Chapter 2 Summary
Key Takeaways
- Modern Synthesis and Population Genetics: The modern synthesis combines Darwin’s theory of natural selection with Mendelian genetics. Evolution is understood as a change in allele frequencies in a population over time (microevolution). Variation in alleles arises through mutation and sexual reproduction, providing the raw material for natural selection to act upon.
- Hardy-Weinberg Principle: The Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium provides a mathematical model to study genetic stability in populations. In the absence of evolutionary forces, allele and genotype frequencies remain constant. The equation
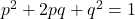 allows scientists to predict genotype frequencies and assess whether evolution is occurring.
allows scientists to predict genotype frequencies and assess whether evolution is occurring. - Biological Species Concept: A species is defined as a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. While useful for sexually reproducing organisms, this concept has limitations (e.g. for asexual species or fossils). Physical appearance alone does not always indicate species boundaries.
- Reproductive Isolation: Reproductive barriers prevent gene flow between species and are crucial for maintaining species boundaries. They include:
- Prezygotic barriers: temporal, habitat, behavioural, mechanical, and gametic isolation.
- Postzygotic barriers: hybrid inviability, hybrid sterility, hybrid breakdown.
- Types of Speciation: Speciation occurs when populations become reproductively isolated:
- Allopatric speciation: involves geographic separation (e.g., mountains, rivers).
- Sympatric speciation: happens without geographic separation, driven by behavioural, ecological, or genetic factors (e.g., habitat use within the same area).
- Rate of Speciation: Speciation can follow different temporal patterns:
- Gradualism: slow, continuous evolution over long periods.
- Punctuated equilibrium: rapid bursts of change followed by long periods of stability, often triggered by environmental shifts.
OpenAI. (2025). ChatGPT. [Large language model]. https://chat.openai.com/chat
Prompt: Summarize the following content into six key takeaways.
Flashcards
Text Description
Front of card:
- Allele
- Population genetics
- List two rates of speciation
- p
- List two types of speciation
- Zygote
- List 5 Prezygotic Barriers
- Habitat isolation
- Postzygotic barrier
- Gradualism
- 2pq
- Microevolution
- Prezygotic barrier
- Hardy-Weinberg principle of equilibrium
- p2
- Reproductive barriers
- q
- Mechanical isolation
- Biological species concept
- Genetic diversity
- Gametic isolation
- Modern synthesis
- Genotype
- Allele frequency
- Sexual reproduction
- Main sources of genetic diversity
- Reproductive isolation
- Blending inheritance
- Phenotype
- Hybrid inviability
- Allopatric speciation
- List 3 Postzygotic Barriers
- Gene pool
- Temporal isolation
- Speciation
- Mutation
- q2
- Punctuated equilibrium
- Behavioural isolation
- Hybrid sterility
- Sympatric speciation
- Hardy-Weinberg equation
- Hybrid breakdown
- Fertile
- Viable
Back of card:
- A version of a gene; different alleles can produce variations in the trait controlled by the gene
- A branch of biology that studies allele frequency changes in populations over time and the evolutionary forces that cause these changes
- gradualism and punctuated equilibrium
- frequency of the dominant allele, Y
- allopatric speciation and sympatric speciation
- The single cell formed when a sperm fertilizes an egg
- Temporal isolation, habitat isolation, behavioural isolation, mechanical isolation, gametic isolation
- A prezygotic reproductive barrier where species live in different habitats and thus do not meet to reproduce
- A reproductive barrier that occurs after fertilization, resulting in non-viable or sterile offspring
- A pattern of evolution characterized by the slow, continuous accumulation of small genetic changes over long periods of time
- frequency of individuals with the heterozygous genotype (Yy)
- Small-scale changes in allele frequencies within a population over time
- A reproductive barrier that prevents fertilization from occurring
- A principle stating that allele and genotype frequencies in a population will remain constant from generation to generation in the absence of evolutionary forces
- frequency of individuals with the homozygous dominant genotype (YY)
- Biological features or behaviours that prevent different species from interbreeding and producing fertile, viable offspring
- frequency of the recessive allele, y
- A prezygotic reproductive barrier where structural differences in reproductive organs prevent mating between species
- A definition of species stating that a species is a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile, viable offspring
- The total variety of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a population
- A prezygotic reproductive barrier where the sperm of one species cannot fertilize the egg of another species due to incompatibilities
- The integration of genetics with Darwin’s theory of natural selection forms a unified theory of evolution that explains how evolutionary processes affect genetic variation
- The genetic makeup of an organism determines the phenotype
- The proportion of a specific allele among all alleles of a gene in a population
- The process of combining genetic material from two parents to produce genetically unique offspring
- mutation and sexual reproduction
- A state in which two populations can no longer interbreed and produce fertile offspring, maintaining species boundaries
- An outdated theory of inheritance where offspring were thought to be a uniform blend of parental traits, making it difficult to understand how traits persist across generations
- The observable physical or physiological traits of an organism, determined by its genotype and environmental influences
- A postzygotic reproductive barrier where hybrid offspring fail to develop properly or die at an early stage
- The formation of new species due to geographic separation of populations, which prevents gene flow between them
- Hybrid inviability, hybrid sterility, hybrid breakdown
- The total set of alleles present in a population
- A prezygotic reproductive barrier where species reproduce at different times, preventing mating
- The evolutionary process by which populations evolve to become distinct species
- A change in DNA sequence that can introduce new genetic variation into a population
- frequency of individuals with the homozygous recessive genotype (yy)
- A pattern of evolution where species undergo rapid changes in short periods, followed by long periods of stability
- A prezygotic reproductive barrier where differences in behaviour, such as mating calls or courtship rituals, prevent mating between species
- A postzygotic reproductive barrier where hybrid offspring are healthy but sterile and cannot reproduce
- The formation of new species within a shared habitat, without geographic separation
- A postzygotic reproductive barrier where first-generation hybrids are fertile, but their offspring are weak, sterile, or less fit
- Able to produce offspring
- Capable of surviving; a viable offspring can grow, develop, and potentially reproduce
OpenAI. (2025). ChatGPT. [Large language model]. https://chat.openai.com/chat
Prompt: Provide definitions for all the bolded terms in the shared content and list all the terms in alphabetical order.

