Uncharacterized Pain
Incidence and Timing
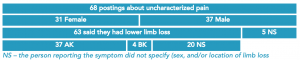
Any type of pain that could not be characterized by symptom type or included multiple symptom types was included in the uncharacterized pain section. For this type of pain, there were 68 postings.
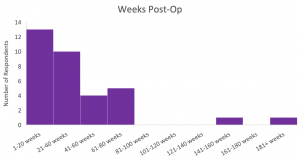
The duration of time since the OI surgery was reported by 36 of the 68 respondents, with median time being 35 weeks post-surgery (range: 6 – 74 weeks).
Symptoms
There were a large variety of pain descriptions by these persons. Some of these descriptions included accounts of nerve pain, stoma pain, ripping/pulling pain when sitting or walking, muscle pain in the stump, or a combination of all the above. There were also reports of pain from a neuroma, unexplained crushing pain in the stump, intense pain occurring at night, pain at the top of the implant and when walking. There were also complaints of joint pain (hip pain was referred to on several occasions), and skin pain similar to that of a sunburn. Respondents also described sharp, stretching, and throbbing pain of their muscle or nerve pain in the associated region. There was reports of pain that felt as though the stoma was going to split open. Some of the pain was described as “growing” or “healing” pain, and descriptions of muscle pain were often accompanied by accounts of respondents experiencing this pain after spending a long period of time wearing sockets, as the OI surgery allowed them to use muscles they had not used while in a socket. There were also several descriptions of nerve pain, with several respondents indicating they had suffered from neuromas or nerve damage after either the injury which caused the amputation, or after the OI surgery. There were also reports of pain after a fall, pain due to fractures, and pain due to swelling and inflammation. There were also reports of pain due to infection.
What People Have Tried
A variety of treatments were used for the pain that was experienced. Often the intervention was to use medications including gabapentin, Lyrica, morphine, codeine, ibuprofen, acetaminophen, cortisone, tapentadol, meloxicam, amitriptyline, and baclofen. Several respondents also reported that they used different types of cream such as xylocaine cream, lidocaine cream, ketamine cream, or Voltaren gel. Others used moisturizing solutions such as beeswax, Viscotears, or Vaseline around the stoma area to decrease pain symptoms. One respondent had steroid injections to help alleviate pain. There were reports of taking antibiotics as an infection was the underlying cause of pain. Some respondents also said that they took supplements or changed their diet to relieve pain. These respondents reported taking potassium, turmeric, magnesium [1], palmitoylethanolamide, and orange juice. Respondents had mixed results with the different medications, and no one medication seemed to work for everyone to relieve the pain.
There were other pain relief strategies as well which differed depending on the type of pain each person described. These included TENS machines, stretching of the stump, elevating the limb, ice packs, heat packs, hot tub, physiotherapy, soaking in Epsom salts, CBD oil, marijuana use, and colloidal silver. One respondent reported lymphatic massage [2] would relieve some symptoms. There was a report of using a compression bandage to reduce pain. One respondent indicated that weight loading would reducing pain and another indicating that maintaining their exercise regime helped. Some respondents also indicated that resting their limb would help, while others stated there was nothing that would give them any pain relief, so they used coping mechanisms to deal with the pain. One respondent indicated that she had undergone surgery to sever nerves in order to relieve pain that she was feeling. Other respondents report having TMR to reduce their pain. As with pharmacological approaches results, were variable with no one treatment providing definitive relief from pain.
Fact Checkers
[1] Magnesium is a micronutrient that can be found in leafy greens, seeds and nuts, supplements are also available. Magnesium may be taken to reduce certain types pain (Bamgbade, 2018).
[2] Massage is a technique used in a variety of cases for many reasons. A study by Boyd et al. (2016) completed a systematic review investigating the impacts of massage on pain and they found that massage had a positive impact on reducing pain.
Help keep this resource alive.
Click this Qualtrics link to fill out a survey on uncharacterized pain so we can continue to grow the information and keep it up to date.