2 Eukaryotic Transcription
In this chapter, we will review several aspects of eukaryotic transcription, including the overall transcription process, the preinitiation complex assembly and the splicing mechanism.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to
- Describe the central dogma.
- Relate the steps involved in the formation of the preinitiation complex.
- Connect the steps involved in the assembly of the splicing machinery.
Transcription
Transcription is how genetic information encoded in DNA is copied into mRNA molecules by the enzyme RNA polymerase. This mRNA serves as a template for protein synthesis during the process of translation, ultimately leading to the production of specific proteins encoded by the DNA sequence.
Central Dogma
Before we get into reviewing transcription, we will start with a brief review of the central dogma. Thinking back, can you recall the Central Dogma and its description?
Complete the following drag-and-drop interactive as a review.
Forming of Preintitation Complex
Now, we will look at the transcription process and begin with forming the preinitiation complex. First, it is important to understand the ‘players’ involved in this assembly. Review the following image before moving on.
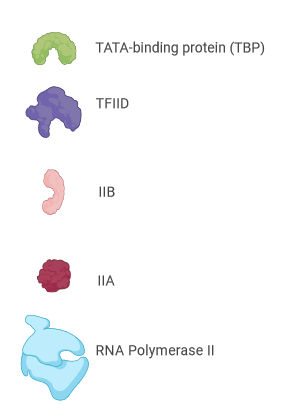
Now that we are familiar with the key components in this assembly let’s look at how this assembly forms and in what order. Complete the following interactive to explore this important initial step in transcription.
Flip each card to reveal the details of each step.
Learning tip! Try to think of each step before you flip the card over!
Stages of Transcription
Complete the following interactive to recall the three stages in transcription.
Assembly of the Splicing Machinery
Once the transcript has been synthesized as a pre-mRNA molecule, it undergoes several modifications.
These modifications include:
- 5’ end capping
- Splicing
- 3’ end formation
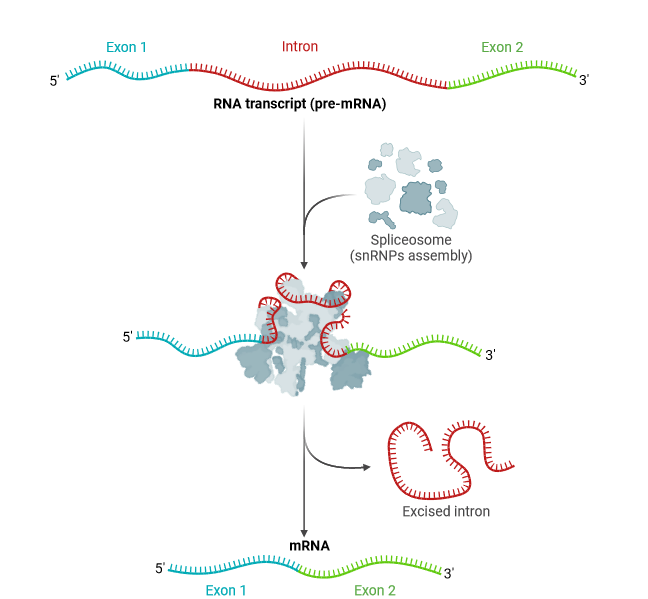
Summary of pre-mRNA splicing. Reprinted from “Spliceosome Complex”, by BioRender.com (2024).
We will now take a closer look at one of these processing events – splicing.
Pre-mRNA Splicing
Pre-mRNA splicing is the process by which the non-coding regions, introns, are removed, and the coding regions, exons, are joined together to form mature mRNA molecules in eukaryotic cells.
In Review
- Pre-mRNA transcript contains exons and introns
- Assembly of splicesome assembly
- Excises introns leading to a mature mRNA transcript

Complete the following interactive to review your understanding of the details of the steps involved in assembling the splicing machinery.
Learning Tip! Before clicking next, see if you can think of the next step yourself!
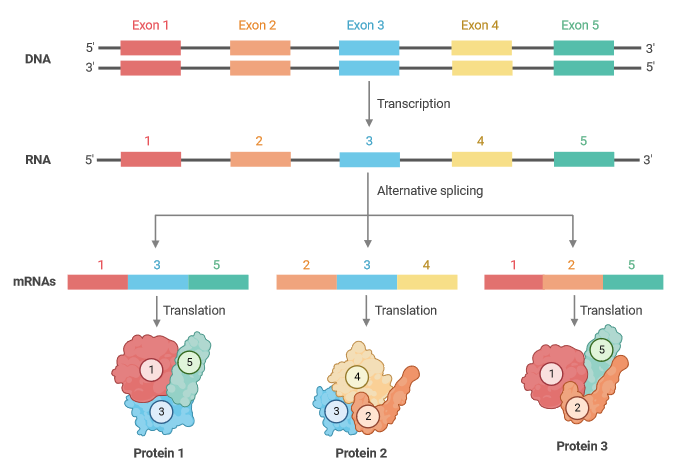
The final result of splicing can vary, leading to variations in the final protein arising from one original pre-mRNA transcript. The following example demonstrates how one transcript can lead to three distinct proteins. These may or may not be functionally and structurally related.