Phases of recovery
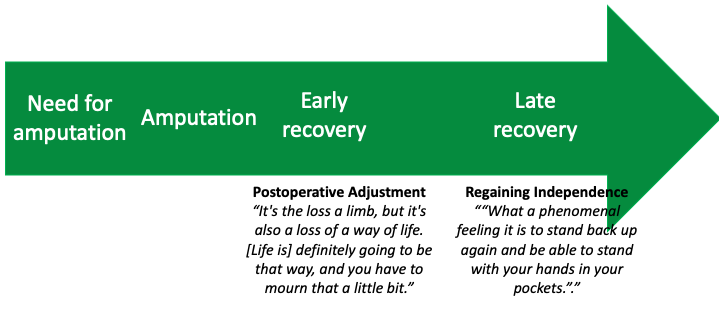
The amputation experience for many begins prior to surgery, with the decision to amputate, and ends when they have regained what the person perceives to be functional independence (Columbo et al, 2018). The definition of functional independence varies from person to person but is often based on their preoperative level of function. In the study by Colombo at al (2018), the post-amputation recovery period was described as having both early (up to six months) and late (six months or more) phases.
The Amputee Coalition (of America) developed a model for recovery which includes phases from enduring to thriving. A modified version of this model is shown in the following table. The table includes the role of the peer visitor at each stage.
| Phase | Characteristic | Description | Role of the peer visitor |
| Enduring | Surviving surgery and pain | Hanging on – may refuse a visit | Silent companion, support family |
| Suffering | Questioning “Why me?” | Feelings about the loss, denial, depression | Listening, empathy, validating, supporting family |
| Reckoning | Becoming aware of the new reality | Coming to terms with the extent of the loss, accepting what is left with the loss | Referral for emotional support |
| Reconciling | Putting the loss in perspective | Increased awareness of one’s strengths and uniqueness, taking control of one’s life | Validation of feelings, referral to a support group |
| Normalizing | Reordering priorities | Allowing priorities other than the loss to dominate | Role model, validating information |
| Thriving | Living life to the fullest | Being more confident, trusting in oneself. | Working side by side |
Recovery from amputation is an ongoing process and it’s important to remember that everybody’s journey is different. Recovery may not occur in a particular order either. Persons with amputation may move from one phase to the next and then back to an earlier phase. They might also skip one or more phases or one phase could overlap with another. Some people may not reach the highest level of recovery. Coping patterns also differ with each phase in the recovery process.
Your visitation is one of the resources that help people successfully recover. Other resources include empathy, support groups, online support groups, counseling with a social worker or a psychologist as well as supportive families and friends.
Instructor Notes:
Concepts: Key Concepts to Cover
- When the amputation process begins and when it ends
- Functional dependence in relation to the recovery process
- How functional independence is based on the preoperative level of function
- The Amputee Coalition of Canadas recovery phase model
- The 6 phases of recovery: Enduring, suffering, reckoning, reconciling, normalizing, thriving
- What each phase means
- The role of the peer visitor in each stage
- Each person will have a unique recovery process and may or may not proceed through all the stages in this exact order
Reflection Exercise Facilitation:
- Ask the group: If they experienced all 6 phases of recovery and if they experienced it in the above order

