2.2 Chemical Bonds
Electrons
How elements interact with one another depends on how their electrons are arranged and how many openings for electrons exist at the outermost region where electrons are present in an atom. Electrons exist at energy levels that form shells around the nucleus. The closest shell can hold up to two electrons. The closest shell to the nucleus is always filled first before any other shell can be filled. Hydrogen has one electron; therefore, only one spot is occupied within the lowest shell. Helium has two electrons; thus, it can fill the lowest shell with its two electrons. If you look at the periodic table (Figure 2.1.3), you will see that hydrogen and helium are the only two elements in the first row. This is because they only have electrons in their first shell. Hydrogen and helium are the only elements with the lowest shells and no other shells.
The second and third energy levels can hold up to eight electrons. For example, Nitrogen has an atomic number of 7. That means that it has 7 protons, so to remain neutral, it must also have 7 electrons. The first energy shell will hold 2 electrons. The second shell will hold the remaining 5 electrons.
Exercise 2.2.1
Build an atom yourself! Click on "Atom" in the activity below. Then, a nitrogen atom can be made by dragging the appropriate number of protons, neutrons, and electrons into the diagram. If you do it properly, you should end with a neutral atom with the proper mass number.
Answer
Your Nitrogen atom should have 7 protons, 7 neutrons, and 7 electrons.
The outermost shell is called the valence shell. An atom is most stable when all of the electron positions in the valence shell are filled. The valence number of an element is the number of electrons required to fill the valence shell. In the case of Nitrogen, it has 5 electrons in the outermost shell, so we would say that it has 5 valence electrons. Since the second shell can hold a maximum of 8 electrons, it means that there are 3 openings that can be filled, meaning a valence number of 3.
These vacancies in the valence shells get filled by sharing electrons, accepting electrons from another atom, or donating electrons to another atom. These interactions between atoms that hold them together are called chemical bonds.
Because the valence shells of the elements with low atomic numbers (up to calcium, with atomic number 20) can hold eight electrons, this is called the octet rule. An atom can donate, accept, or share electrons with other elements to fill its valence shell and satisfy the octet rule.
Types of Chemical Bonds
There are three main types of bonds: ionic, covalent, and hydrogen.
Ionic Bonds
An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond formed through the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions. This occurs when one atom transfers one or more of its electrons to another atom, resulting in the formation of ions.
An ion is an atom that has lost or gained one or more electrons, resulting in a net electrical charge. Positive ions are formed by losing electrons and are called cations. Negative ions are formed by gaining electrons and are called anions.
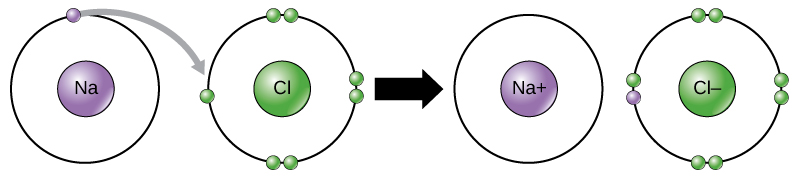
For example, sodium only has one electron in its outermost shell. It takes less energy for sodium to donate that one electron than to accept seven more electrons to fill the outer shell. If sodium loses an electron, it has 11 protons and only 10 electrons, leaving it with an overall charge of +1. It is now called a sodium ion. The chlorine atom has seven electrons in its outer shell. Again, it is more energy-efficient for chlorine to gain one electron than to lose seven. Therefore, it tends to gain an electron to create an ion with 17 protons and 18 electrons, giving it a net negative (–1) charge. It is now called a chloride ion.
This movement of electrons from one element to another is referred to as electron transfer. Both ions now satisfy the octet rule and have complete outermost shells. Because the number of electrons is no longer equal to the number of protons, each is now an ion and has a +1 (sodium) or –1 (chloride) charge.
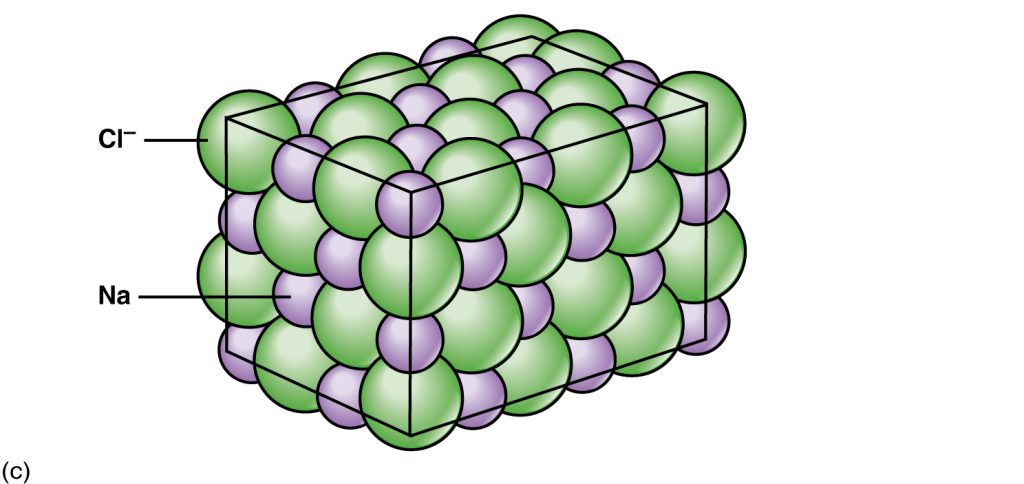
These ions stay together because positive and negative charges attract, creating an ionic bond between ions. When Na+ and Cl– ions combine to produce NaCl, an electron from a sodium atom stays with the other seven from the chlorine atom, and the sodium and chloride ions attract each other in a network of ions with a net zero charge.
Covalent Bonds
A covalent bond is another chemical bond between two or more atoms. These bonds form when a pair of electrons is shared between two elements. They are the strongest and most common chemical bonds in living organisms. Covalent bonds form between the elements that make up the biological molecules in our cells. Unlike ionic bonds, covalent bonds do not dissociate in water.
A group of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds is called a molecule. For example, covalent bonds combine the hydrogen and oxygen atoms together to form water molecules. Two electrons from two hydrogen atoms are needed to fill the outer shell of an oxygen atom, hence the subscript “2” in H2O. The electrons are shared between the atoms, dividing their time between them to “fill” the outer shell of each.
There are two types of covalent bonds: polar and nonpolar. Nonpolar covalent bonds form between two atoms of the same element or between different elements that share the electrons equally. For example, an oxygen atom can bond with another oxygen atom to fill its outer shell. This association is nonpolar because the electrons will be equally distributed between each oxygen atom. Two covalent bonds (double bond) form between the two oxygen atoms because oxygen requires two shared electrons to fill its outermost shell. Nitrogen atoms will form three covalent bonds (triple covalent) between two nitrogen atoms because each nitrogen atom needs three electrons to fill its outermost shell. Another example of a nonpolar covalent bond is found in the methane (CH4) molecule. The carbon atom has four electrons in its outermost shell and needs four more to fill it. It gets these four from four hydrogen atoms, each atom providing one. These elements all share the electrons equally, creating four nonpolar covalent bonds.
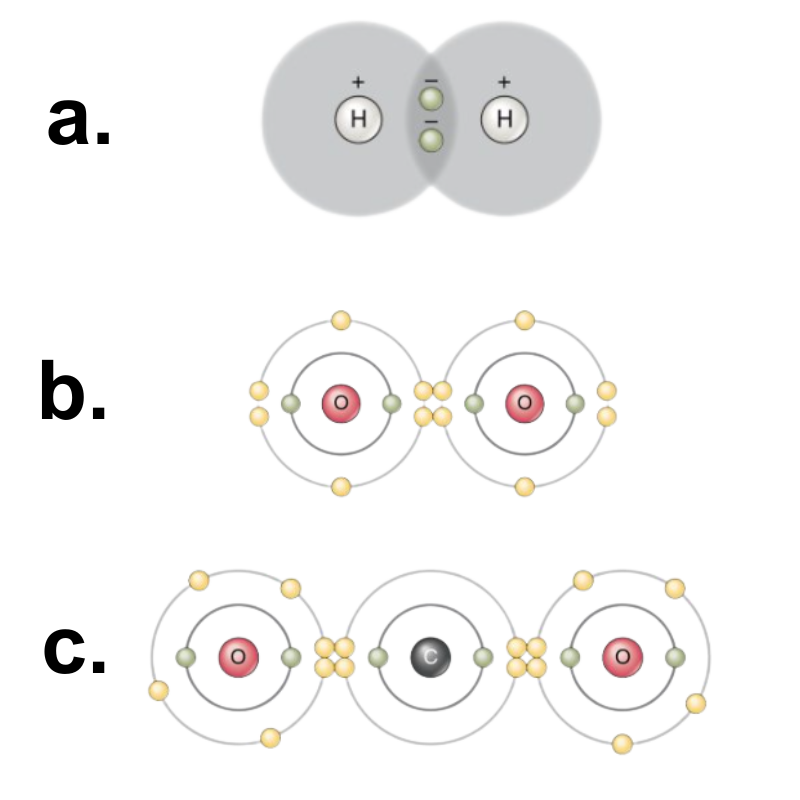
(O=O). c. Two double covalent bonds: carbon dioxide (O=C=O). Image by OpenStax, CC-BY 4.0. Mods: Removed text; increased letters.
In a polar covalent bond, the electrons shared by the atoms spend more time closer to one nucleus than to the other nucleus. Because of the unequal distribution of electrons between the different nuclei, a slightly positive (δ+) or slightly negative (δ–) charge develops. The covalent bonds between water hydrogen and oxygen atoms are polar. The shared electrons spend more time near the oxygen nucleus, giving it a slight negative charge, than the hydrogen nuclei, giving these molecules a slight positive charge.
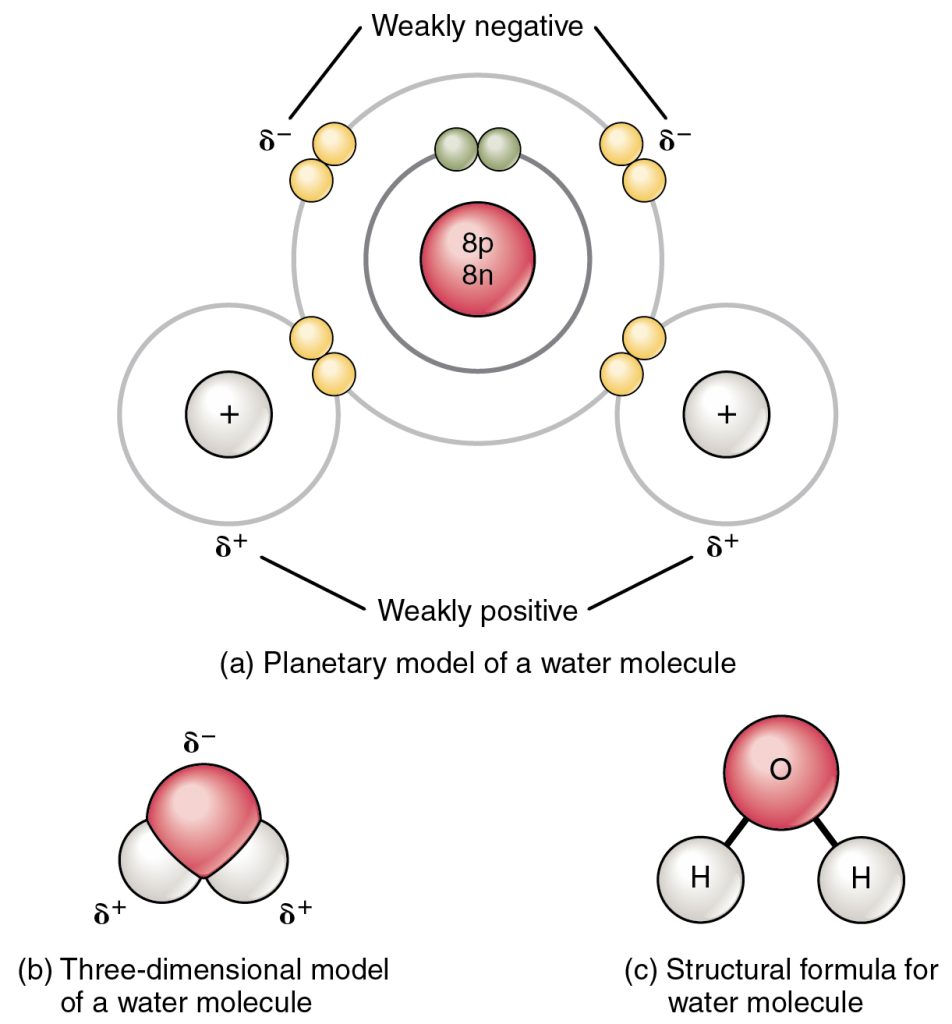
Hydrogen Bonds
Hydrogen bonds are weak electrical attractions between neighbouring polar molecules. When polar covalent bonds containing a hydrogen atom form, the hydrogen atom in that bond has a slightly positive charge because the shared electron is pulled more strongly toward the other element and away from the hydrogen nucleus. Because the hydrogen atom is somewhat positive (δ+), it will attract neighbouring negative partial charges (δ–). When this happens, a weak interaction occurs between the δ+ charge of the hydrogen atom of one molecule and the δ– charge of the other molecule. This interaction is called a hydrogen bond. This type of bond is common; for example, the liquid nature of water is caused by the hydrogen bonds between water molecules. Hydrogen bonds give water the unique properties that sustain life. If not for hydrogen bonding, water would be a gas rather than a liquid at room temperature.
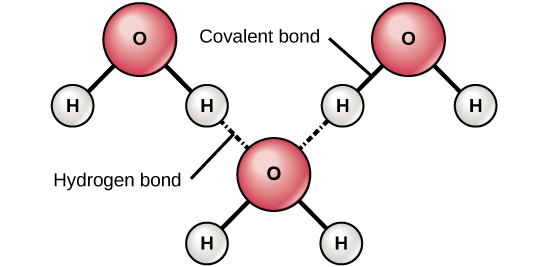
Hydrogen bonds can form between different molecules and do not always have to include a water molecule. Hydrogen atoms in polar bonds within any molecule can form bonds with other adjacent molecules. For example, hydrogen bonds hold two long strands of DNA together to give the DNA molecule its characteristic double-stranded structure. Hydrogen bonds are also responsible for some of the three-dimensional structure of proteins.
Exercise 2.2.2
Molecules and compounds are not the same thing!
Covalent bonds join the atoms in molecules. Compounds contain two different atoms joined by either covalent or ionic bonds. Molecular oxygen (O2) is a molecule containing two of the same atoms joined by nonpolar covalent bonds. However, O2 is not a compound because it contains only one type of atom. Water (H2O) is both a molecule and a compound because covalent bonds join the atoms in water and contain two different atoms: O and H.
Text Description
Options: Inert, Reactive, 0, 5, 5, 3, 8, 10
- Hydrogen bonds allow water to change temperature rapidly
- Hydrogen bonds occur within (inside of) molecules, not between molecules
- Hydrogen bonds occur between hydrogens and the atoms they share electrons with
- Hydrogen bonds form between hydrogens
- Hydrogen bonds occur between molecules, not within (inside of) molecules
- One more electron than protons
- One more proton than neutrons
- One more neutron than electrons
- One more proton than electrons
- One more neutron than protons
- Polar covalent bonds
- Hydrogen bonds
- Covalent bonds
- Molecular bonds
- Polar ionic bonds
- Isotopes; protons
- Atoms; orbitals
- Isotopes; neutrons
- Ions; electrons
- Electrons; protons
- Atomic
- Electronic
- Hydrogen
- Covalent
- Ionic
Neon - inert, valence number = 0, valence electrons = 8, atomic number = 10
"2.1 The Building Blocks of Molecules" from Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian Edition by Jane Gair is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted.

