Pre-Simulation
The virtual simulation-based scenario provides undergraduate nursing students with an opportunity to apply theoretical knowledge to an unfolding case study with a post-mastectomy patient. Students gain new knowledge and apply their learning in the areas of wound assessment, drainage care, and relational practice. Questions will be presented for learners to answer along with opportunities to problem solve when situations are presented that require further action.
To Prepare
To prepare for this community home visit simulation on wound care, drainage care, infection assessment, removal of a Jackson Pratt (JP) drainage device and the development of relational practice skills read the following references:
- Jarvis, C. (2019). Breast and Regional Lymphatic System. In A. Browne, J. Macdonald-Jenkins, & M. Luctkar-Flude. Physical Examination & Health Assessment (3rd Canadian ed.). (pp. 418-446). Elsevier.
- Potter, P., Perry, A., Stockert, P., & Hall, A.(2019). In B. Astle & W. Duggleby (Eds.) Canadian Fundamentals of Nursing (6th ed.). Elsevier.
- Communication and Relational Practice (pp. 272)
- Infection Control: Hand Hygiene (pp. 701-706) and Performing Sterile Procedure (pp. 713-720)
- Care of Surgical Patients (pp. 1363)
- Skin Integrity and Wound Care: Character of Wound Drainage (pp. 1306-1307) and Drains (pp. 1328-1329)
- Self-Concept (pp. 460-472)
- Cobbett, S., Perry, A., Potter, P., & Ostendorf, W. (2018). Managing Wound Drainage Evacuation. In N. Laplante (Ed.). Canadian Clinical Nursing Skills + Techniques. Elsevier.
- Managing Wound Drainage Evacuation (pp. 1063-1067)
- Freysteinson, W., Deutsch, A., Lewis, C., Sisk, A., Quest, L., & Cesario, S. (2012). The experience of viewing oneself in the mirror after a mastectomy. Oncology Nursing Forum, 39, 361-369. DOI: 10.1188/12.ONF.361-369
- Freysteinson, W. (2020). Demystifying the mirror taboo: A neurocognitive model of viewing self in the mirror. Nursing Inquiry, 27, 1-9. DOI: 10.1111/nin.12351
- Knowlton, M. (2015). Nurse’s guide to surgical drain removal. Nursing, 45, 59-61. DOI: 10.1097/01.NURSE.0000470418.02063.ca.
Jackson Pratt (JP) Drains
Jackson Pratt (JP) drains are an example of a closed-drain system. These drains use a vacuum to create suction in order to remove accumulated drainage from around a wound bed into a collection device. Drains are used when a large amount of drainage is expected and to help facilitate healing. If fluid accumulates in a wound bed, the wound healing is delayed and can become infected. JP drains can be used after breast, abdominal, or other general surgeries.
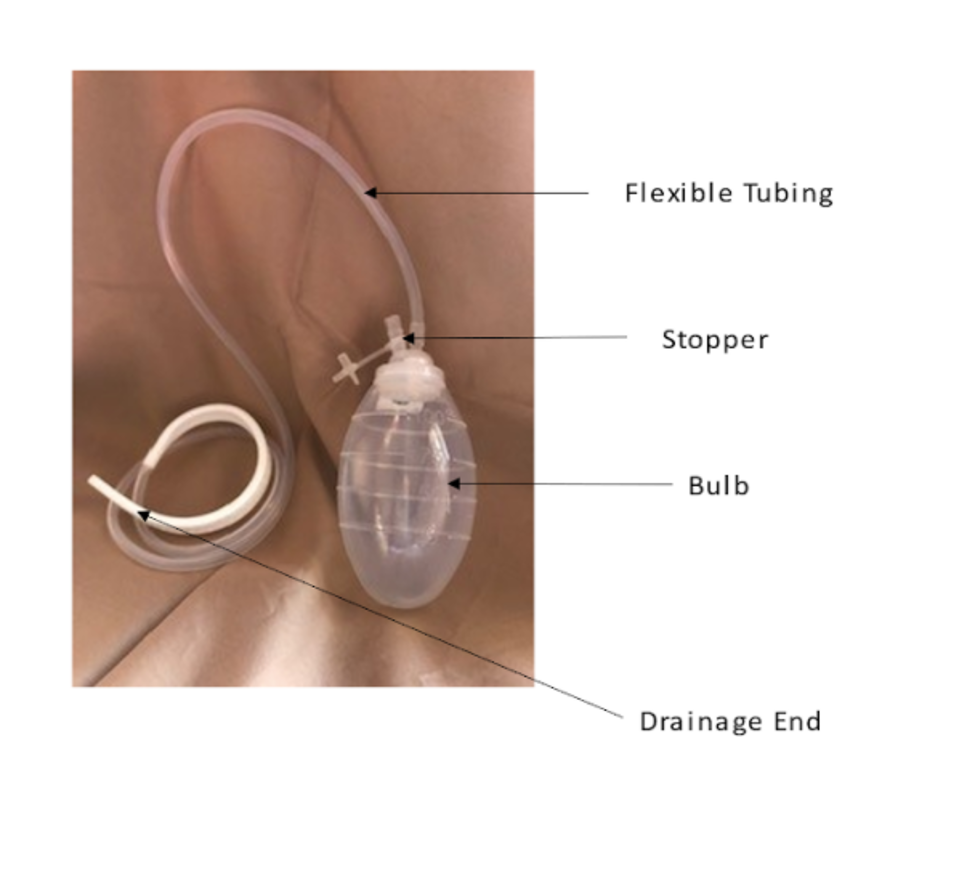
The drainage end is inserted through an incision near the suture line into the area of the wound. The flexible tubing is what the fluid uses to drain from the wound into the bulb. The bulb collects the drainage and must remain below the wound in order for the fluid to accumulate within it. The stopper breaks the vacuum which allows the discard of fluid that has accumulated in the bulb (Potter et al., 2019).
Nursing Process
Each chapter in the community home visit simulation will incorporate the nursing process.
The Nursing Process guides all nursing care. There are 5 steps: assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. Diagnosis will not be discussed in this simulation.
Assessement
Assessment is the first step, it involves data collection, such as subjective data (verbal comments from the patient), objective data (measurable data), and critical thinking skills. Health records help obtain data for assessment practices (Toney-Bulter & Thayer, 2021)
Planning
Step 2 of the nursing process is planning which incorporates goals and outcomes for the patient. The plan sets direction and interventions to obtain positive outcomes (Toney-Bulter & Thayer, 2021).
Implementation
The implementation of the nursing process involves action to carry out the direction and interventions set in the planning step. Some examples of implementation are the application of equipment, treatments, and administration of medications (Toney-Bulter & Thayer, 2021).
Evaluation
The evaluation of the nursing process involves reassessment of the plan and implementation to ensure the outcomes have been met (Toney-Bulter & Thayer, 2021).

