5 Gene Expression
In this chapter, we will review several approaches the cell takes to control gene expression.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to
- Identify the overall approaches the cell takes to regulate transcription.
- Describe the role of transcription factors in regulating the rate of transcription.
- Compare functional roles of RNA editing.
- Describe the approaches taken in translational control.
Regulation of gene expression can occur at multiple levels in the cell.
- Transcriptional control – control of mRNA transcripts
- Processing control – control of the processing of mRNA transcripts
- Translational control – control of the translation of a particular transcript
- Post-translational control – regulation of activity and stability of polypeptides
Transcriptional Control
We will begin reviewing the regulation of gene expression by reviewing transcriptional control. The following interactive demonstrates the varying approaches that can be observed in regulating transcription in the eukaryotic cell.
Adapted from “Regulation of Transcription in Eukaryotic Cells”, by BioRender.com (2024).
Transcription Factors
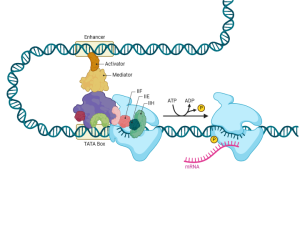
The first approach we will review is how the cell utilizes transcription factors and associated complexes to turn ‘on’ and ‘off’ certain genes at specific times and to certain amounts in the cell.
Adapted from “DNA Looping in Transcriptional Regulation”, by BioRender.com (2024).
Let’s review some of the key terms we just saw in the previous interactive.
In Review
The regulation of transcriptional initiation can involve many factors, as shown in the following illustration. These can collectively influence gene expression.
Histone-DNA Interactions
In our second example of transcriptional control, we will look at the type of interactions between histones and DNA. As we saw previously, the ability to access genetic regions is greatly influenced by the state of the histones. Before you complete the following interactive review, can you think of the types of disruptions that can occur in relation to the histone–DNA interactions?
Learning tip! Be sure to hover over the image to learn about each type of change in chromatin structure.
Adapted from “Epigenetic Levels”, by BioRender.com (2024).
Processing Control
The cell also undergoes several processing control mechanisms that serve to determine the path by which a primary mRNA transcript is processed into a mature mRNA that can translated into a polypeptide.
RNA Editing: alterations in the chemical structure of RNA molecules occurring after DNA transcription and synthesis by the RNA polymerase enzyme.
These can include two broad categories:
- insertion/deletion
- base modification
Now, we will review the types of functions of RNA editing. These functions can include influence:
- pre-mRNA splicing
- RNA stability
- mRNA translation
- miRNA regulation
Learning tip! Be sure to hover over the image to learn about each type of function.
Adapted from “Epigenetic Levels”, by BioRender.com (2024).
Translation Control
We will now review the regulation of gene expression through translational control. Translational control is a mechanism that determines whether a particular mRNA is actually translated and, if so, how often and for how long a period.
Complete the following interactive to review the possible approaches the cell can take to control translational levels.
Learning tip! Think about each type of control mechanism before you click the reveal.

