6.3 GenAI to Support Learning
What is Scaffolding?
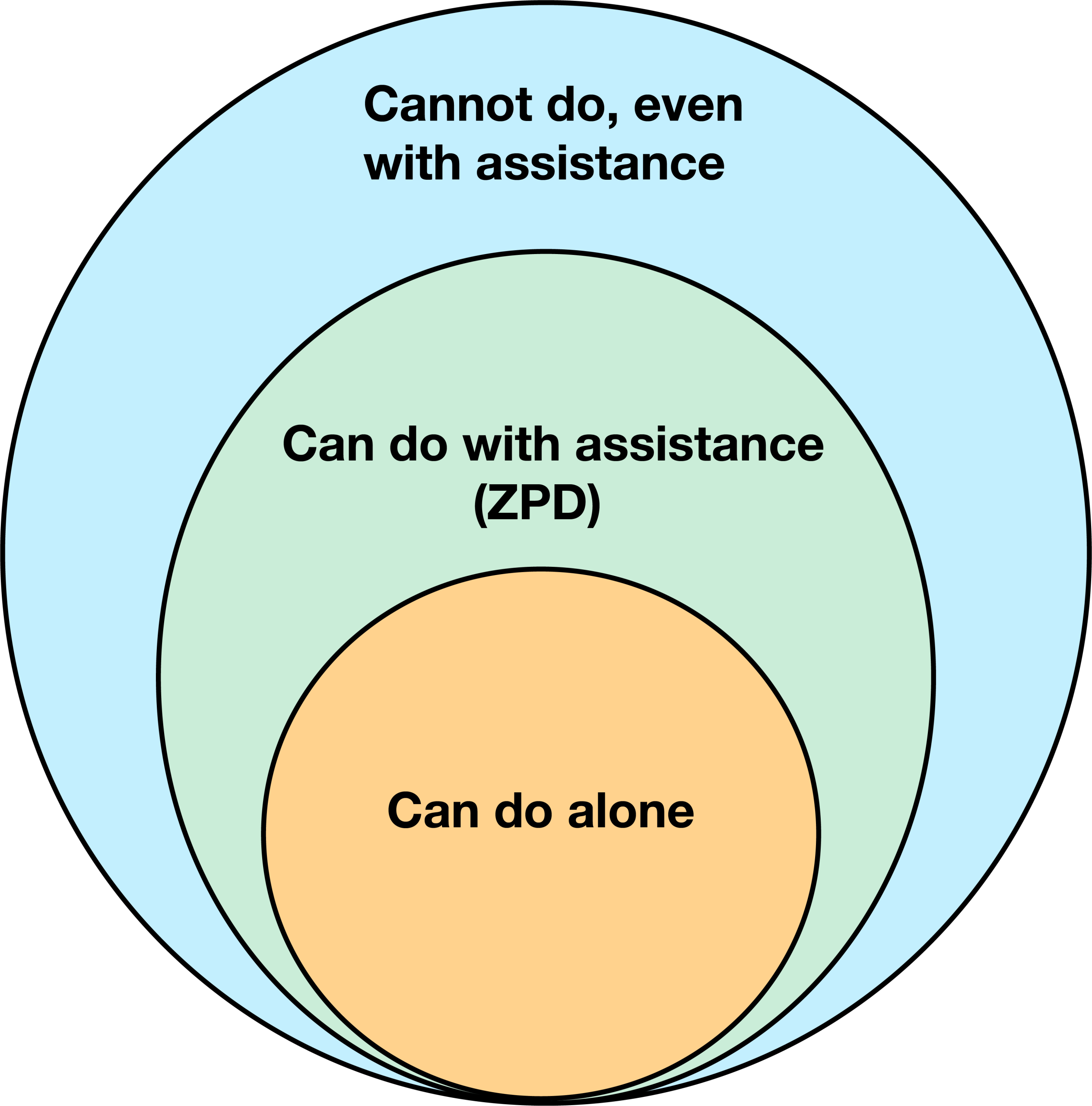
Scaffolding works by initially providing support for learners on tasks that they may not be able to complete without assistance. These supports are then removed as students gain higher proficiency levels.
The concept of scaffolding grew out of Vygotsky’s work on the Zone of Proximal Development, an area of learning where students don’t yet have the skills to independently demonstrate a learning outcome but can learn to do so by building on their prior skills and knowledge with the guidance and support of others (TMU, 2021).
Traditionally, ‘assistance’ has meant other people, like learners, teaching assistants, or even peers, but generative AI could also help provide this assistance. The next part of this section will outline some ways in which instructors can use generative AI to help scaffold learning.
For example:
- Create unity of effect in a short story through the application of literary devices such as irony, symbolism, metaphor, allegory, and other figurative language.*
Generative AI could be a useful tool for helping students develop a deeper understanding of each of these literary devices, allowing them to then apply these to their own writing.
- Analyse examples of digital learning environments or scenarios and identify which educational theories are inherent in each example.
Generative AI could help explain each theory to the students, allowing them to develop a deeper understanding of the theories that they could then apply to each of the specific examples provided.
*This Learning Outcome was generated with the help of ChatGPT.
Oregon State University published an updated version of Bloom’s Taxonomy ![]() that distinguishes between Distinctive Human Skills and how generative AI can supplement learning. This can be a helpful tool for understanding the ways in which generative AI can support learning.
that distinguishes between Distinctive Human Skills and how generative AI can supplement learning. This can be a helpful tool for understanding the ways in which generative AI can support learning.
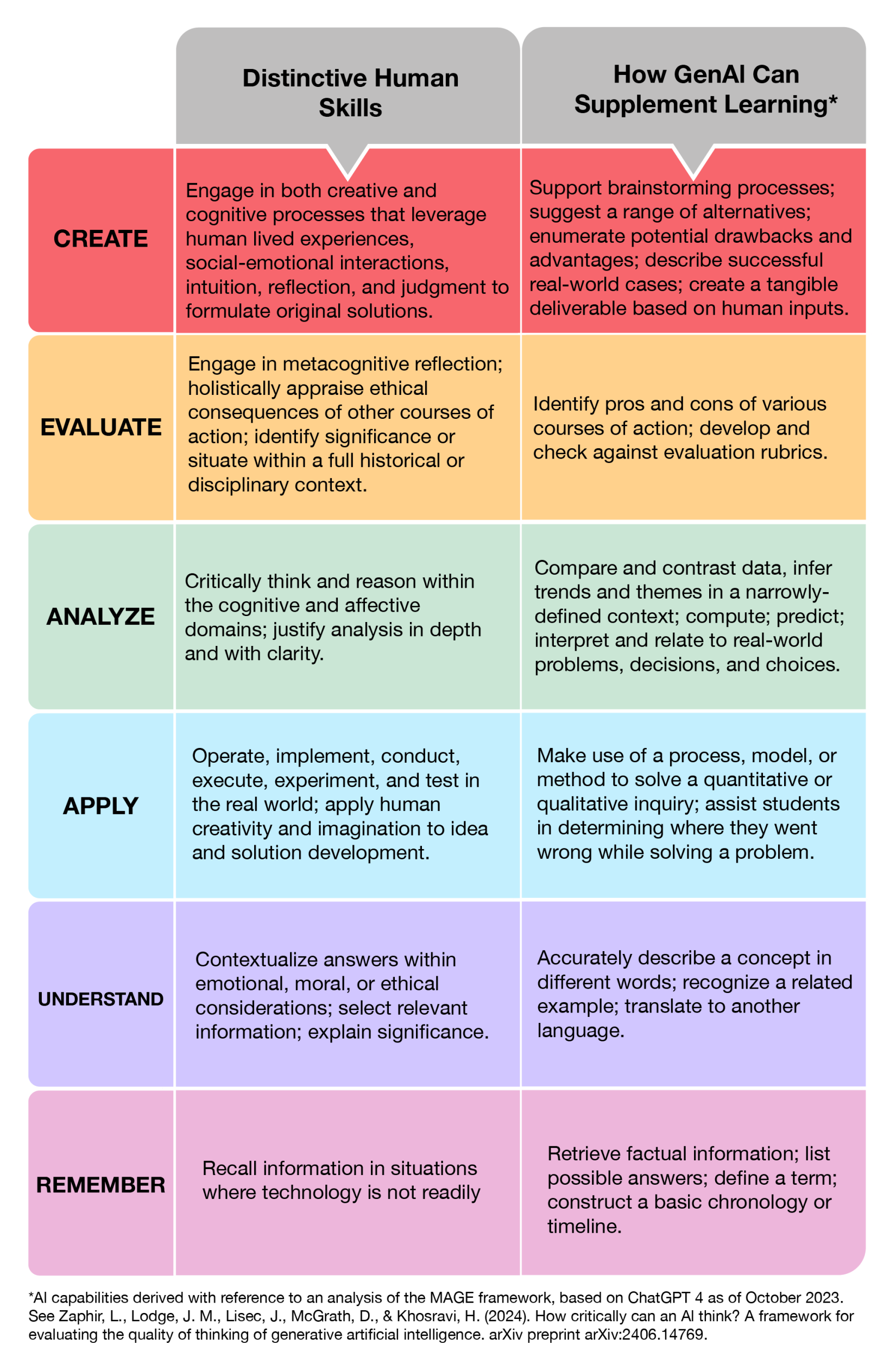
When considering the potential impact of generative AI on learning, it’s important to distinguish between ways in which generative AI tools can replace learning and ways in which generative AI can support learning. Consider the following examples:
Learning with AI
The follow chart provides a summary of some of the potential roles that AI could play to support learning, identifying both the benefits and the constraints or limitations of each.
| Role | Function | Benefits | Constraints |
| Mentor | Provide Feedback | Provides immediate feedback which can be focused. | Requires feedback literacy; feedback may contain errors |
| Tutor | Provide direct instruction | Provides personalised learning and can be instructed to level based on students’ understanding. | Possibility of incorrect or inaccurate information |
| Coach | Promote metacognition | Provides opportunites for reflection on learning process and progress | The tone or style of the AI may create an adverse emotional response; advice may be unsound or contradictory |
| Teammate | Support groupwork | Provide alternative perspectives; Improve team functioning | Overreliance on AI team member; reducing team functioning |
| Student | Provide opportunity for the student to explain a concept and get feedback on their explanation | Provide personalised support and encouragement | Difficult to check for accuracy of information |
| Simulator | Provide opportunities for deliberate practice | Can quickly generate authentic or pseudo-authentic simulations and examples for students to work through | May generate inappropriate or inaccurate simulations or examples; may provide biassed representation of certain roles |
| Rubber Duck | Provide a sounding board for ideation. | Can help learners think through a problem in judgement-free zone | May provide inappropriate or unhelpful responses; requires critical thinking from learner to assess value of responses |
(Adapted from Mollick & Mollick, 2023)
 Activity Prompting AI
Activity Prompting AI
Imagine you’re a learner. Using the generative AI tool of your choice, try out some of the prompting techniques shared by Mollick and Mollick ![]() to test how AI might support your learning. Customise the prompts to something you’re interested in learning or related to your discipline.
to test how AI might support your learning. Customise the prompts to something you’re interested in learning or related to your discipline.
Generative AI is a type of Artificial Intelligence that creates new content, including text, images, videos, audio, and computer code.



Feedback/Errata