Bone Infection
Incidence and Timing
For the experience of bone infection, the search terms used were “bone infection” and “infection”.
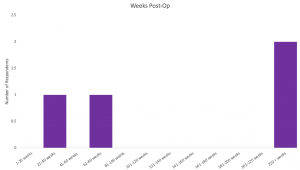
The duration of time since the osseointegration surgery was reported by four of the 15 respondents, with a median time of 294.5 weeks (proximately 5.5 years). The range in reports was from 21 weeks to 624 weeks.
Symptoms
Respondents described recurrent infections that led to a diagnoses of a bone infection (osteomylitis), a bone infection secondary to a surgery on the bone (fracture, hip replacement) and bone infections that took a long time to diagnose. One respondent reported that they had a deep bone infection that tests did not reveal, but the pain she was experiencing told her it was infected. Only after removing the implant was her extensive infection found. A number of respondents reported their bone infections being chronic infections now.
What People Have Tried
People reported their course of action with a bone infection included antibiotics, steroids, and surgery to remove the implant. Antibiotic therapy included oral antibiotics, IV antibiotics, and one report of antibiotics through a PICC line. Some respondents also shared that they had had their implants removed. A couple of the respondents reported having new OI implants after their infection was eradicated.
Help keep this resource alive.
Visit this Qualtrics link to fill out a survey on bone infections so we can continue to grow the information and keep it up to date.
