Tactics).
Microsoft also provides a series of articles and tutorials on prompting. See Copilot: AI Prompt Writing 101, Learn About Copilot Prompts, the Microsoft AI Art Prompting Guide, and more.
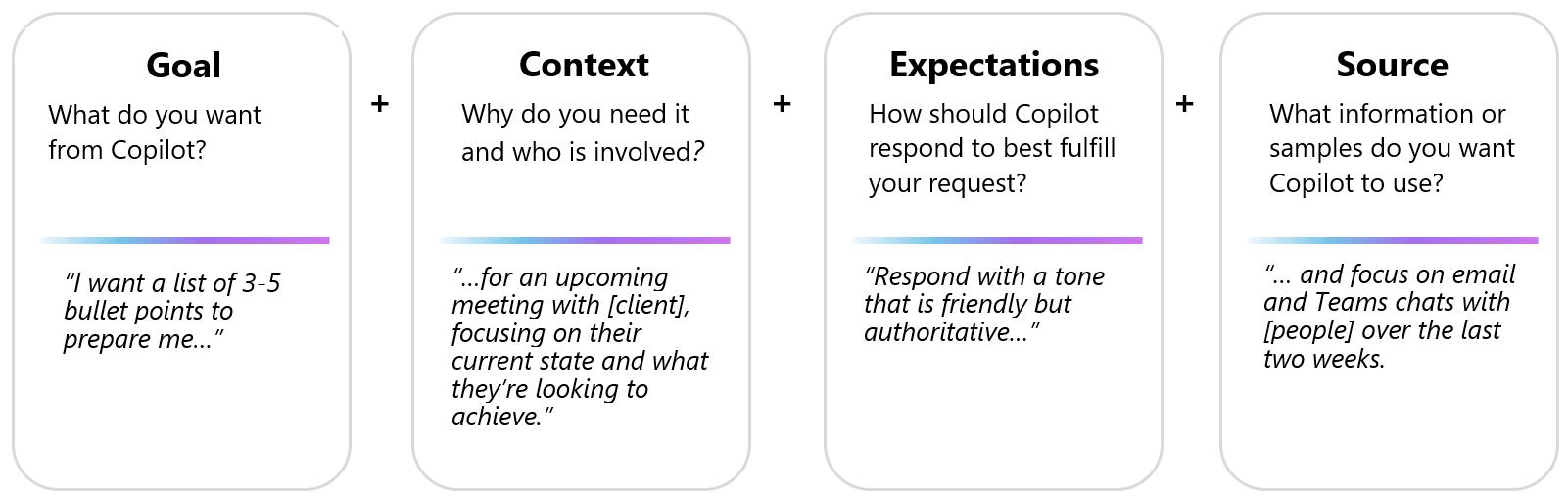
Figure 1. Example of a Copilot prompt. Adapted from Microsoft (2024).
Try This!
The AI Pedagogy Project provides a brief LLM tutorial where users can learn about the basics of prompting while using an online chatbot. Give it a try!

Learn More
Learn more about prompting at Generative AI Prompting Techniques (Faculty Learning Hub).
General Prompting Tips to Share with Students
Model these prompting tips and share them with students.
- Provide context: Give the AI enough context to understand your request. For example, if you need help with a math problem, provide the problem statement and any relevant information.
- Be clear and specific: When asking the AI for help, be as clear and specific as possible. For example, instead of saying, “Tell me about history,” say, “Give me a summary of the causes of World War II.”
- Break down the tasks: If you have a complex task, break it down into smaller steps. This makes it easier for the AI to provide accurate and helpful responses.
- Use examples: Provide examples to show the AI the response you are looking for. This helps the AI understand your expectations better.
- Review and revise: Always review the AI’s responses and make any necessary revisions. The AI can provide a good starting point, but it’s important to ensure the final output meets your needs. Always check instructions to ensure you are using AI in permitted ways.
- Keep track and document AI use: Always track how you use AI tools and document your interactions. This helps you understand how AI contributes to your work and ensures transparency. Simple suggestions include noting down the prompts you used, the responses you received, and how you incorporated the AI’s output into your final work.
More Prompting Strategies
Various strategies can be used to improve your prompting technique. Use these strategies to generate the kinds of outputs you desire. See the table below for each strategy’s terms, explanations, and examples.
Select the accordion items below to learn more about prompting strategies.
Try This! Copilot Prompt Practice Activities
Use Copilot to practice and gain familiarity with the tool. Try these prompt activities in Copilot to practice crafting clear instructions, including references, breaking down complex tasks, and more.
Copy and paste the prompt(s) below into Copilot. Add any information that may help to refine the output. What ideas might be helpful for you?
Activity: Crafting Clear Instructions
Goal: Practice writing clear and specific prompts by asking Copilot to rewrite the following vague prompt to make it more specific and detailed: “Explain climate change.”
Example: “Explain the main causes of climate change, focusing on human activities such as fossil fuel combustion and deforestation, in a 200-word summary suitable for high school students.”
Activity: Locating and Summarizing a Source
Goal: Learn how to locate reliable sources on the internet and summarize their content. Find a reliable source about the benefits of renewable energy, include a hyperlink to the source, and provide a summary of the resource.
Example: “Find a reliable online source about the benefits of renewable energy, include a hyperlink to the source, and provide a summary of the resource, including its references.”
Activity: Breaking Down Complex Tasks
Goal: Practice decomposing complex tasks into simpler subtasks. Break down writing a research paper on social media’s impact on mental health into smaller, manageable steps.
Example: “Follow these instructions step by step and in order. 1. Conduct a literature review on social media and mental health. 2. Identify key themes and findings on a particular position. 3. Develop a thesis statement. 4. Outline the paper. 5. Write the introduction. 6. Write the body sections. 7. Write the conclusion. 8. Edit and revise the entire document to ensure all sections follow the thread of the original position.”
Activity: Generating Lesson Plans
Goal: Create a comprehensive lesson plan on photosynthesis for a high school biology class. Include objectives, materials needed, activities, and assessment methods.
Example: “Create a lesson plan for a high school biology class on photosynthesis. Include objectives, materials needed, activities, and assessment methods.”
See Section 4 for more details on generating lesson plans.
Activity: Creating Study Guides
Goal: Develop comprehensive study guides for final exams. Create a study guide for the final exam in a course, covering the main topics and key concepts.
Example: “Create a study guide for the final exam in a course, covering the main topics and key concepts, using the course learning outcomes as a reference.”
Activity: Crafting Discussion Questions
Goal: Develop five thought-provoking discussion questions for a college-level course on the ethics of artificial intelligence.
Example: “Generate five discussion questions for a college-level course on the ethics of artificial intelligence. Make the questions simply worded and plainspoken, requiring scaffolded and increasingly complex critical thinking.”
Activity: Enhancing Writing
Goal: Improve the clarity and coherence of the following paragraph: [insert paragraph].
Example: “Improve the clarity and coherence of the following paragraph: [insert paragraph].”
Activity: Summarizing Research Articles
Goal: Obtain a summary and key points about research.
Example: “Summarize the key findings of a provided research article in a plainspoken way in 200 words, noting strengths and limitations of the research.”
Try This! More Copilot Prompting Activities
Use prompting resources and Copilot to practice prompting. What ideas might be helpful for you?
Exploring Copilot Prompts
Visit the Copilot Lab: Prompts to Try. Scroll through the “Prompts to Try.” Find a prompt to practice with. Select the prompt. Select the Copy button, then paste it to Copilot. Follow the ” Make it Your Own” instructions to experiment and take the prompt to the next level. Bookmark prompts that you find useful.
Teach Me to Prompt
Use this “reverse prompting” prompt to be guided through a learning exercise about prompting using Copilot. Copy this prompt into Copilot and follow the prompts.
“You are an expert in AI prompting. I would like to have an interactive lesson in lesson prompting. Please give me a suggestion for improving my prompting technique, then ask me first a closed question based on that suggestion and second an example of the technique. Do not proceed until I have answered the question. If I give the incorrect answer, please correct me or give me further guidance with examples. All the questions should be related to teaching and learning in higher education. Once you have given me lessons and corresponding practice questions, conclude with a summary of what I learned, where my strengths were, and how I can practice further.”
Learn More
Students can learn more about prompting at the Generative AI Toolkit for Students.
