1 DNA, RNA and Protein
This chapter will review the structure and function of DNA, RNA and proteins.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to
- Identify the structure of DNA.
- Differentiate DNA and RNA molecules.
- Categorize the types of RNA molecules.
- Identify the levels of a protein structure.
- Categorize membrane proteins.
DNA
If you think of DNA, you are most likely reminded of its structure as a double helix molecule that acts as the cell’s genetic blueprint. But can you recall the specific components that make up this biomolecule?
Complete the following interactive to review your understanding of the structure of DNA.
Learning Tip! Try thinking about the differences before you click to see the answer!
Adapted from “Molecular Structure of DNA”, by BioRender.com (2024).
Great job! Now, you should be able to recall the structure of DNA, which will help you as we move on to assess the structure of RNA in comparison with DNA.
In Review
DNA is composed of a series of nucleotides. A single nucleotide comprises three components: a nitrogen-containing base, a five-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group. The nitrogenous base is either a purine or a pyrimidine.
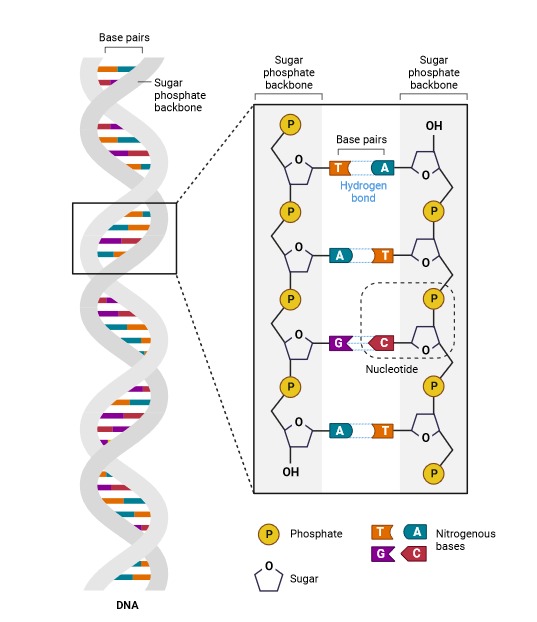
RNA
RNA, ribonucleic acid, is also a nucleic acid and is important in transmitting genetic information in living organisms.
Before we look at the possibilities of RNA in the cell, let’s begin with a review of DNA and RNA.
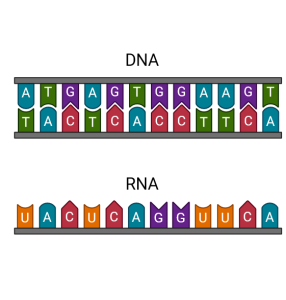
Complete the following interactive to review this comparison further. Click each title to reveal the comparison between DNA and RNA.
Learning Tip! Try thinking about the differences before you click the reveal button!
RNA’s main function is protein synthesis through translation, where genetic information is carried and translated into essential proteins by ribosomes.
The three main types of RNA that are involved in this process are
- mRNA
- rRNA
- tRNA
RNA can also function as the genetic material for viruses and plays roles in RNA editing, gene regulation, and RNA interference. Small regulatory RNAs, such as small nuclear RNA, microRNA, and small interfering RNA (siRNA), are involved in these processes.
Complete the following interactive to test your understanding of the types of RNA.
Adapted from “Types of RNA Produced in Cells”, by BioRender.com (2024).
Proteins
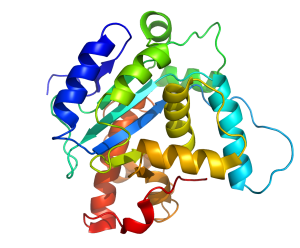
Now, we will review the structure and function of proteins. First, we will start by reviewing the levels of protein structure. Complete the following interactive to test your understanding.
As a result of the diverse structure that proteins can take on, they can perform and participate in various functions and roles in the eukaryotic cell. These roles can include some of the following.
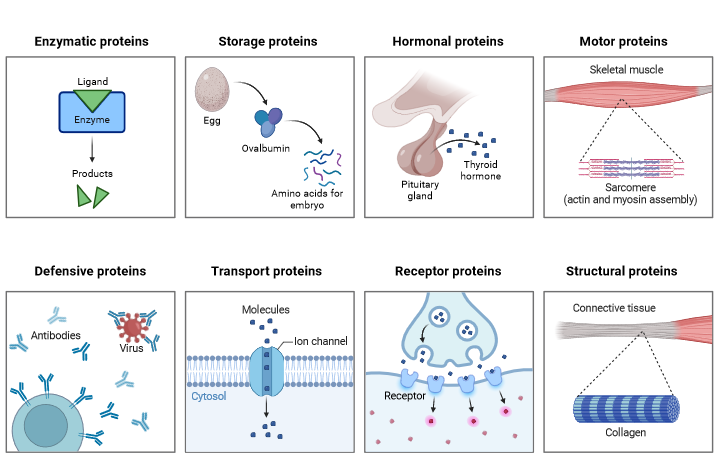
Proteins can be broadly classified into three categories based on their structure:
- fibrous proteins
- globular proteins
- membrane proteins
In our review, we will take a closer look at membrane proteins.
Membrane Proteins
Membrane proteins can consist of integral and peripheral membrane proteins.
Integral membrane proteins are transmembrane proteins that span the membrane more than once.
- These can be further classified into lipid-linked and transmembrane membrane proteins.
Peripheral membrane proteins are associated either with the lipid bilayer or integral proteins by various interactions.
Here, we will review membrane proteins. Complete the following interactive activity to identify the types of membrane proteins.
Learning tip! Be sure to think about it before you click to see the answer!
Adapted from “Membrane Proteins”, by BioRender.com (2024).

