6.2 Impact on Learning
Identifying the potential impact of generative AI on course learning outcomes
Some learning outcomes may be easily demonstrated through the use of generative AI tools, which may be undesirable if the student needs to master the learning outcome independently.
Alternatively, incorporating generative AI into an activity or assessment may increase a student’s ability to successfully achieve and demonstrate the outcome, potentially leading to higher level learning.
By thinking about how generative AI may impact learning and demonstrating each learning outcome, we can identify which assessments and learning activities may need to be redesigned so that the outcomes, learning activities, and assessments all align to support each other.
Generative AI Strengths and Limitations
To understand how each Learning Outcome may be impacted using generative AI, we need to recall what generative AI does well and its limitations. Below are some key strengths and limitations to consider in assessment and activity design. You can also revisit the sections on knowledge ![]() and skills
and skills ![]() for a more detailed discussion of how generative AI works.
for a more detailed discussion of how generative AI works.
Strengths
- Generative AI is particularly good at text-based tasks, including text generation, text processing, text manipulation and evaluation of texts.
- Generative AI is trained to recognize patterns so is well-suited to identifying or classifying data.
- Generative AI is also trained to replicate patterns so can generate well-structured facsimiles of common text types, such as outlines, reports, essays, or other.
- Generative AI models have been trained on massive datasets of information and are able to provide definitions, explain concepts, and generate examples with some accuracy.
Limitations
- Most generative AI models are not transparent, meaning they don’t share key details on how output was generated or what sources were used.
- Generative AI does not fact-check and some models have a knowledge cut-off date that may be months or years in the past, meaning that it can often generate inaccurate or outdated outputs.
- Generative AI lacks true human creativity and is trained to produce generic or average responses.
- Generative AI can struggle to contextualize information or respond to a specific real-world situation.
- Generative AI is not human and cannot generate true self-reflections or personal narratives but can mimic these skills.
Learning Outcomes
Bloom’s taxonomy is a helpful method for determining whether generative AI can “demonstrate” certain learning outcomes. (more information about learning outcomes and Bloom’s Taxonomy is available here ![]() ).
).
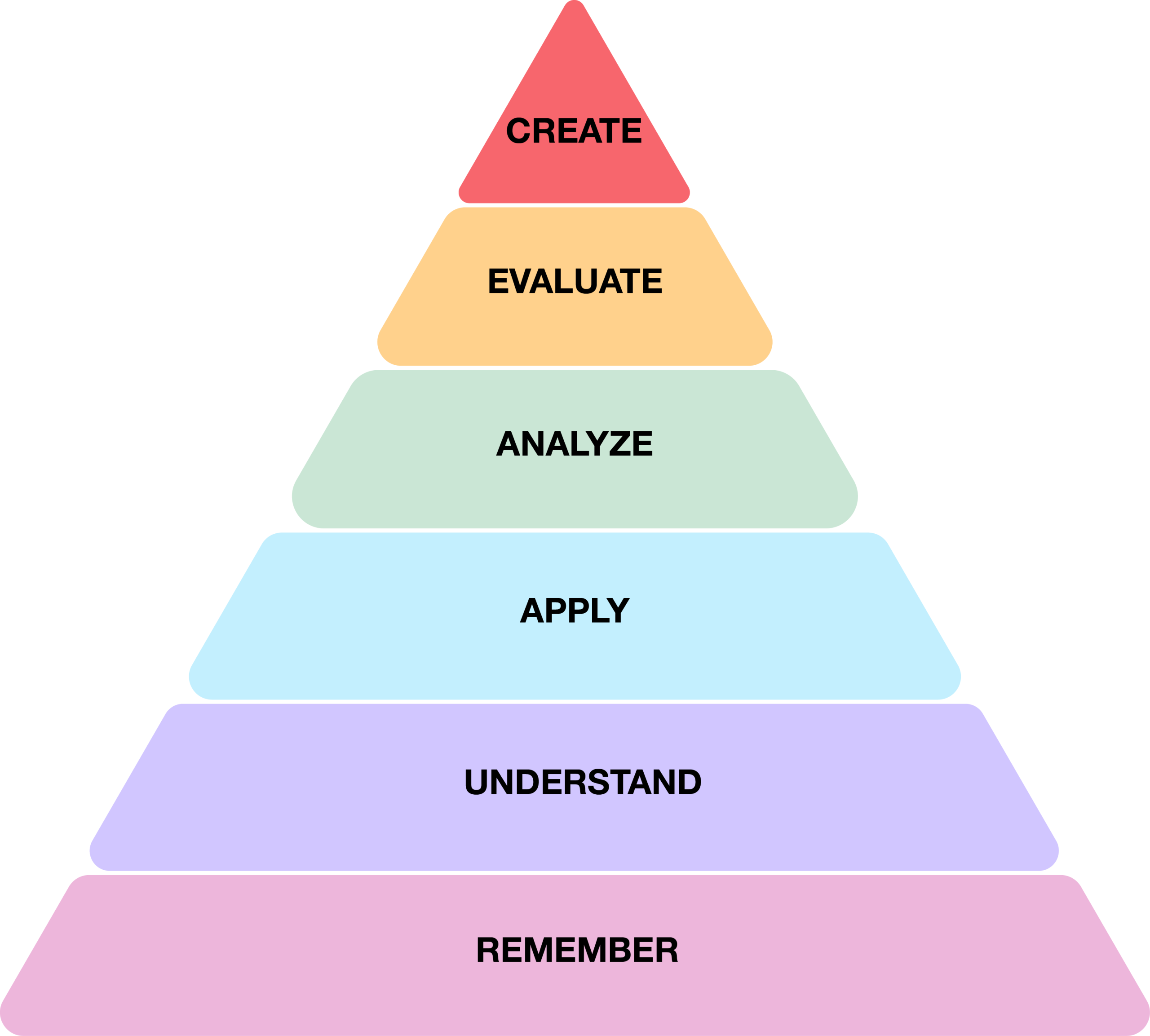
Generative AI tools are more likely to successfully demonstrate tasks on the lower levels of Bloom’s taxonomy because:
- Generative AI is particularly good at simple tasks of knowledge reproduction, description, or explanation. When learning tasks at these levels are completed using generative AI, students who have not yet developed the ability to perform these tasks will lack the opportunity to develop them. However, students who have successfully learned these skills may benefit from using generative AI tools to more quickly do this work so that they have more time to concentrate on tasks in the higher levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy.
- Generative AI can be used to support higher order cognitive tasks as well but may struggle to produce accurate or high-quality output for more complex tasks. For these Learning Outcomes, generative AI may be a helpful tool to scaffold certain tasks and increase student learning.
NOTE: Learning Outcomes in the affective (related to attitude or emotions) or psychomotor (related to physical skills) domains of learning are less likely to be successfully demonstrated by generative AI tools.
Analysing learning outcomes
As you review your course Learning Outcomes (LOs), it’s important to reflect on how each LO could be impacted using generative AI.
1. The ability to demonstrate some Learning Outcomes will not be impacted by using generative AI tools.
For example:
- Deliver effective oral presentations in professional settings to a large interdisciplinary audience.
- Proficiently bandage a sport injury to facilitate safe return-to-play.
- Use appropriate speech levels in conversation, including the correct forms of polite (-e/a yo) as well as deferential (-supnita) language.*
*This Learning Outcome was generated with the help of ChatGPT.
2. For some learning outcomes, relying solely on generative AI will not allow students to develop that skill.
For example:
- Paraphrase an excerpt from an academic article to accurately convey the key ideas to a generalist audience.
Generative AI tools would be able to complete this task without the student demonstrating that they have learned the fundamental skill of paraphrasing or audience differentiation.
3. For some learning outcomes, generative AI tools could remove barriers or enable students to focus on higher level cognitive skills in a way that supports learning. This is called Scaffolding.
Generative AI is a type of Artificial Intelligence that creates new content, including text, images, videos, audio, and computer code.



Feedback/Errata