7 Medical Reports
Since patient medical reports are created and used by many different people within the patient’s circle of care, these reports must be absolutely clear and unambiguous.
For this reason, standards for formatting medical reports have been created.
There are different types of medical reports, each used for a different purpose.
Examples of Types of Medical Reports
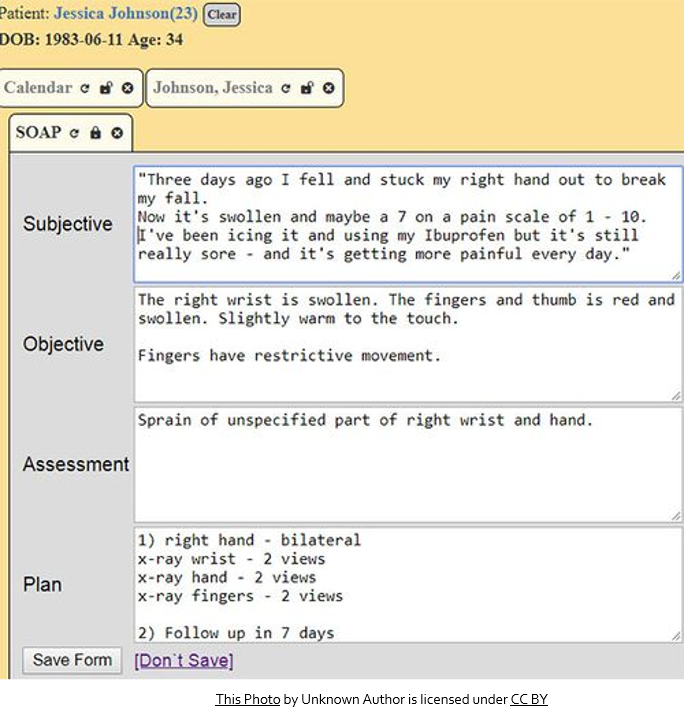
SOAP Notes
SOAP is an acronym for the 4 headings commonly found in this type of report:
SUBJECTIVE: What the patient is experiencing and what they report to the doctor.
OBJECTIVE: Information the doctor finds out through observation (examining the patient or running tests).
ASSESSMENT: sometimes called ‘Impression,’ it is the most likely diagnosis of the problem.
PLAN: what the doctor intends to do about the problem, including further testing to verify the diagnosis.
Did you get it?
Formatting Reports
Use Arial size 12 font.
Use regular margins (1″ or 2.5 cm”) on all sides.
Single space within a paragraph. Double space between sections/paragraphs.
All headings and subheadings: ALL CAPS followed by a colon (:) and 2 spaces before the section text.
- If some headings have been omitted from the dictation, add them in. If there are no headings dictated at all, you do not need to add them. Some dictators do not use headings.
Begin by creating your footer
Opening of a report contains:
- Patient’s name (LASTNAME, Firstname)
- Their medical record number (MR# or MRN)
Example
PATIENT NAME: SURNAME (all caps), Firstname
MR#: 12345 (see eConestoga for actual number)
Closing of a report contains:
- Signature line
- Dictating physician’s name
- Dictating physician’s initials/transcriptionist’s initials
- Date dictated (usually unknown)
- Date transcribed (the day you are working on the report)
Example
Quadruple space before signature line
_______________________ (signature line)
Julia M. Waters, MD (dictator’s name. If unknown, use Xxxx Xxxx, MD)
JMW/ed (dictator’s initials in all caps or XX, if unknown/your initials lowercase)
D: xx/xx/20xx (date that the textbook reports were dictated is unknown)
T: dd/mm/yyyy (date that you are transcribing the report)
If your report goes onto a second page:
Type ‘continued’ on the last line of page 1, and follow these page break rules:
- Minimum of 2 lines of a paragraph at the bottom of a page.
- Minimum of 2 lines of a paragraph at the top of a page.
- Do NOT place a paragraph heading on the bottom of a page and its accompanying text on the next page.
- Do NOT place the closing and signature lines on a page by themselves.
- Do NOT hyphenate words between pages.
Example
PATIENT NAME: SURNAME (ALL CAPS), Firstname
MR#: 12345
DATE:
Page 2
Formatting the Physical Examination Section
Here is an example of correct formatting for the physical examination section of a report:
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: VITAL SIGNS: Temperature 98.1, pulse 72, respiratory rate 19, and weight 180 pounds. GENERAL: The patient is a well-nourished male in no apparent distress, who is cooperative with the exam. HEENT: No abnormalities. NECK: No masses or lymphadenopathy. LUNGS: Mild crackles heard at both bases. HEART: Regular rate and rhythm. No gallops, murmurs or rubs. ABDOMEN: Soft and nontender. EXTREMITIES: Minimal bilateral edema. NEUROLOGIC: The patient is grossly intact.
Physical Examination Techniques
Please watch this short video to learn how a physical exam is performed.
Physical Examination Techniques
Try this quiz
Also called office note or clinic note, this type of report details a patient's visit with their physician or a clinic.
An acronym is a word made from the first letter of each word of a phrase. The acronym is used to remember the phrase and also to shorten it when using it. Example: PHIPA (Personal Health Information Protection Act).



Feedback/Errata